Total text: 888 words, 24 images,Estimated reading time: 1 minute
Previously, we successfully deployed OpenWrt on an x86 ESXi server (Deploying OpenWrt on x86 servers), but we did not set a root password, which is very insecure. Let’s quickly set a password under “system” → “Administration”, with a minimum length requirement of 6 characters.
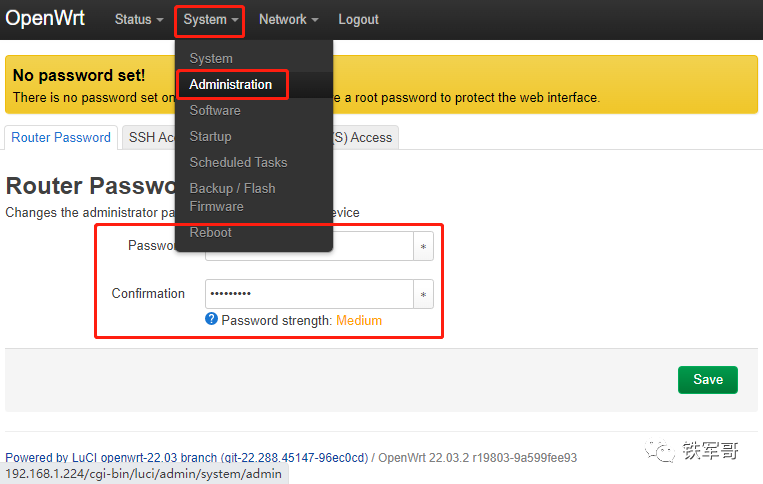
 System Settings
System Settings
Upon entering the system options, we noticed that the clock was incorrect. The system is configured with NTP by default, so let’s quickly modify the time zone.
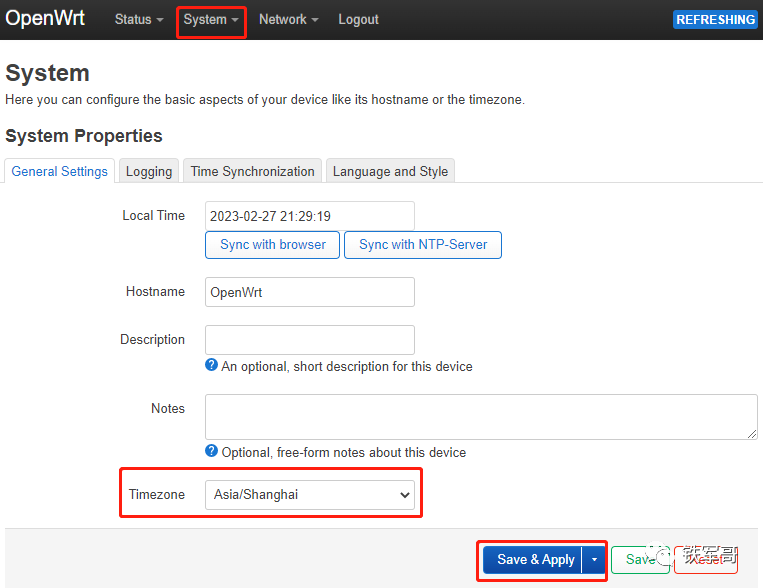
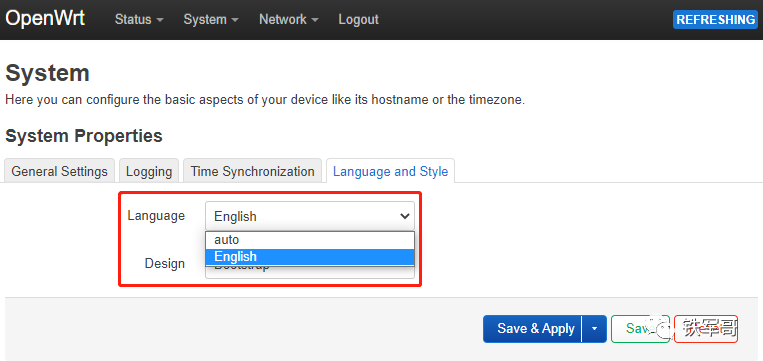
There are other settings, such as logs, time synchronization servers, and language options. Of course, the default language is only English, but there are 3 styles available for switching.
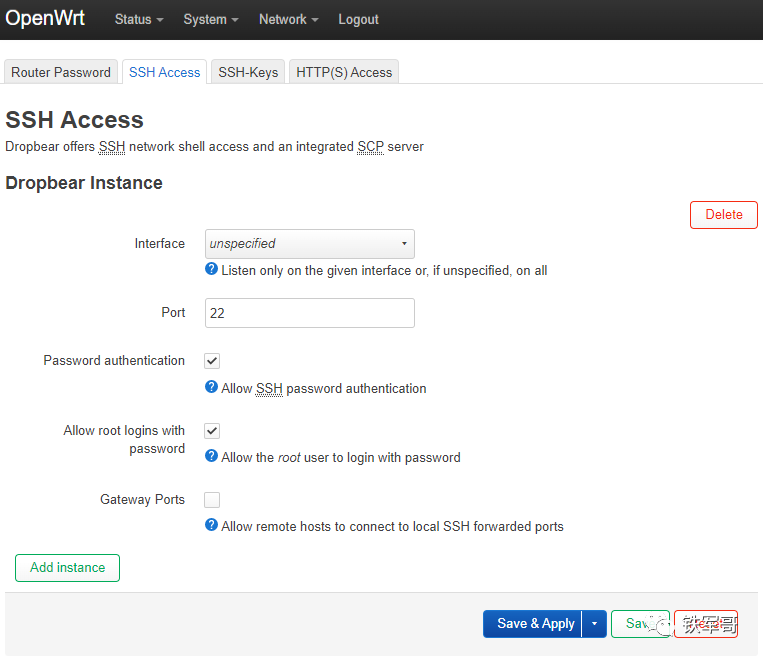
The “Administration” page, besides the password setting page we just configured, also includes settings for SSH access.
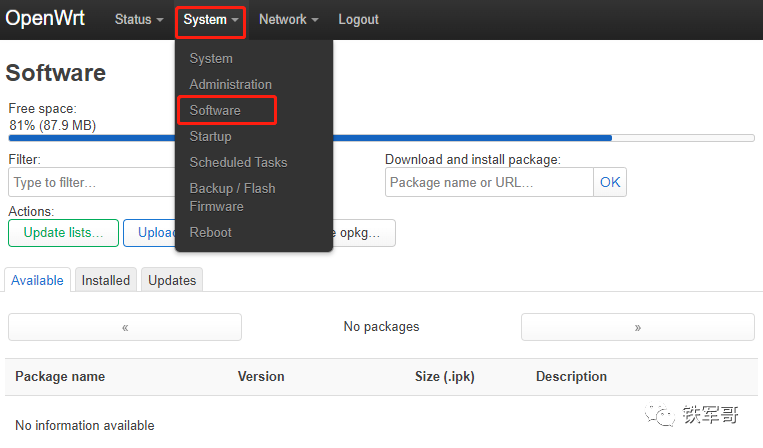
The “Software” page allows you to install various software packages. We previously tested installing the SmartDNS software (SmartDNS reported! How can it still be called “scientific internet access”?).
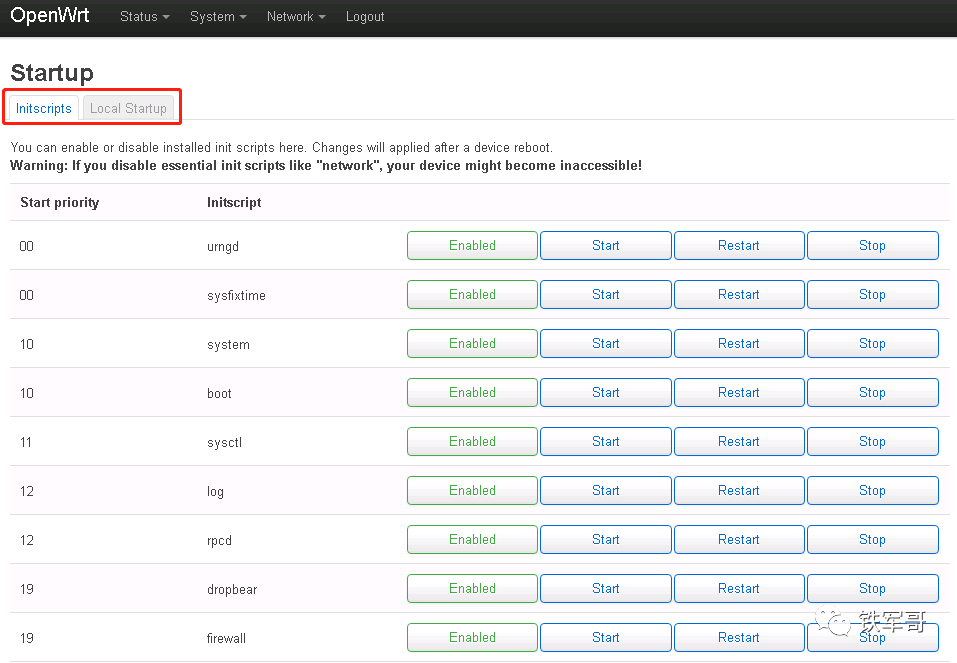
The “Startup” page allows you to set commands to execute automatically from “Local Startup”.
The “Scheduled Tasks” page allows you to define system scheduled tasks using crontab.
The “Flash operations” page is for firmware upgrades, resets, and backups.
There is also a “Reboot” option.
 Network Settings
Network Settings
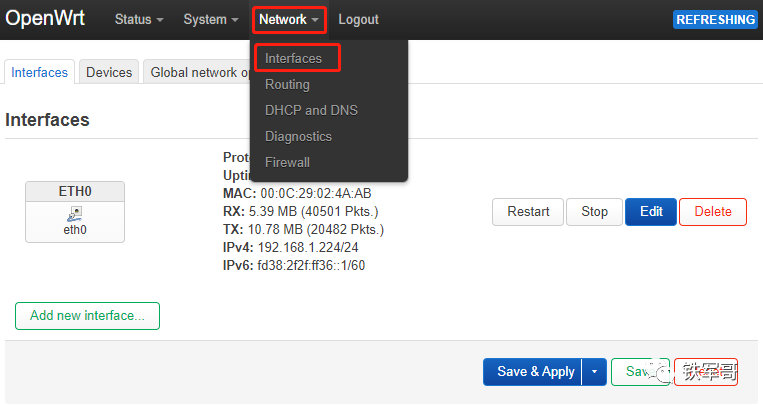
In the “Interfaces” settings, we only configured one interface ETH0, and we also want to test whether this interface works well in one-arm routing.
Next is the routing page, which currently has no routing information.
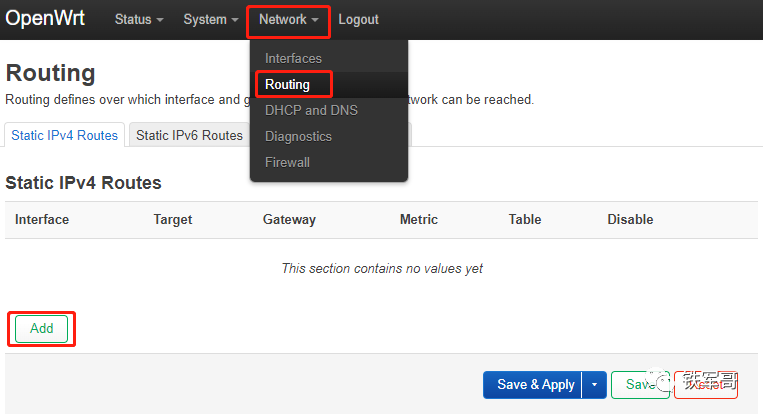
We click the “Add” button in the lower left corner to add a default route pointing to the gateway.
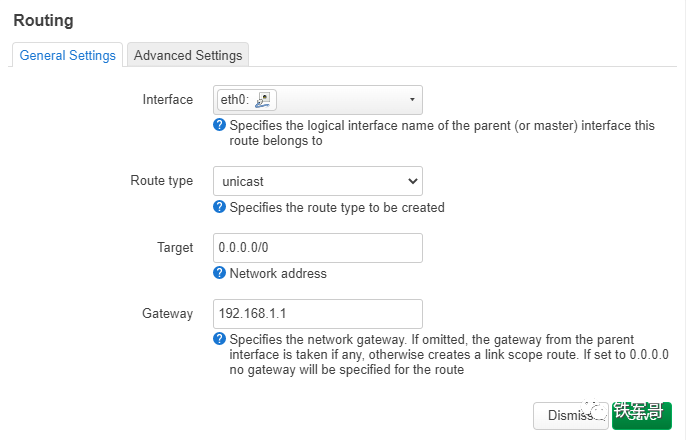
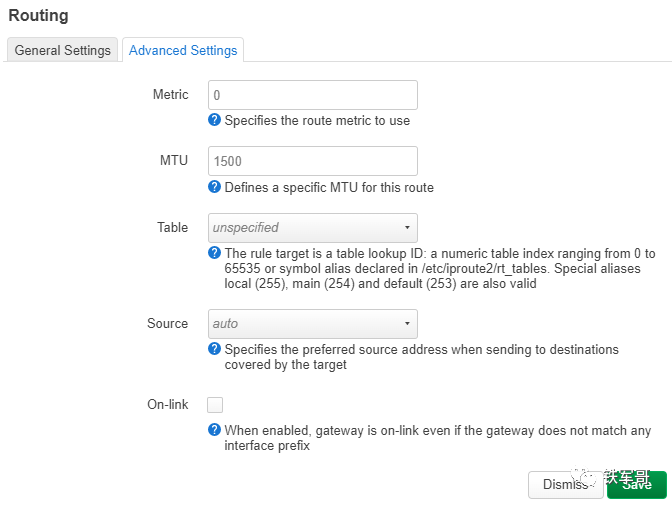
In addition to the basic configuration shown above, advanced configuration parameters such as priority, MTU, routing table, and source interface can also be configured.
In the DHCP and DNS settings page, the DNSmasq function is integrated by default (Notes on IP and UDP proxy transmission in MASQUE), and we need to configure the address information of the upstream DNS server on this page.
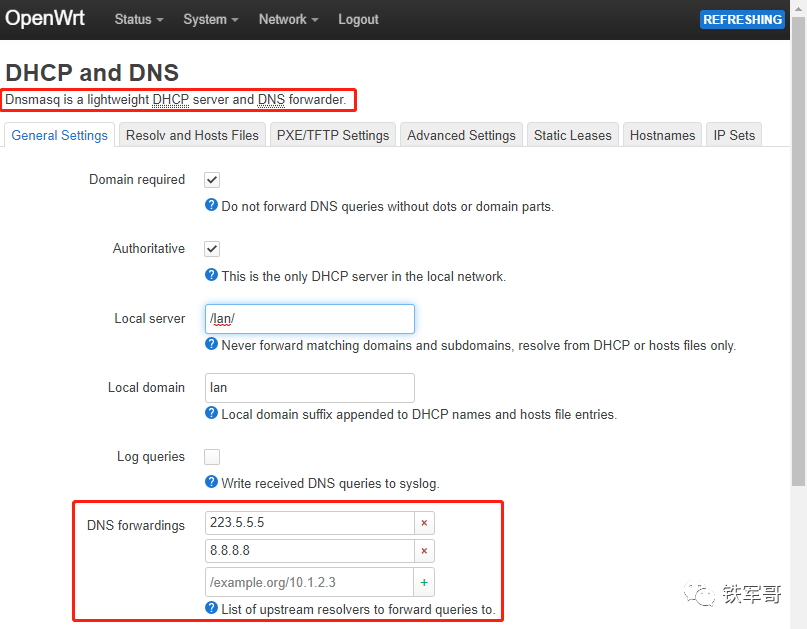
At this point, we can enable OpenWrt to access domain names.
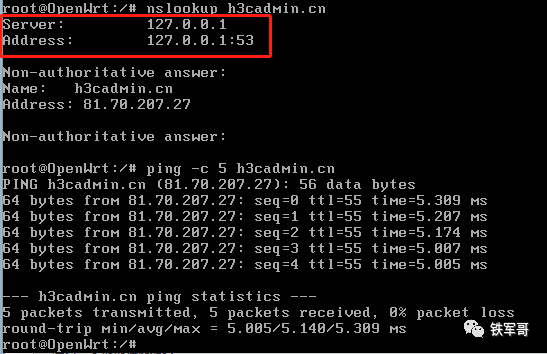
Through domain name resolution, we can see that the local DNS proxy function is enabled. Therefore, we can configure local domain name resolution in “Hostnames”.
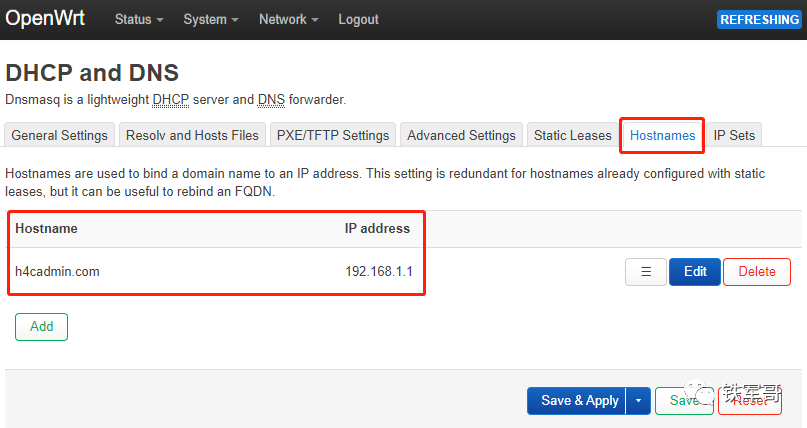
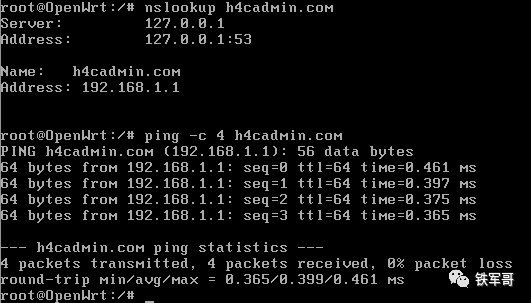
Let’s test the resolution effect.
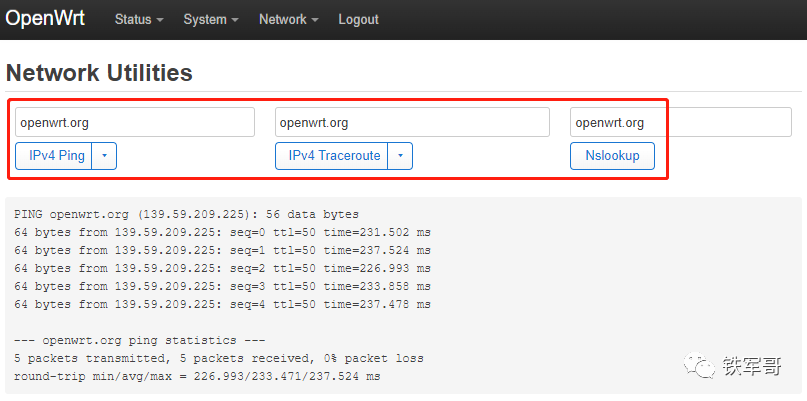
Of course, you can also test on the “Network Utilities” page, which supports dual-stack ping, traceroute, and nslookup functions.
The “Firewall” settings also include the concept of security zones, and you can set NAT rules on this page.
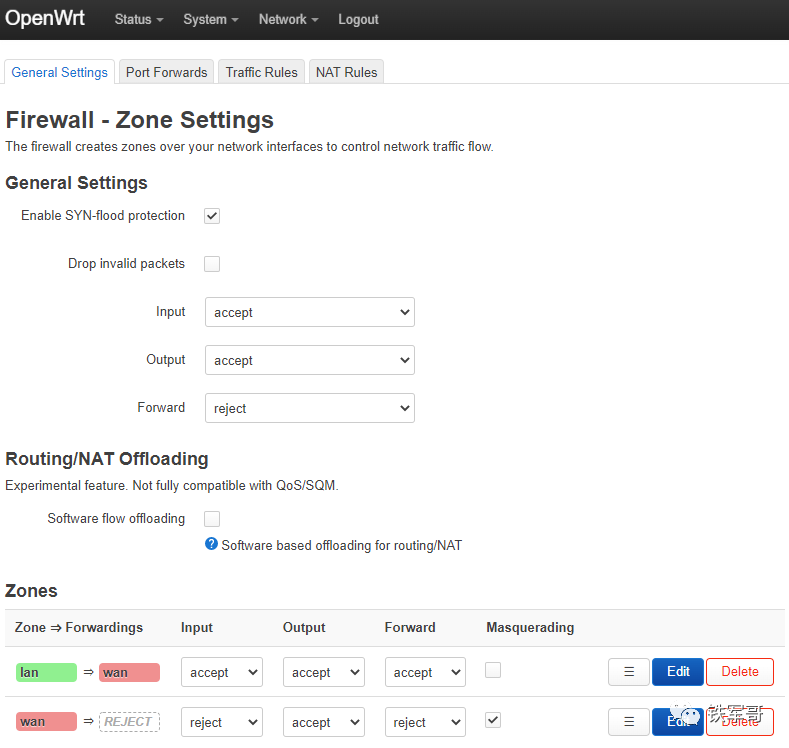
At this point, we can test whether the one-arm routing works well.
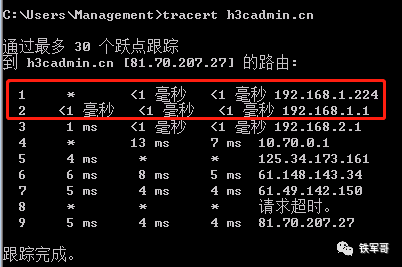
We set the host gateway to OpenWrt, and by tracing the path, we can see that it has successfully forwarded through OpenWrt, with minimal latency change.
 Status Information
Status Information
Finally, we return to the status information to check the connection information.
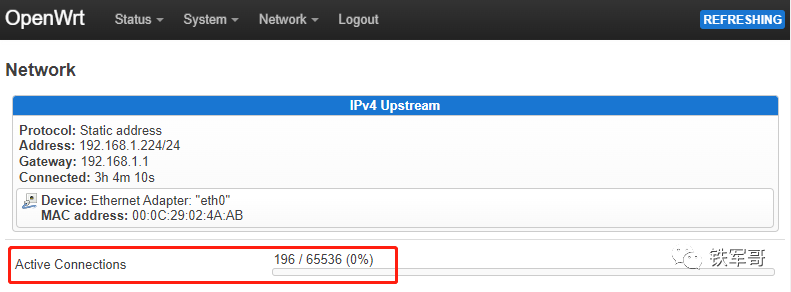
We can see that with one host online, there are about 200 connection information in the background. If calculated this way, a typical public IP address can handle about 65535 connections, which means it can support around 300 users accessing the internet.
Then let’s test the speed.
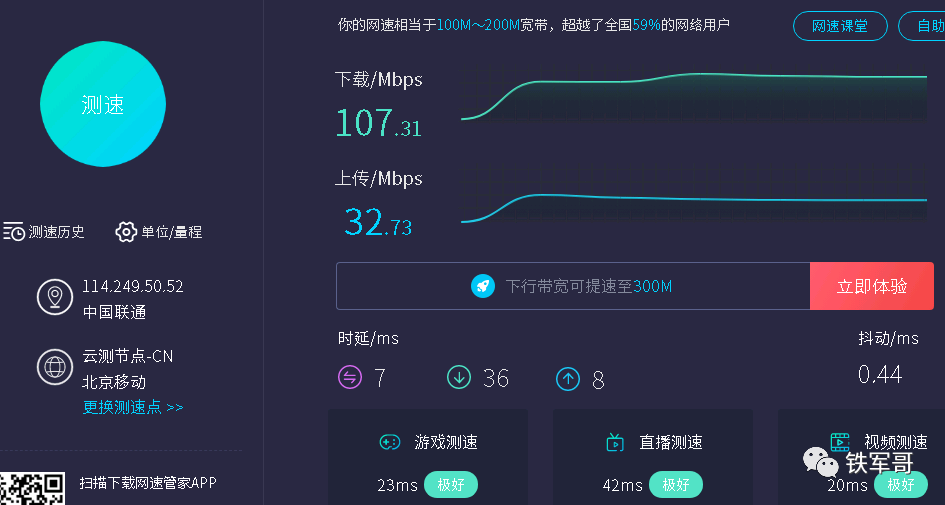
Overall, the performance is similar to that of a direct connection to the gateway router, which is quite good.
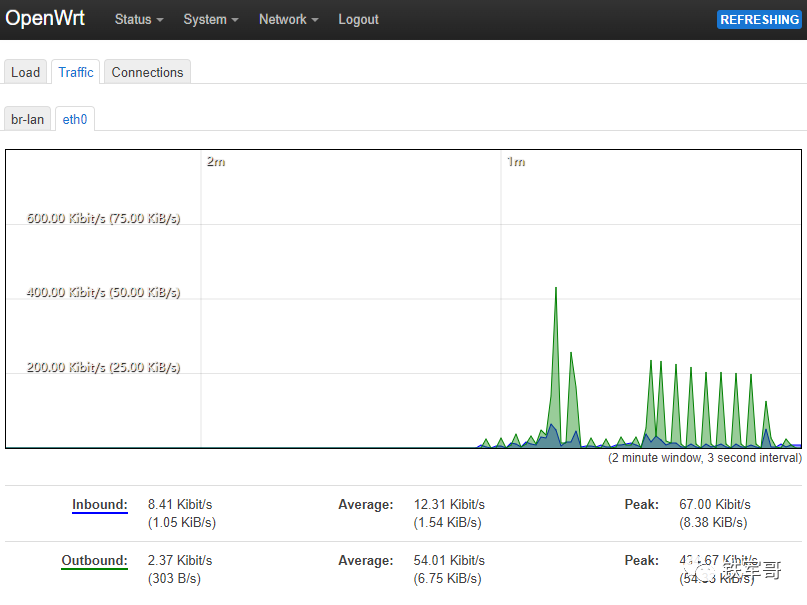
There is also traffic monitoring information, refreshing every 3 seconds.
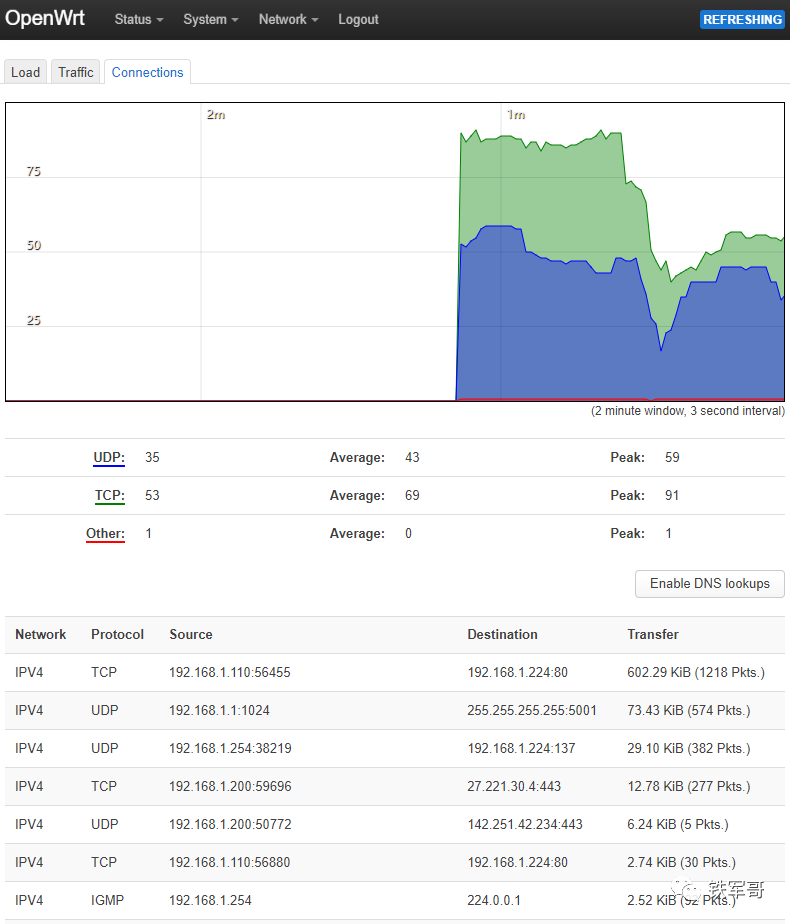
Monitoring information for session connections.
In one-arm mode, there is no need to configure complex firewall rules and SNAT, which (Turning OpenWrt into a real router on ESXi) is quite simple.

Long press the QR code to follow us.

 Deploying OpenWrt on x86 servers openVPN+SmartDNS=openDNS or smartVPN? Configuring SSH remote login for Kali Linux Connecting to remote desktop via MSTSC for Kali Quick configuration of MSR810-LM for internet dialing through LTE module With a public IP address, it must be used with DDNS! Detailed DDNS configuration How many ports are actually blocked for public IPv4 addresses in home broadband? Guide for connecting/disconnecting openVPN with authentication Ubuntu compiling and installing VPP23.02 Using Python to batch process Excel content How to extract fixed cell content from Excel using Python Deploying SmartDNS based on CentOS
Deploying OpenWrt on x86 servers openVPN+SmartDNS=openDNS or smartVPN? Configuring SSH remote login for Kali Linux Connecting to remote desktop via MSTSC for Kali Quick configuration of MSR810-LM for internet dialing through LTE module With a public IP address, it must be used with DDNS! Detailed DDNS configuration How many ports are actually blocked for public IPv4 addresses in home broadband? Guide for connecting/disconnecting openVPN with authentication Ubuntu compiling and installing VPP23.02 Using Python to batch process Excel content How to extract fixed cell content from Excel using Python Deploying SmartDNS based on CentOS