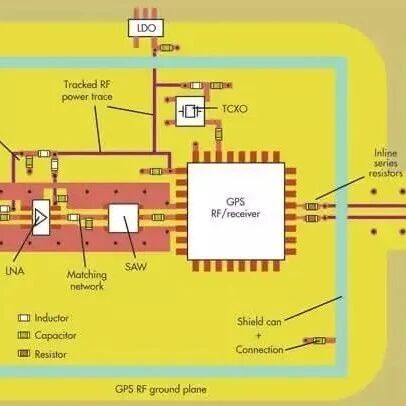
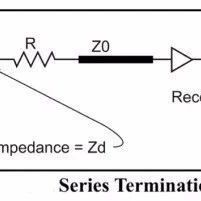
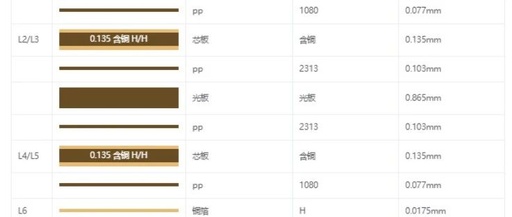
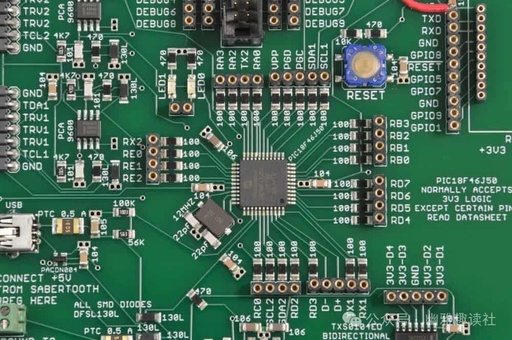
Impedance Testing of PCB Boards
Definition of Impedance In a circuit with resistance, inductance, and capacitance, the hindrance to the current in the circuit is called impedance. Impedance is commonly represented by Z, which is a complex number. The real part is called resistance, and the imaginary part is called reactance. The hindrance caused by capacitance in the circuit to … Read more