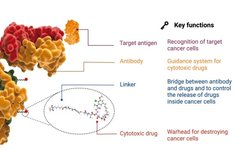
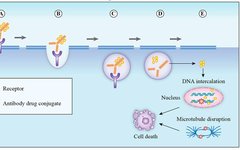
Advanced Development with STM32
For most beginners, understanding how a compiler compiles a .c file into an .o file is not very difficult, but it is challenging to grasp the purpose of the final linking process and why it is done this way.Additionally, why is the startup file in our sample project one that we wrote ourselves, and how … Read more