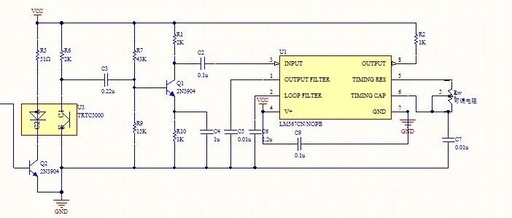
Key Considerations for Developing FPGA UART with EIA/TIA-232
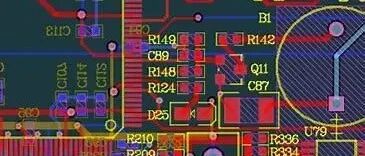
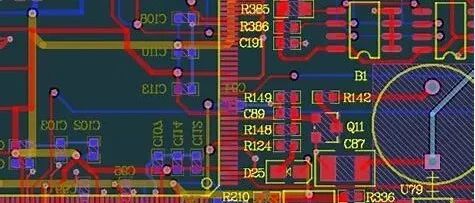
In FPGA development, the design of the wiring for the UART interface, specifically the EIA/TIA-232 (commonly known as RS-232) interface, is crucial. A reasonable wiring layout not only enhances communication stability but also effectively reduces signal interference. Below are the key points for EIA/TIA-232 interface in FPGA UART development. 1. Signal Line Layout TX/RX Pair: … Read more