PCB Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing of PCBs is very complex. Taking a four-layer printed circuit board as an example, the main steps include PCB layout, core board manufacturing, inner layer PCB layout transfer, core board drilling and inspection, lamination, drilling, copper plating of the hole walls, outer layer PCB layout transfer, and outer layer PCB etching.
01
PCB Layout
The first step in PCB manufacturing is to organize and check the PCB layout. The PCB manufacturing factory receives CAD files from the PCB design company. Since each CAD software has its unique file format, the PCB factory converts it into a unified format—Extended Gerber RS-274X or Gerber X2. Then, the factory’s engineers will check whether the PCB layout meets the manufacturing process and if there are any defects or issues.
02
Core Board Manufacturing
Clean the copper-clad board; any dust may cause a short circuit or open circuit in the final circuit.

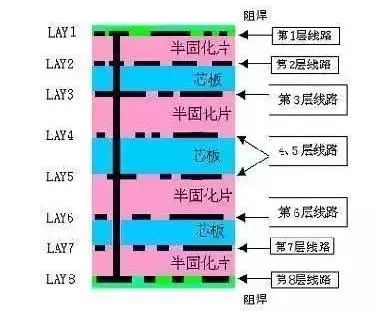
The following image illustrates an 8-layer PCB, which is actually made up of 3 copper-clad boards (core boards) and 2 copper films, bonded together with prepreg. The manufacturing order starts from the innermost core board (layers 4 and 5) and continuously stacks outward, then secures them. The production of a 4-layer PCB is similar, but only uses 1 core board and 2 copper films.
03
Inner Layer PCB Layout Transfer
First, the two layers of circuits on the innermost core (Core) need to be manufactured. After cleaning the copper-clad board, a photosensitive film is applied to the surface. This film cures when exposed to light, forming a protective layer on the copper foil of the copper-clad board.

Two-layer PCB layout films and double-layer copper-clad boards are then inserted with the upper layer PCB layout film to ensure precise alignment of the upper and lower PCB layout films.
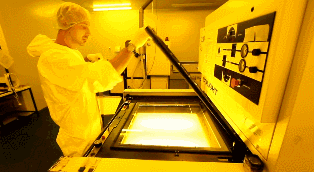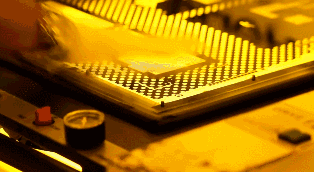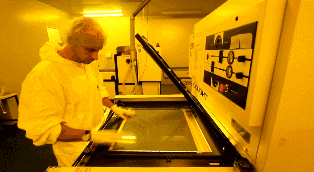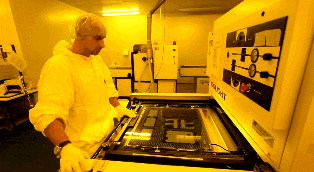
The UV lamp of the exposure machine irradiates the photosensitive film on the copper foil. Under the transparent film, the photosensitive film is cured, while under the opaque film, the photosensitive film remains uncured. The copper foil covered by the cured photosensitive film represents the required PCB layout traces, similar to the role of ink in a manual PCB laser printer.
Then, an alkaline solution is used to wash away the uncured photosensitive film, leaving the required copper foil traces covered by the cured photosensitive film.

Next, use a strong alkali, such as NaOH, to etch away the unnecessary copper foil.

Peel off the cured photosensitive film to reveal the required PCB layout traces on the copper foil.
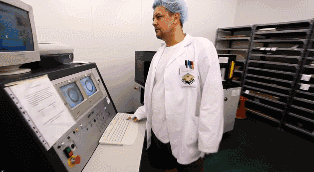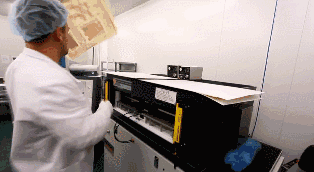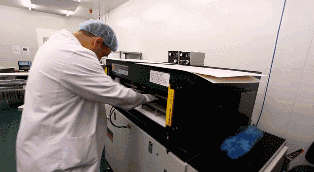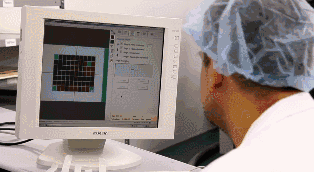
04
Core Board Drilling and Inspection
The core board has been successfully made. Next, alignment holes are drilled on the core board to facilitate alignment with other materials.
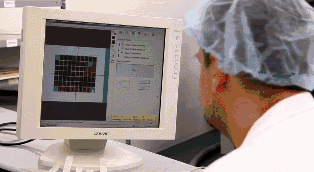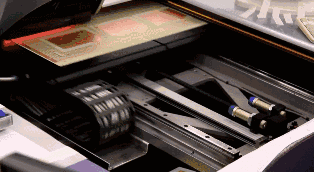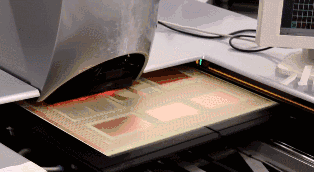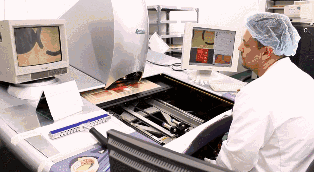
Once the core board is pressed together with other layers of PCB, it cannot be modified, so inspection is very important. Machines will automatically compare with the PCB layout drawings to check for errors.

05
Lamination
This step requires a new material called prepreg, which serves as the adhesive between core boards (for PCBs with more than 4 layers) and between core boards and outer copper films, while also providing insulation.
The lower copper film and two layers of prepreg have been pre-positioned using the alignment holes and fixed to the lower iron plate. The manufactured core board is also placed in the alignment holes, and finally, two layers of prepreg, one layer of copper film, and one layer of pressure-bearing aluminum plate are sequentially covered on the core board.

The PCB boards clamped by the iron plates are placed on a rack and sent into a vacuum hot press machine for lamination. The high temperature in the vacuum hot press machine melts the epoxy resin in the prepreg, fixing the core boards and copper films together under pressure.

After lamination, remove the upper iron plate that pressed the PCB. Then, take away the pressure-bearing aluminum plate, which also serves to isolate different PCBs and ensure the smoothness of the outer copper foil of the PCB. At this point, the PCB taken out will be covered on both sides with a layer of smooth copper foil.
06
Drilling
To connect the four layers of non-contact copper foils in the PCB, first, through holes must be drilled to penetrate the PCB, and then the hole walls must be metalized to become conductive.
A X-ray drilling machine is used to locate the inner layer core board. The machine will automatically find and locate the hole positions on the core board, then drill positioning holes in the PCB to ensure that the subsequent drilling passes through the center of the hole position.

Place a layer of aluminum plate on the drilling machine bed, then place the PCB on top. To improve efficiency, 1 to 3 identical PCBs can be stacked together for drilling, depending on the number of layers in the PCB. Finally, cover the top PCB with a layer of aluminum plate to prevent the copper foil on the PCB from tearing when the drill bit goes in and out.

During the previous lamination process, the melted epoxy resin was pressed out of the PCB, so it needs to be cut away. The milling machine cuts the periphery of the PCB according to the correct XY coordinates.
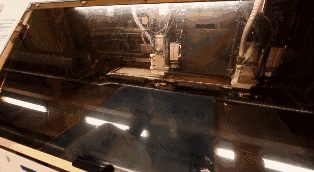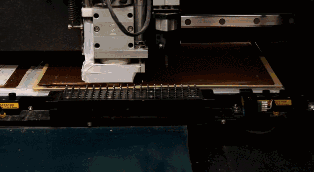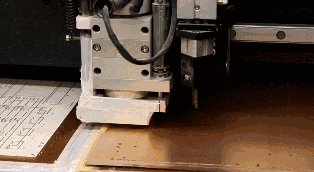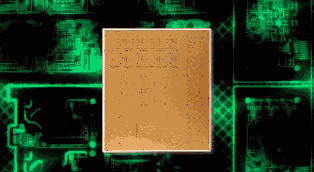
07
Copper Chemical Deposition on Hole Walls
Since almost all PCB designs use vias to connect different layers of traces, a good connection requires a 25-micron copper film on the hole walls. This thickness of copper film needs to be achieved through electroplating, but the hole walls are made of non-conductive epoxy resin and fiberglass.
So the first step is to deposit a layer of conductive material on the hole walls, forming a 1-micron copper film on the entire PCB surface, including the hole walls, through chemical deposition. The entire process, including chemical treatment and cleaning, is controlled by machines.

Fix the PCB

Clean the PCB

Transport the PCB
08
Outer Layer PCB Layout Transfer
Next, the outer layer PCB layout will be transferred to the copper foil. The process is similar to the previous inner layer core board PCB layout transfer, using photocopied films and photosensitive films to transfer the PCB layout to the copper foil. The only difference is that positive films will be used for the outer layer.
The inner layer PCB layout transfer uses a negative film. The areas covered by the cured photosensitive film are the traces, and the uncured photosensitive film is washed away, leaving the copper foil that is etched, while the traces are protected by the cured photosensitive film.
The outer layer PCB layout transfer uses a normal method, employing positive films. The areas covered by the cured photosensitive film are non-trace areas. After washing away the uncured photosensitive film, electroplating is performed. The areas without the film will be first plated with copper and then with tin. After stripping the film, alkaline etching is done, followed by stripping the tin. The trace patterns are retained on the board because they are protected by tin.
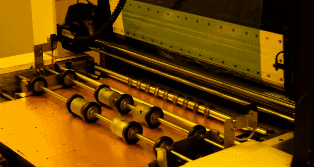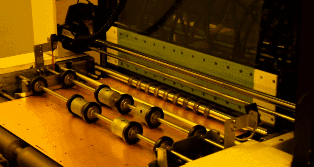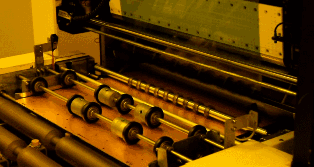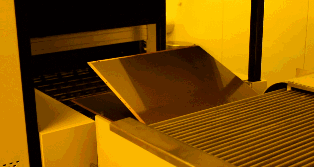


Clamp the PCB with clips to electroplate the copper. As mentioned earlier, to ensure that the via has sufficient conductivity, the copper film plated on the hole wall must have a thickness of 25 microns, so the entire system will be controlled by a computer to ensure accuracy.
09
Outer Layer PCB Etching
Next, a complete automated assembly line will perform the etching process. First, the cured photosensitive film on the PCB board is washed away. Then, strong alkali is used to remove the unnecessary copper foil covered by it. Finally, the tin plating on the PCB layout copper foil is stripped. After thorough cleaning, the four-layer PCB layout is complete.



Turning Mechanical Frontiers
Source: PCB Industry Integrated New Media
Copyright Statement: This article’s copyright belongs to the original author and does not represent the association’s views. Articles promoted by the “Jiangxi Province Electronic Circuit Industry Association” are for sharing purposes only and do not represent the stance of this account. If there are copyright issues, please contact us for removal.
