▲ Click the blue text above to follow us and never miss any valuable articles!
In electronic circuit systems, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the key carriers for mounting electronic components and achieving electrical connections. The PCB Layout design is the core aspect that determines the performance of the PCB. From the signal integrity of electronic products to electromagnetic compatibility, and from product reliability to production costs, the quality of PCB Layout design plays a decisive role. The following is a comprehensive analysis of the core points of PCB Layout design from multiple dimensions.
Layout of Special Components
- Heating components should be placed in positions favorable for heat dissipation, such as the edges of the PCB, and away from microprocessor chips;
- Special high-frequency components should be placed close together to shorten their interconnections;
- Sensitive components should be kept away from noise sources such as clock generators and oscillators;
- The layout of adjustable components such as adjustable inductors, variable capacitors, push-button switches, and potentiometers should meet the structural requirements of the entire device for easy adjustment;
- Heavier components should be secured with brackets;
- EMI filters should be placed close to EMI sources.
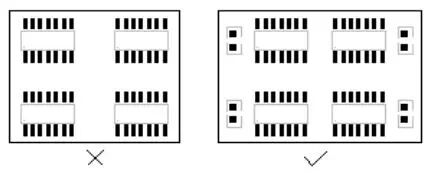
Placement of Crystals
Crystals are made of quartz and are easily affected by external impacts or drops, so during layout, it is best not to place them at the edge of the PCB, but rather as close to the chip as possible.The placement of crystals should be away from heat sources, as high temperatures can also affect the frequency offset of the crystal.
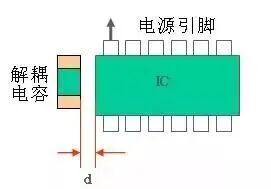
Decoupling Rules for Devices
 Adding necessary decoupling capacitors on the printed circuit board filters out interference signals on the power supply, stabilizing the power supply signal. It is recommended that the power supply be connected to the power pin after filtering through capacitors.
Adding necessary decoupling capacitors on the printed circuit board filters out interference signals on the power supply, stabilizing the power supply signal. It is recommended that the power supply be connected to the power pin after filtering through capacitors.
Placement of Decoupling Capacitors for ICs
 Decoupling capacitors need to be placed near the power ports of each IC, as close to the IC’s power port as possible. When a chip has multiple power ports, decoupling capacitors should be arranged for each port.
Decoupling capacitors need to be placed near the power ports of each IC, as close to the IC’s power port as possible. When a chip has multiple power ports, decoupling capacitors should be arranged for each port.
Electrolytic Capacitors Away from Heat Sources
When designing, PCB engineers must first consider whether the environmental temperature for electrolytic capacitors meets requirements, and secondly, keep the capacitors as far away from heat-generating areas as possible to prevent the internal liquid electrolyte of the electrolytic capacitor from drying out.
Spacing Between SMDs
The spacing between surface mount devices (SMDs) is a critical issue that engineers must pay attention to during layout. The spacing should not be too large (wasting PCB area) or too small, to avoid solder paste printing adhesion and difficulties in soldering repairs.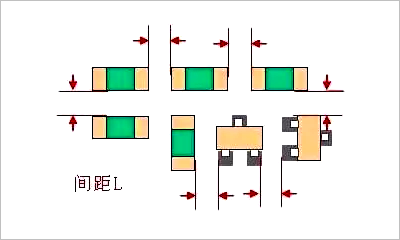 Spacing can refer to the following specifications:
Spacing can refer to the following specifications:
- Same components: ≥ 0.3mm
- Different components: ≥ 0.13×h+0.3mm (h is the maximum height difference between neighboring components)
- For manual soldering and SMD, the distance requirement between components: ≥ 1.5mm.
Consistent Width of Component Leads
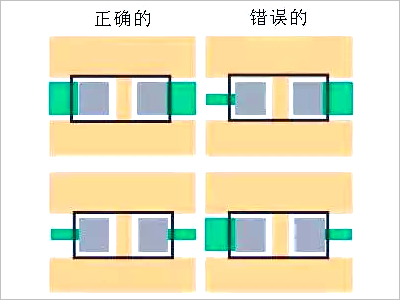
Retain Unused Pin Pads
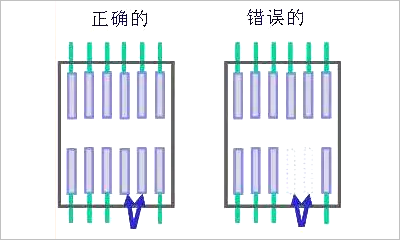 For example, in the case where two pins of a chip are not used, the physical pins still exist. If the two pins are left floating as shown on the right, it can easily cause interference.If the chip pins are internally unconnected, adding pads and grounding them can help avoid interference.
For example, in the case where two pins of a chip are not used, the physical pins still exist. If the two pins are left floating as shown on the right, it can easily cause interference.If the chip pins are internally unconnected, adding pads and grounding them can help avoid interference.
Use of Vias with Caution
In almost all PCB layouts, vias must be used to provide electrical connections between different layers. PCB design engineers need to be particularly careful, as vias can introduce inductance and capacitance, and in some cases, they can also cause reflections due to changes in characteristic impedance when making vias in traces.It is also important to remember that vias increase the length of traces, requiring matching. If differential traces are used, vias should be avoided as much as possible; if unavoidable, vias should be used in both traces to compensate for delays in the signal and return path.
· END ·
Follow the subscription account of EEWorld: "Automotive Development Circle"
Reply "DS" to receive the complete materials of "DeepSeek: From Beginner to Pro"

Scan the code to add the assistant and reply “Join Group”
To exchange experiences face-to-face with electronic engineers