Want to view the PCB industry directory?
Currently, Xiaofan has compiled directories for Shenzhen, Huizhou, Zhuhai,
Jiangxi, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, and 18 other locations
Just follow the “Electronic Manufacturing Service Platform”
After following, reply with the location:
For example, reply with “Zhuhai” to get the Zhuhai PCB industry directory!

Introducing the following 5 aspects:
1. Introduction to PCBs
2. Introduction to PCB materials
3. Basic PCB stacking structure
4. PCB manufacturing process
5. PCB case sharing
1. Introduction to PCBs
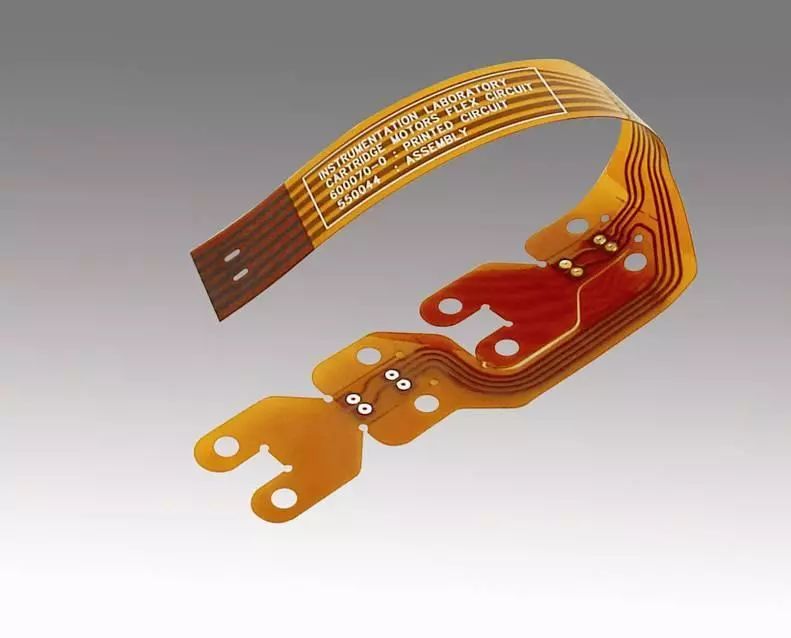
1. Flexible Printed Circuit Board
A Flexible Printed Circuit Board (Flex Print Circuit, abbreviated as “FPC”) is a printed circuit board made using flexible substrates with single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer circuits. It features light weight, thinness, compactness, high density, high stability, and flexible structure. It can be statically bent as well as dynamically bent, rolled, and folded.

2. Rigid Printed Circuit Board
A Rigid Printed Circuit Board (Printed Circuit Board, abbreviated as “PCB”) is a printed circuit board made from rigid substrate materials that are not easily deformed, remaining flat during use. It has high strength, is not easily warped, and securely mounts surface-mounted components.

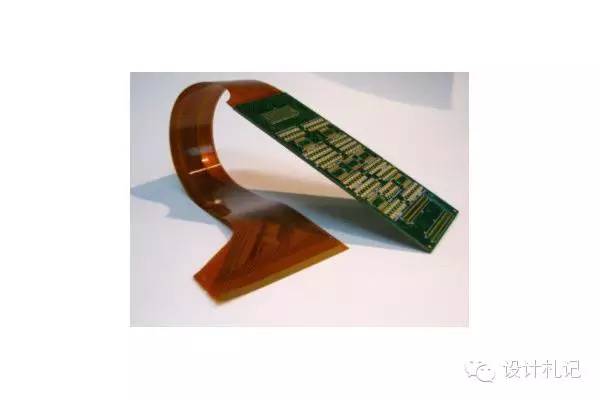
3. Rigid-Flex Board
A Rigid-Flex Board (Rigid Flex) is a special flexible printed circuit board formed by selectively laminating rigid and flexible substrates together, with a dense structure and electrical connections formed by metallized holes. It features high density, fine lines, small apertures, compact size, light weight, and high reliability, maintaining stable performance under vibration, impact, and humid environments. It can bend and be mounted in three dimensions, effectively utilizing installation space, and is widely used in portable digital products such as mobile phones, digital cameras, and camcorders. Rigid-flex boards are increasingly used in areas to reduce packaging, especially in consumer fields.
 2. Introduction to PCB Materials
2. Introduction to PCB Materials
1. Conductive Medium: Copper (Cu)
﹣Copper foil: Rolled copper (RA), Electrolytic copper (ED), High ductility electrolytic copper (HTE)
﹣Thickness: 1/4 OZ, 1/3 OZ, 1/2 OZ, 1 OZ, 2 OZ; these are common thicknesses
﹣OZ (ounce): Unit of copper foil thickness; 1 OZ = 1.4 mil
2. Insulation Layer: Polyimide (PI), Polyester (Polyester), Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN)
﹣The most commonly used is Polyimide (abbreviated as “PI”)
﹣PI thickness: 1/2 mil, 1 mil, 2 mil; these are common thicknesses
﹣1 mil = 0.0254 mm = 25.4 um = 1/1000 inch
3. Adhesive: Epoxy resin-based, Acrylic-based.
﹣The commonly used is epoxy resin-based, with thickness varying by manufacturer
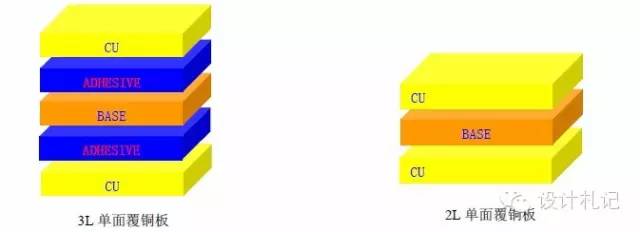
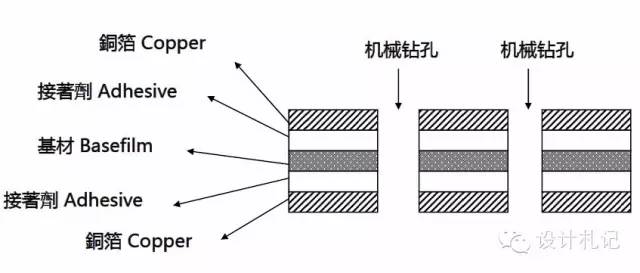
4. Copper Clad Laminate (Cuclad laminates, abbreviated as “CCL”):
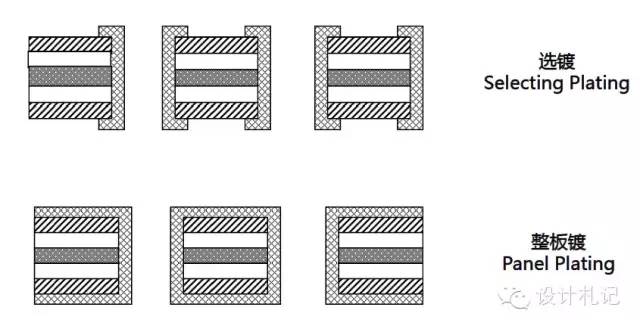
﹣Single-sided copper-clad laminate: 3LCCL (with adhesive), 2LCCL (without adhesive); see illustration below.
 ﹣Double-sided copper-clad laminate: 3LCCL (with adhesive), 2LCCL (without adhesive); see illustration below.
﹣Double-sided copper-clad laminate: 3LCCL (with adhesive), 2LCCL (without adhesive); see illustration below.
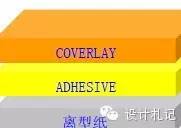
5. Covering Film (Coverlay, abbreviated as “CVL”): Composed of an insulation layer and adhesive, covering the conductive lines, serving the purpose of protection and insulation. The specific stacking structure is as follows:
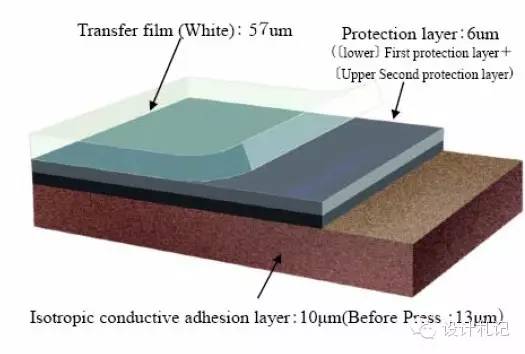
2. Conductive Silver Foil: Electromagnetic wave shielding film
﹣Type: SF-PC6000 (black, 16um)
﹣Advantages: Ultra-thin, good sliding and bending properties, suitable for high-temperature reflow soldering, good dimensional stability.
The commonly used is SF-PC6000, the stacking structure is as follows:
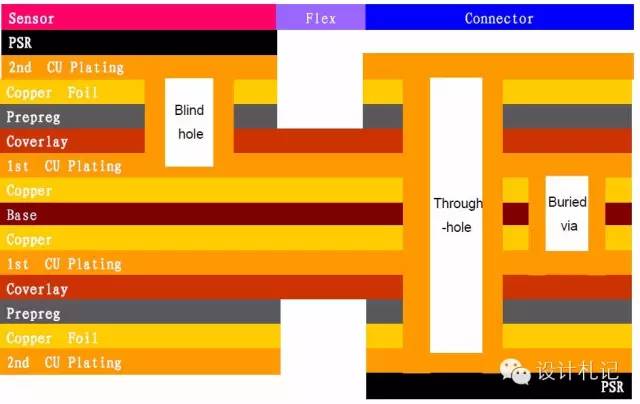
 3. Rigid-Flex Stacking Display
3. Rigid-Flex Stacking Display
 4. PCB Manufacturing Process
4. PCB Manufacturing Process
1. Material Cutting: Cutting/Shearing

2. Mechanical Drilling: CNC Drilling
 3. Plating Through Hole
3. Plating Through Hole
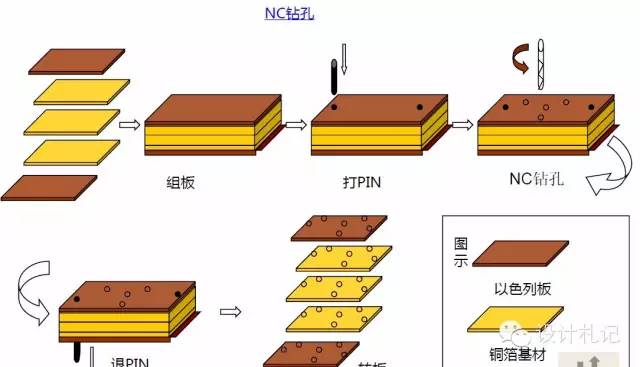
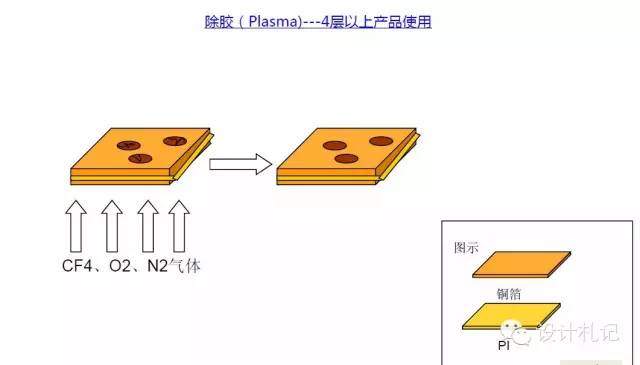
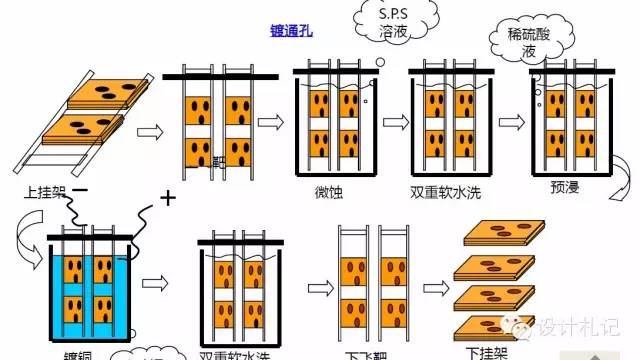
4. DES Process (Five Steps)
(1). Film Application (Dry Film Application)
 (2). Exposure
(2). Exposure
Working Environment: Yellow Light
Purpose: Through UV light exposure and film blocking, the areas where the film is transparent and the dry film undergo optical polymerization reactions, while the areas where the film is brown cannot undergo optical polymerization reactions.
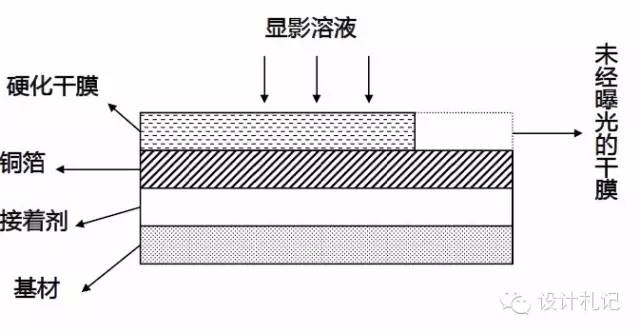
 (3). Development
(3). Development
Working Solution: Na2CO3 (K2CO3) weak alkaline solution
Purpose: To wash away the undeveloped dry film parts using a weak alkaline solution
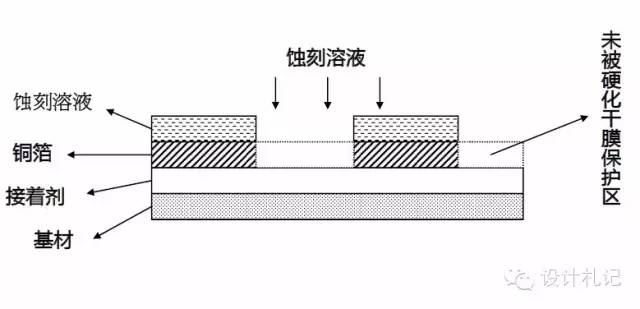
 (4). Etching
(4). Etching
Working Solution: Acidic Hydrogen Peroxide: HCl+H2O2
Purpose: To etch away the copper exposed after development using the chemical solution to form a transfer pattern.
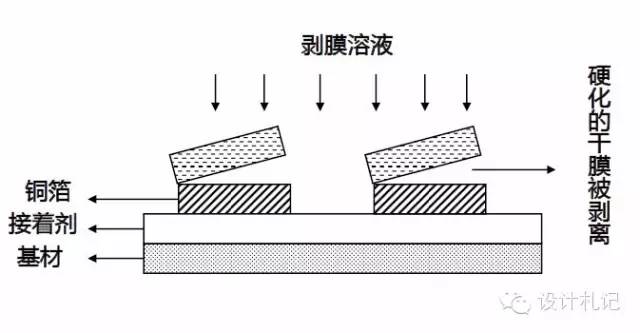
 (5). Film Stripping
(5). Film Stripping
Working Solution: NaOH strong alkaline solution
5. AOI
Key Equipment: AOI, VRS System
The copper foil with formed circuits must pass through the AOI system for scanning to detect circuit omissions. The standard circuit image information is stored in data form within the AOI mainframe, and through the CCD optical imaging head, the circuit information on the copper foil is scanned into the mainframe and compared with the stored standard data. If there are anomalies, the positions of the anomalies will be numbered and recorded, then transmitted to the VRS mainframe. The VRS will magnify the copper foil 300 times, displaying the recorded defect locations sequentially, allowing operators to determine whether they are true defects. For true defects, operators will mark the defect locations with a water-based pen for easy classification, statistics, and repairs by subsequent workers. Operators use a 150x magnifying glass to determine the defect types, forming a quality report and feeding back to the previous processes for timely improvement measures. Due to the fewer defects in single-sided boards, which are lower in cost, it is difficult to use AOI for reading, thus direct visual inspection is used.

6. Dummy Paste
Protective Film Functions: 1) Insulation, Anti-soldering; 2) Protects the circuit; 3) Increases flexibility of soft boards.
 7. Hot Pressing
7. Hot Pressing
Working Conditions: High temperature and high pressure

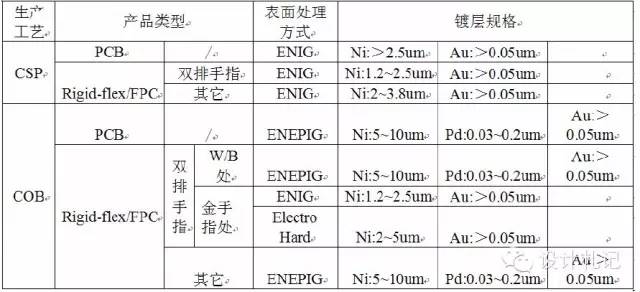
8. Surface Treatment
After hot pressing, the exposed copper foil areas need surface treatment.
The method depends on customer requirements
 9. Screen Printing
9. Screen Printing
Key Equipment: Screen printer, Oven, UV dryer, Screen making equipment Using screen printing principles, the ink is transferred onto the product, mainly printing product batch numbers, production cycles, text, black shielding, simple circuits, etc. The product is positioned with a positioning PIN to align with the screen, and the ink is pressed onto the product with a squeegee. The screen is open for the text and pattern parts, while the non-text or pattern parts are blocked by the photosensitive emulsion, preventing ink leakage. After printing, the product enters the oven for drying, and the printed text or pattern layer tightly adheres to the product surface. Some special products require certain special circuits, such as adding a few circuits on a single-sided board to achieve dual-sided board functionality, or adding a shielding layer to a double-sided board must be realized through printing. If the ink is UV-curable, a UV dryer must be used for drying. Common issues include ink leakage, contamination, gaps, protrusions, and peeling.
 10. Testing (O/S Inspection)
10. Testing (O/S Inspection)
Testing jigs + testing software conduct full functional inspection of the PCB
 11. Punching
11. Punching
Corresponding shape molds: knife molds, laser cutting, etching molds, simple steel molds, steel molds
 12. Processing and Assembly
12. Processing and Assembly
Processing and assembly refer to assembling materials according to customer requirements, such as suppliers assembling:
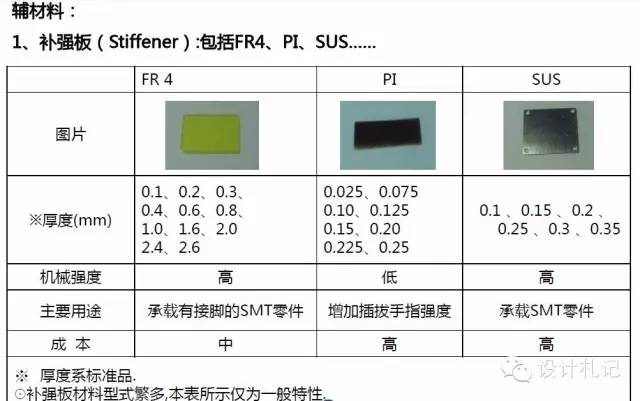
A. Stainless steel reinforcement
B. Beryllium copper sheets/Phosphor bronze sheets/Nickel-plated steel sheets reinforcement
C. FR4 reinforcement
D. PI reinforcement
13. Inspection
Inspection Items: Appearance, Dimensions, Reliability
Testing Tools: Two-dimensional, Micrometer, Caliper, Magnifying glass, Solder furnace, Tension tester
 14. Packaging
14. Packaging
Working Methods: 1. Plastic bags + cardboard 2. Low-adhesion packaging materials 3. Standard vacuum boxes 4. Special vacuum boxes (anti-static grade)
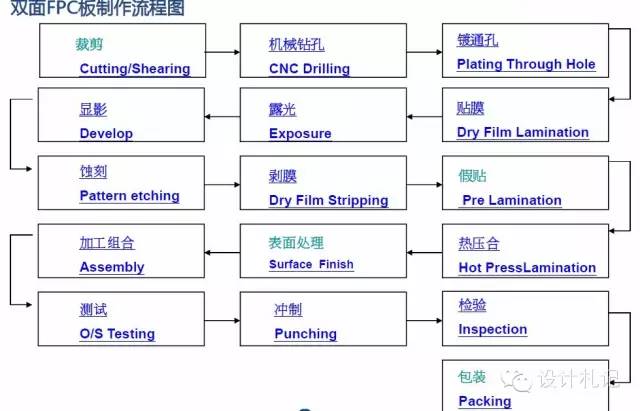
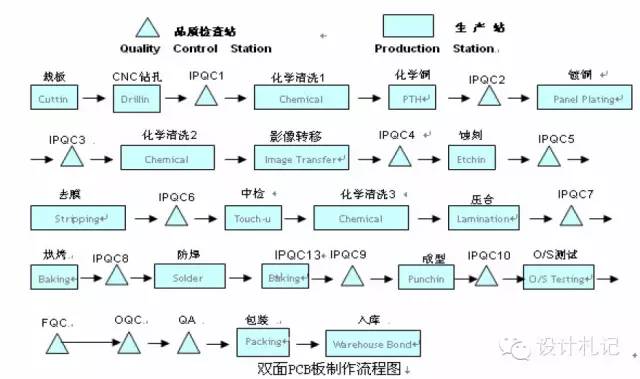
 Double-sided PCB Manufacturing Process Flowchart
Double-sided PCB Manufacturing Process Flowchart
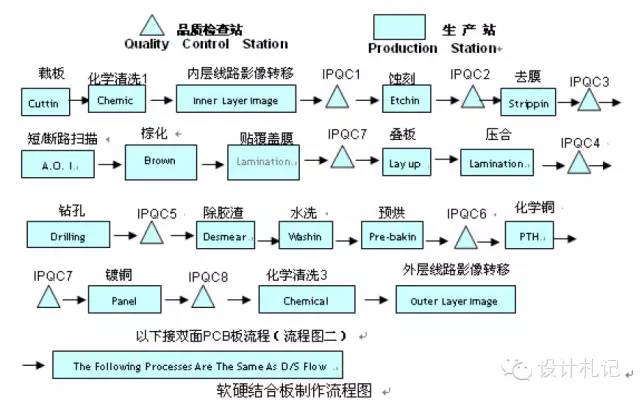
Rigid-Flex Board Manufacturing Process Flowchart
 5. PCB Case Sharing
5. PCB Case Sharing
1. Design Scheme
1. Scheme Description:
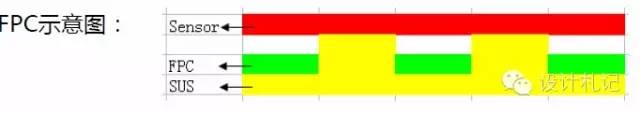
• The new COF scheme integrates reinforcement and chip attachment area onto a single steel plate, as shown in the FPC diagram.
• Main uses:
• 1. To minimize sensor attachment to uneven PCB surfaces, directly attaching the sensor to a flat steel plate surface, ensuring the sensor is perpendicular to the optical lens optical axis, reducing image blurriness.
• 2. In the ≤0.3mm scheme, the new COF flatness is superior to rigid-flex boards, achieving a reduced module height while ensuring flatness.
• 3. Direct contact between the sensor and the steel plate enhances thermal conductivity.
2. Design Scheme
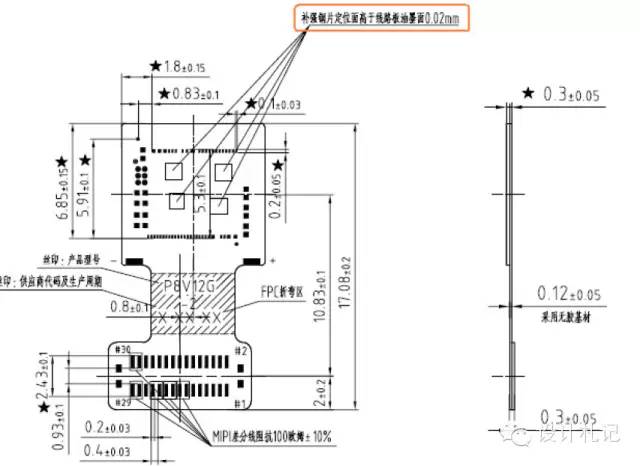
1) P8V12G-621-00 PCB (Structural diagram below):
PCB design thickness 0.3mm, steel plate protrusion height 0.02mm.
 2) P8V12G-621-00 PCB (Wiring diagram below):
2) P8V12G-621-00 PCB (Wiring diagram below):
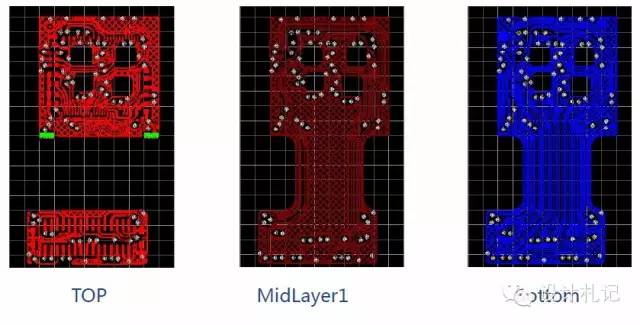 3) P8V12G-621-00 PCB (Stacking diagram below):
3) P8V12G-621-00 PCB (Stacking diagram below):
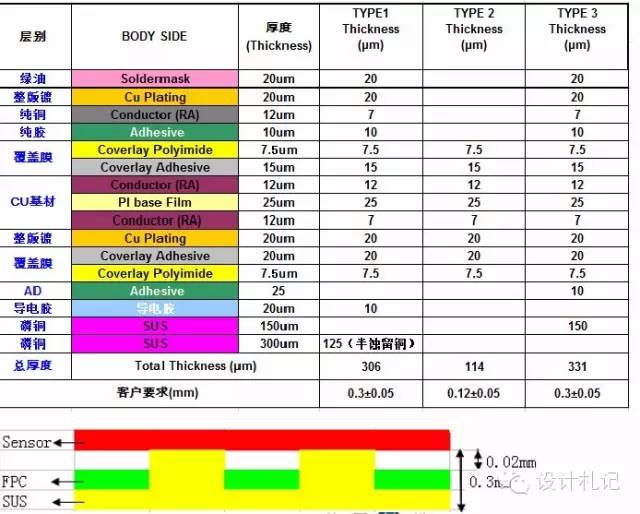
4) PCB scheme design limitations assessment:
1. The purple small box in the diagram indicates the steel plate support area;
2. The support area is distributed diagonally from the SENSOR;
3. The minimum window area of the support area is 0.5*0.5, the larger the area, the better the flatness;
4. Module head size ≥8.5*8.5;
5. SENSOR pin count ≤80;
6. MIPI 2 Lane output is more favorable for routing compared to 4 Lane output;
7. When MIPI is near the connector, it is more favorable for routing (as shown in the right picture, the MIPI routing is below the pad);
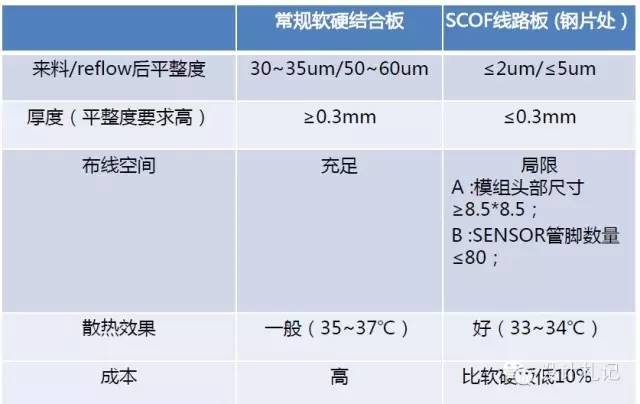
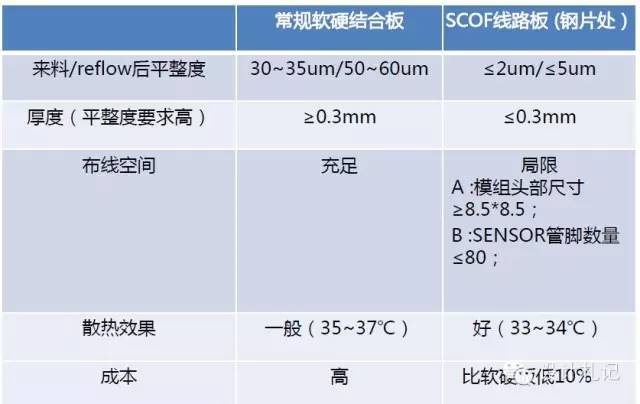 3. Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison Analysis
3. Advantages and Disadvantages Comparison Analysis
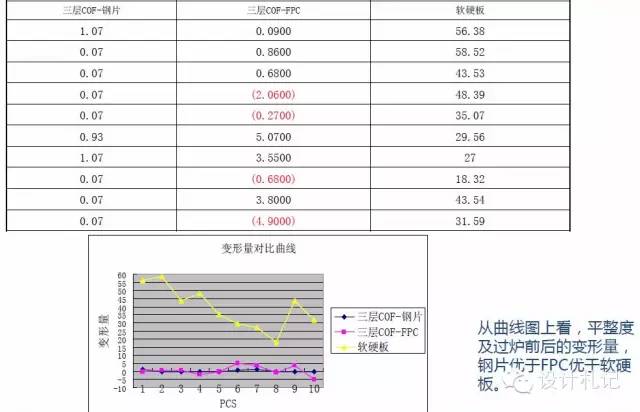
4. Flatness Data Comparison:
Flatness comparison of P8V12G under different types:
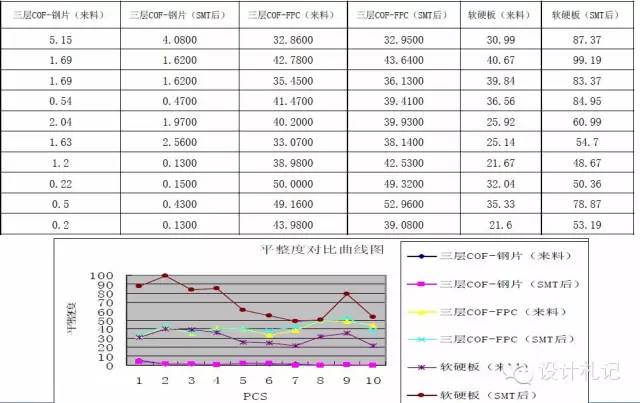 Flatness deformation comparison before and after furnace for P8V12G under different types:
Flatness deformation comparison before and after furnace for P8V12G under different types: