
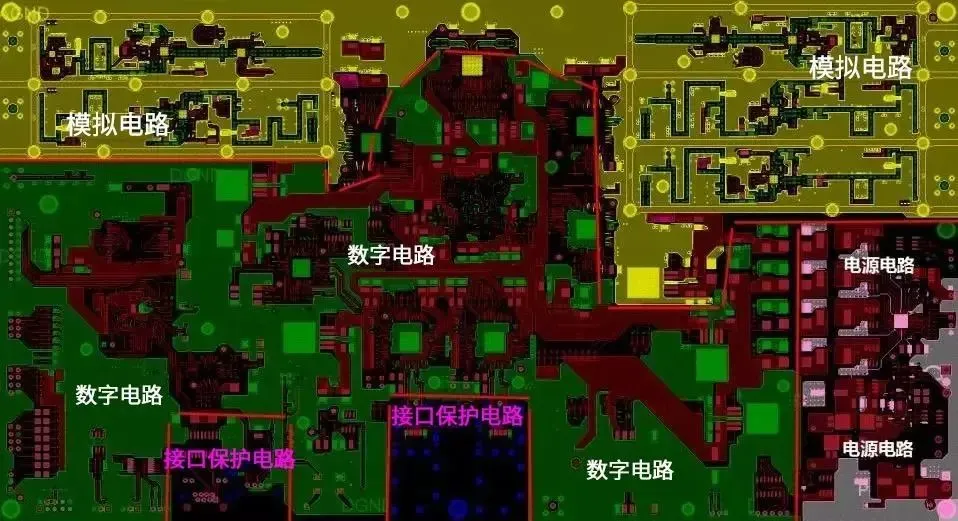

-
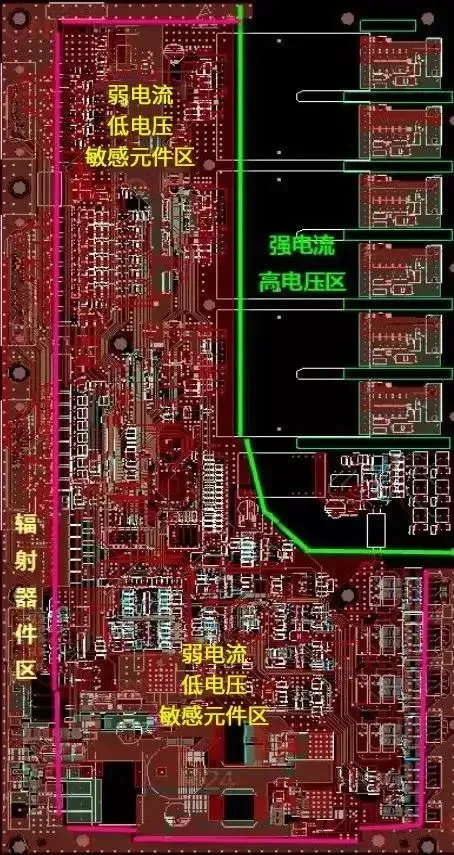
The typical sequence for power surge protection devices is: varistor, fuse, suppression diode, EMI filter, inductor or common mode inductor. For any missing components in the schematic, layout them sequentially. -
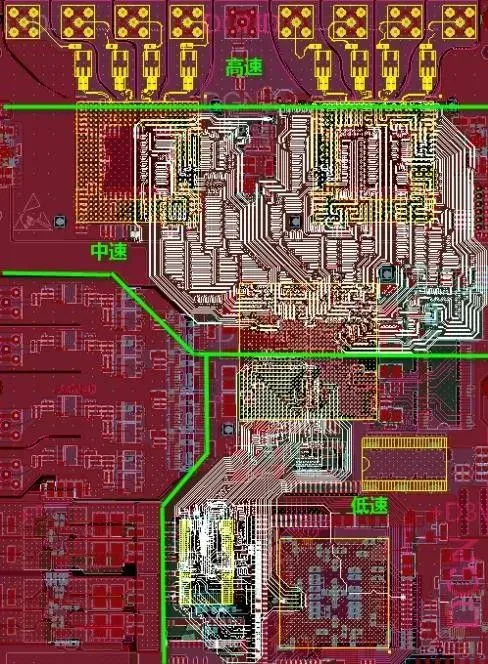
The typical sequence for interface signal protection devices is: ESD (TVS diode), isolation transformer, common mode inductor, capacitor, resistor. For any missing components in the schematic, layout them sequentially, strictly according to the schematic order (ability to judge the correctness of the schematic is required) in a “linear” layout.
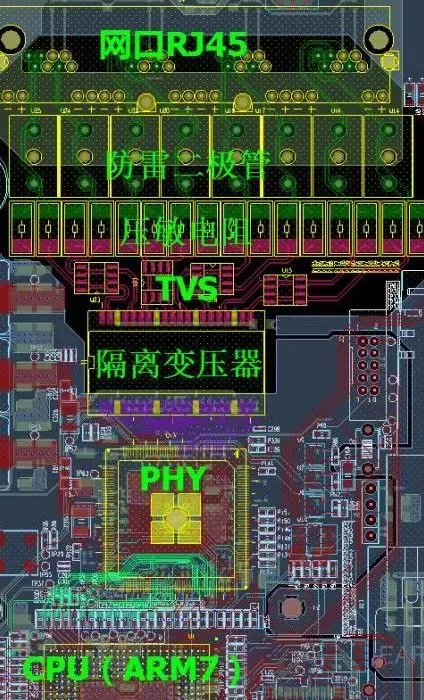
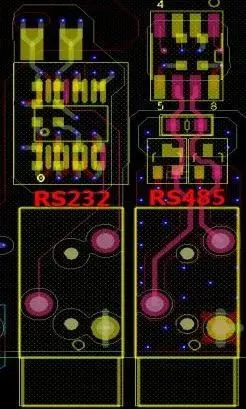
-
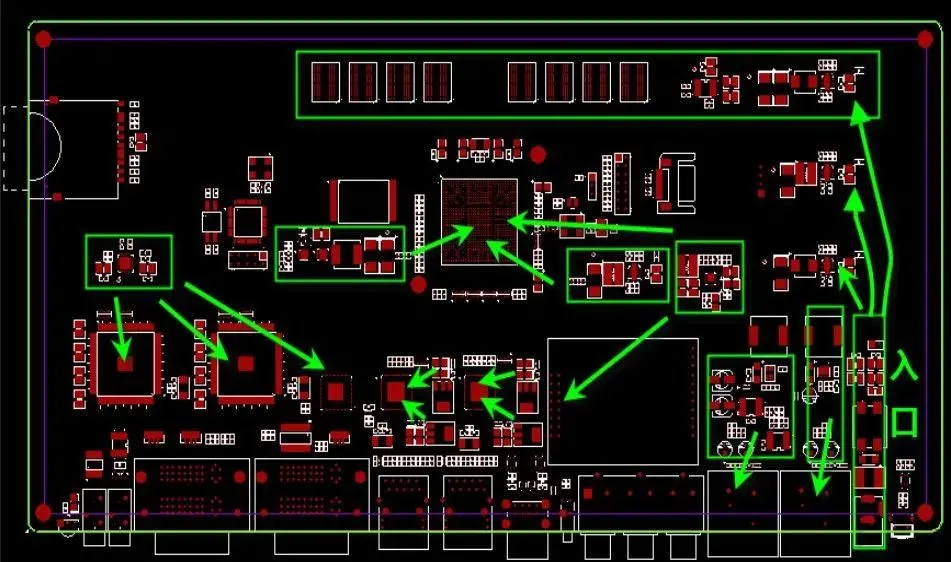
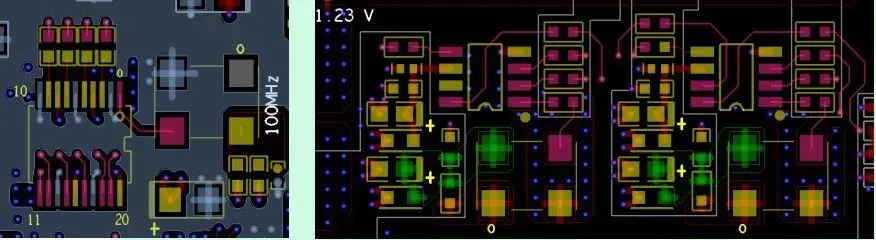
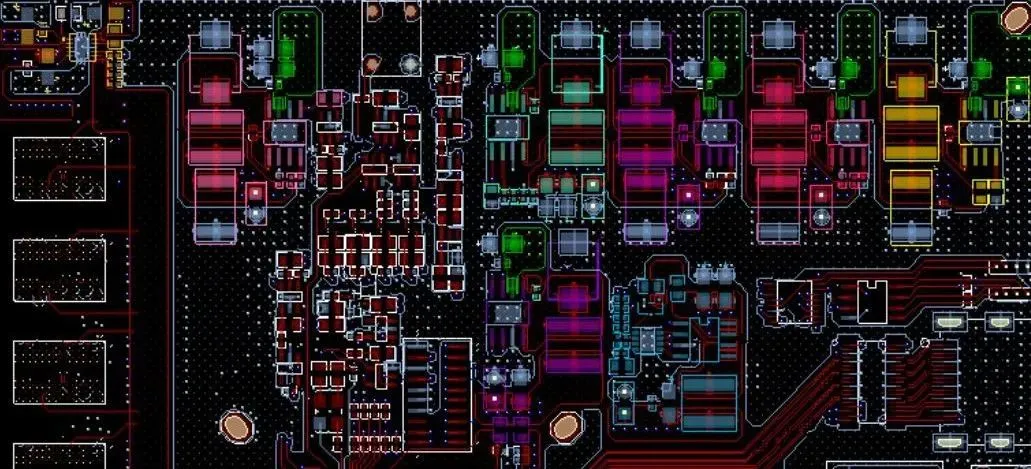
Crystals, oscillators, and clock distributors should be placed as close as possible to the relevant IC devices; -
The filter for the clock circuit (preferably use a “∏” type filter) should be close to the power input pin of the clock circuit; -
Check if there is a 22-ohm resistor in series with the output of the oscillator and clock distributor; -
Check if the unused output pins of the clock distributor are grounded through a resistor; -
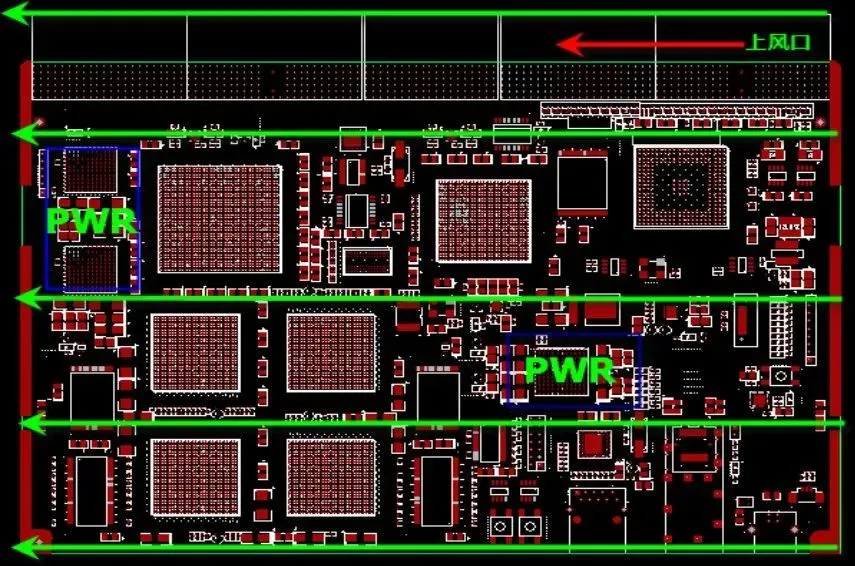
The layout of crystals, oscillators, and clock distributors should be kept away from high-power components, heat sinks, and other heat-generating devices; -
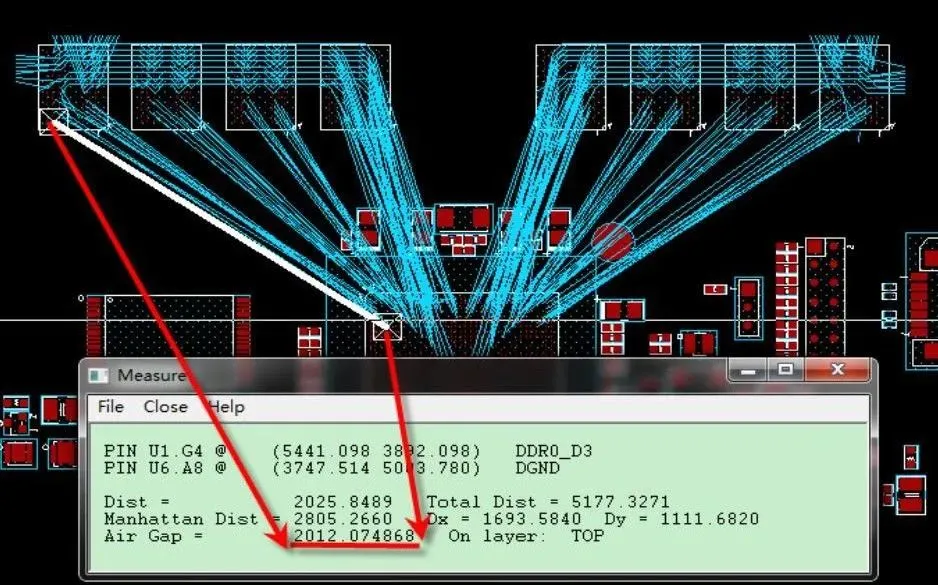
Check if the distance from the crystal oscillator to the board edge and interface devices is greater than 1 inch.
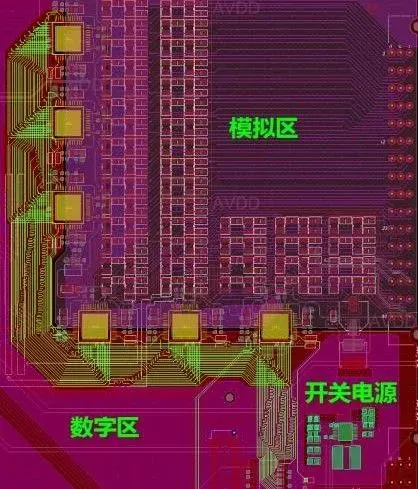

-
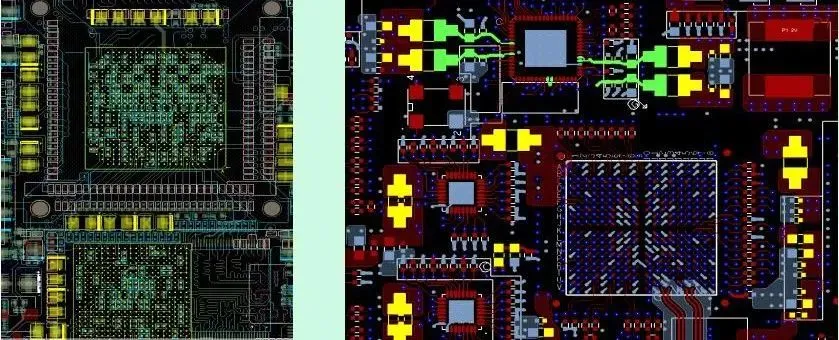
Capacitors must be placed close to the power pins, and the smaller the capacitance value, the closer it should be to the power pins; -
EMI filters should be close to the power input of the chip; -
In principle, each power pin should have a 0.1uF small capacitor, and each integrated circuit should have one or more 10uF large capacitors, which can be adjusted according to the specific situation.
Copyright Notice: This article is copyrighted by the original author and does not represent the views of the association. Articles pushed by the “Jiangxi Province Electronic Circuit Industry Association” are for sharing purposes only and do not represent the position of this account. If there are copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.
