Click the “blue text” above to follow for more exciting content.
This article contains a total of 835 words, and reading it will take about 2 minutes.
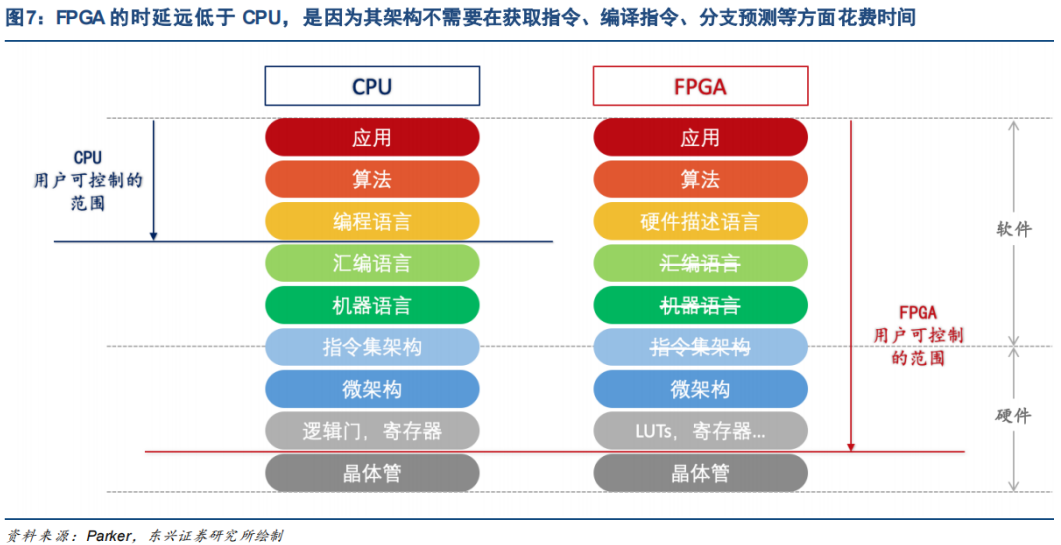
The significant advantage of FPGA over CPU lies in its deterministic low latency, which is due to architectural differences.The latency of a CPU is non-deterministic; as utilization increases, the CPU must handle more tasks, requiring task scheduling and reordering, which often leads to uncontrollable increases in processing latency. In contrast, the latency of an FPGA is deterministic because, during the layout and routing phase, design tools ensure that the worst-case path meets timing requirements, eliminating the need for time-consuming steps such as fetching and decoding instructions that general-purpose processors require, thus avoiding the subsequent issues of reordering execution and instruction scheduling delays.
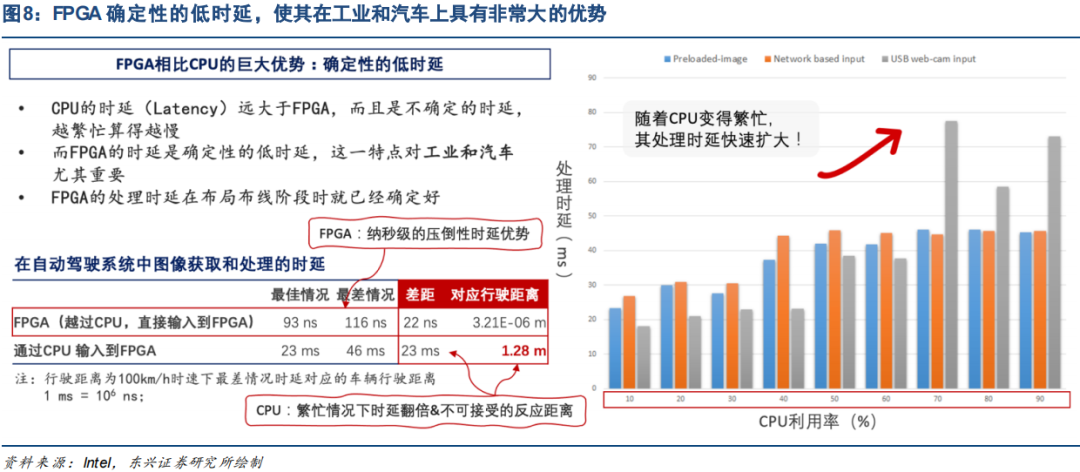
The higher the utilization of the CPU, the greater the processing latency, while the processing latency of FPGA remains stable regardless of utilization. FPGA can provide processing latencies in the nanosecond range, whereas CPUs typically operate in the millisecond range. For example, in an autonomous driving system, transmitting camera data directly to the FPGA’s MIPI interface results in a latency difference of only 22ns between the best and worst cases, while involving a CPU in data transmission leads to a difference of over 23ms. This means that under heavy load, the CPU’s latency can double. Furthermore, when utilization rises to 90%, the CPU’s processing time can reach 46ms. For a car traveling at 100km/h, 46ms means that the vehicle has already traveled at least 1.28 meters from the moment the camera detects an obstacle until the car’s system initiates braking, whereas the FPGA can respond in just 3-6 meters, effectively allowing for instantaneous reaction. The 1.28m distance saved could significantly reduce the likelihood of collision accidents. Therefore, in scenarios such as automotive and industrial applications that require deterministic low latency, FPGA has a substantial advantage.
FPGA offers greater flexibility compared to CPU. In industrial settings, there are often many fine adjustments needed, such as making precise control adjustments to motors based on conveyor belt wear or updating devices with new protocols. CPUs often struggle with these tasks. Since FPGAs are dynamically reconfigurable, they can be adjusted on-site to adapt to new changes at any time. Additionally, FPGAs can simultaneously integrate various devices in the industrial field, such as PLCs, gateways, sensors, motors, and HMIs, enabling real-time control and communication between different devices.

Risk Warning:This content only represents the analysis, speculation, and judgment of the author, and is published here solely for the purpose of conveying information. It should not be used as a basis for specific investment targets. Investment carries risks; proceed with caution!Copyright Statement:This content is copyrighted by the original author or organization. If reproduced, please indicate the source and author, retain the original title and ensure the integrity of the article content, and bear legal responsibility for copyright and other issues.
END
