Project Overview
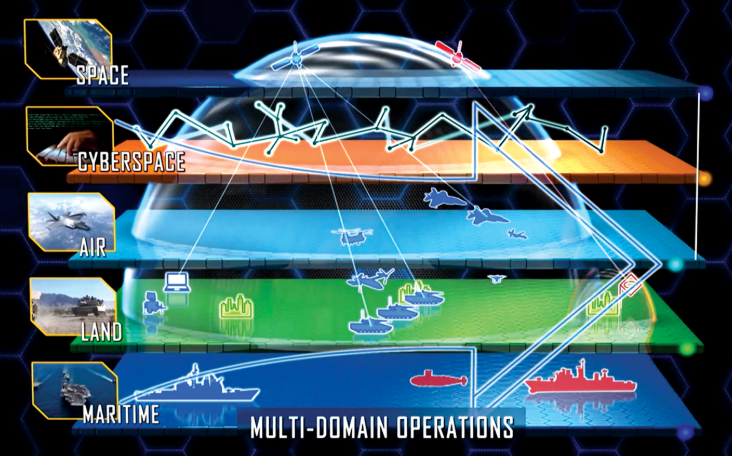
The U.S. Department of Defense (DOD) seeks to implement global operational capabilities, requiring intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance, and targeting (ISRT) across all conflict domains. For the Navy, this encompasses operations from the deep seabed, underwater, surface, air, space, and cyberspace. Global ISRT integrates sensor information across all dimensions from seabed to space, providing commanders with a comprehensive situational awareness of adversary activities. This capability supports the Navy’s “Distributed Maritime Operations” (DMO) concept—enabling dispersed naval units to collaboratively execute sensing, command and control, and weapon strikes, forming a cohesive operational force.
Global ISRT requires the construction of a network system that allows dispersed sensors to exchange, correlate, and fuse data, thereby generating a complete operational situational picture and providing target information necessary for long-range engagements in DMO. This study models and evaluates the role of space constellations in sensing and relay communications, validating the feasibility of beyond-line-of-sight ISRT. The research concludes that the collaborative concept of seabed-to-space sensors through the planned DOD low Earth orbit (LEO) space constellation relay is feasible and can support DMO beyond-line-of-sight operations in high-intensity surface warfare scenarios. The study also confirms that, despite the complexity of coordinating firepower strike processes from seabed early warning to space sensing with heterogeneous sensors, it is practically feasible under high availability conditions of the space relay constellation.
For example, the research indicates that using a constellation planned by the DOD Space Development Agency (SDA) (or larger models) can provide distributed search, detection, and tracking capabilities covering the entire domain, although terminal engagements may require local unmanned aerial/surface vehicle support. It is recommended that the next step involves dynamic maritime battlefield scenario simulations to expand case analyses of constellation parameters and sensor combinations.
Keywords:Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA); Distributed Maritime Operations (DMO); Seabed-to-Space; Artificial Intelligence (AI); Commander Intelligence Requirements (CIR); Command Control Communications Computers Intelligence Surveillance Reconnaissance and Targeting (C5ISRT); Department of Defense (DoD); Intelligence Surveillance Reconnaissance (ISR); Intelligence Surveillance Reconnaissance and Targeting (ISRT); Internet Protocol (IP); Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2); Low Earth Orbit (LEO); Machine Learning (ML); Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
 Convenient access to ZHUANZHI
Convenient access to ZHUANZHI
Click the lower left corner“Read the original text” or copy the following URL to view
https://www.zhuanzhi.ai/vip/d3521513424f0cb8638588c8c010a74a
Welcome to scan the WeChat code to addZHUANZHI Assistant, for consulting services:Access to Chinese report materials


Click “Read the original text” to view and download