

1. Mechanism of ADC Action
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) (Click to enter the database to search for global ADC drug information) enter the body, the antibody part binds to the targeted antigen on the surface of tumor cells, tumor cells will endocytose the ADC molecule. Among them, some can bind to Fc receptors in the endosome, thus some ADC is transported to the cell surface and released into the extracellular space through FcRn-mediated transcytosis, while other ADC-antigen complexes enter lysosomes, where enzymes or the acidic environment can degrade ADC, thus releasing cytotoxic chemicals that damage DNA or prevent tumor cell division, thereby achieving the purpose of killing tumor cells.

Any component of the ADC structure can become abnormal or lead to the development of resistance under periodic treatment stress.ADC’s resistance mechanisms may include: excessive ADC exposure; downregulation, deletion, or mutation of target antigen genes; loss of internalization pathways; decreased lysosomal proteolytic function; mutations of lysosomal transport proteins; cell cycle arrest; abnormal expression of drug efflux transporters; activation of downstream signaling pathways; dysregulation of apoptosis, etc.
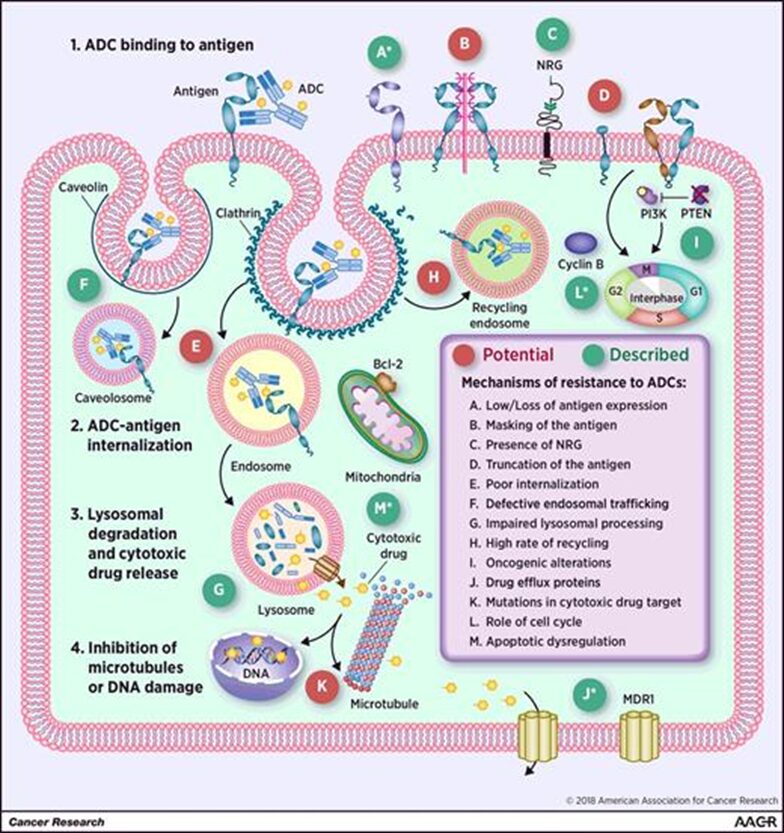
Image source: Resistance to Antibody–Drug Conjugates. Cancer Res 1 May 2018; 78 (9): 2159–2165.

Repeated exposure to ADC can induce tumor cells to develop resistance. For example: repeated exposure to anti-HER2 Trastuzumab-emtansine (T-DM1)(click to view drug details), will make HER2-positive breast cancer cell lines develop resistance to T-DM1. This is also the current routine experimental method for constructing ADC-resistant mouse models.
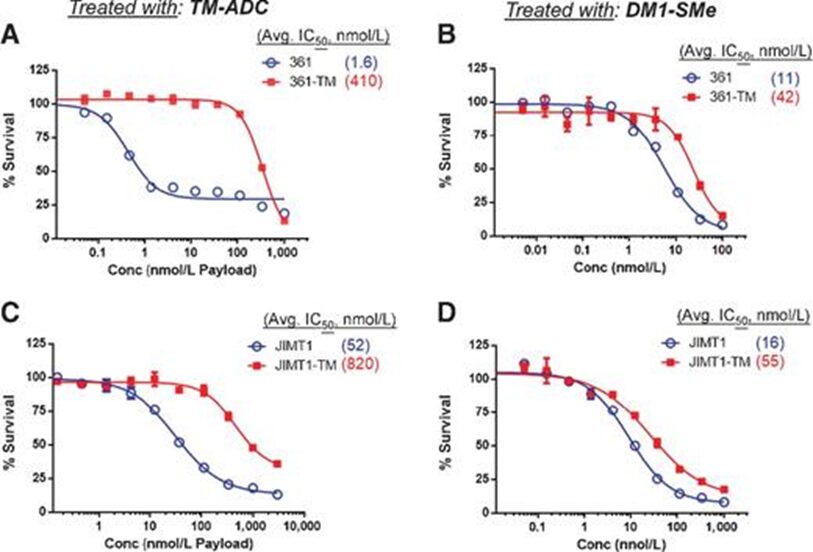
Cell toxicity characteristics of parental cells and resistant cells treated with TM-ADC and pure drug DM1-SMe
Image source: Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Apr;14(4):952-63.doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0862. Epub 2015 Feb 2. PMID: 25646013
Ironically, high antigen expression may also reduce ADC effectiveness. This mainly occurs in Gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg®), where high CD33 antigen load in peripheral blood is an independent adverse prognostic factor. Gemtuzumab intravenous infusion leads to complete saturation of CD33 in peripheral blood, which is significantly lower than the saturation of CD33 in the corresponding peripheral blood samples (>>90%) compared to the saturation of CD33 in the bone marrow (40-90%). Clearly, high CD33 antigen load in the blood depletes Gemtuzumab, thus limiting its penetration into the bone marrow. This may also be the reason why Gemtuzumab ozogamicin only induces remission in about 30% of relapsed AML patients.

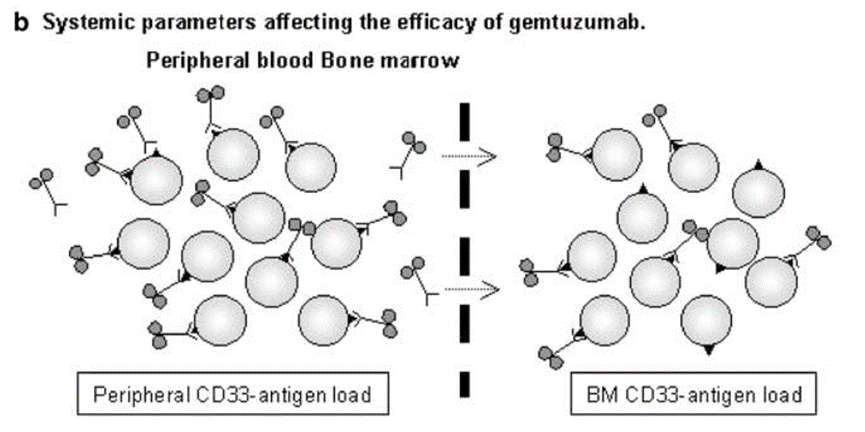
Image source: High CD33-antigen loads in peripheral blood limit the efficacy of gemtuzumab ozogamicin (Mylotarg) treatment in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Leukemia. 2004 May;18(5):983-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2403350. PMID: 15029214.
Truncation of the antigen extracellular domain or masking of extracellular matrix components may be related to HER2(click to enter the mini-program to search for global drug data on HER2) resistance mechanisms to trastuzumab. Tumor subgroups that overexpress HER2 also express p95HER2, a truncated receptor with kinase activity. In samples from 46 HER2-overexpressing late-stage breast cancer patients receiving trastuzumab treatment, immunofluorescence assessment of p95HER2 expression showed a direct correlation with trastuzumab resistance (P = .029, calculated using two-sided chi-square test).

Image source: Expression of p95HER2, a truncated form of the HER2 receptor, and response to anti-HER2 therapies in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007 Apr 18;99(8):628-38. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djk134.
The presence of antigen ligands may affect sensitivity to ADC. Studies have shown that ligands that promote HER2 heterodimerization with HER3 and HER4 (such as neuregulin NRG-1β) can weaken the efficacy of T-DM1. The effect of NRG-1β on T-DM1 activity in HER2-amplified breast cancer cell lines (as shown in the figure below).A, BT-474, SK-BR-3, and ZR-75-30: NRG-1β (2 nmol/L) nearly completely inhibits T-DM1 activity (left).The right figure shows the dose-dependent reduction of T-DM1 activity by NRG-1β.

Image source: Dual targeting of HER2-positive cancer with trastuzumab emtansine and pertuzumab: critical role for neuregulin blockade in antitumor response to combination therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Jan 15;20(2):456-68. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0358. Epub 2013 Oct 4. PMID: 24097864.

4. Defects in Internalization and Transport to the Lysosome Pathway
After binding to the target, the antibody is internalized into the cell. Endocytosis can occur through different internalization pathways, such as clathrin-mediated (CME), caveolin-mediated, and clathrin-caveolin-independent endocytosis. It has been reported that CME is the central route used by various ADCs.


ADC needs to reach the lysosome, and then the cytotoxic agent is released through chemical or enzymatic cleavage. In cells that have developed resistance to T-DM1 after long-term exposure to the drug, it has been observed that T-DM1 accumulates in lysosomes. In these cells, the drug reaches the lysosomal compartment, but proteolytic activity is lower than that in sensitive cells. This defect is due to elevated lysosomal pH, which in turn inhibits lysosomal protease activity.
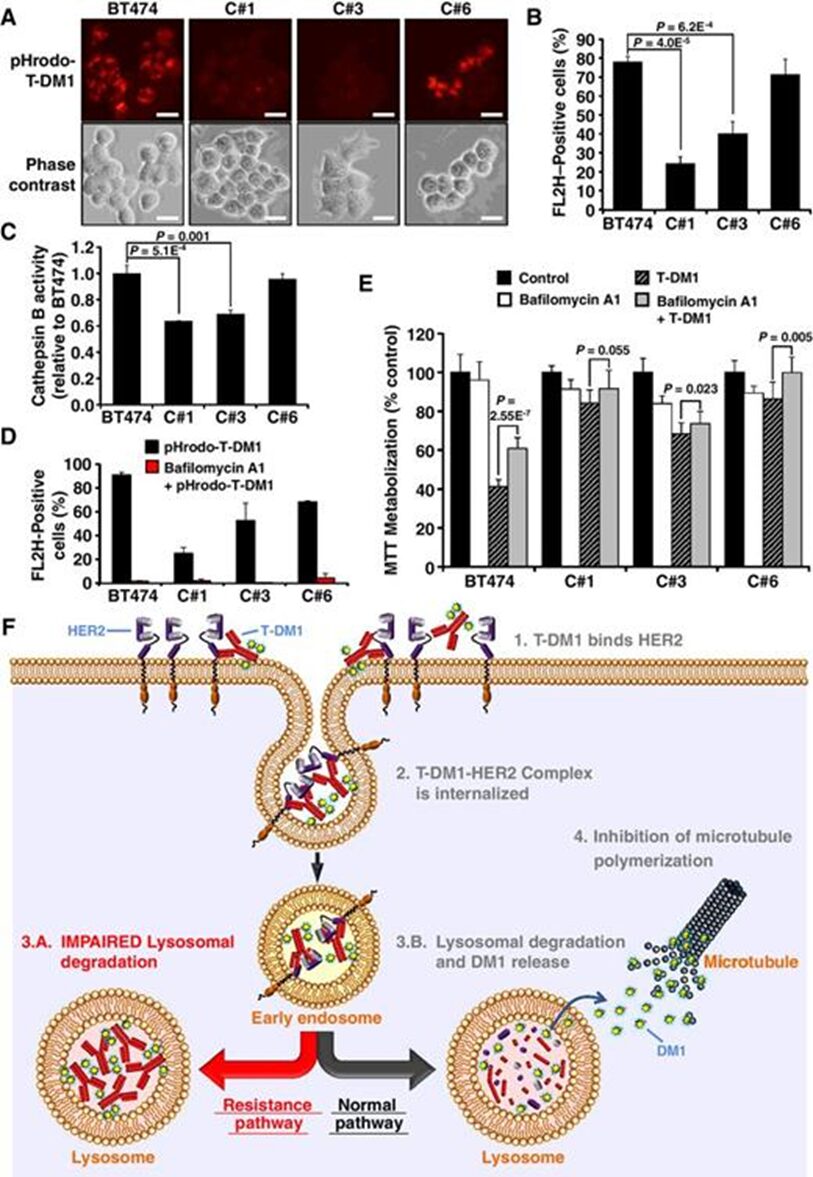 Image source: Resistance to the Antibody-Drug Conjugate T-DM1 Is Based in a Reduction in Lysosomal Proteolytic Activity. Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;77(17):4639-4651. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3127. Epub 2017 Jul 7. PMID: 28687619.
Image source: Resistance to the Antibody-Drug Conjugate T-DM1 Is Based in a Reduction in Lysosomal Proteolytic Activity. Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;77(17):4639-4651. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3127. Epub 2017 Jul 7. PMID: 28687619.Another mechanism of resistance to ADC is related to the transport of cytotoxic agents from the lysosomal lumen to the cytoplasm. This is associated with ADCs that have non-cleavable linkers, where the metabolism of the ADC releases the linker-cytotoxic agent attached to amino acid residues. The lysosomal membrane is impermeable to these metabolites and requires a transport mechanism to move them from the lysosomal lumen to the cytoplasm.
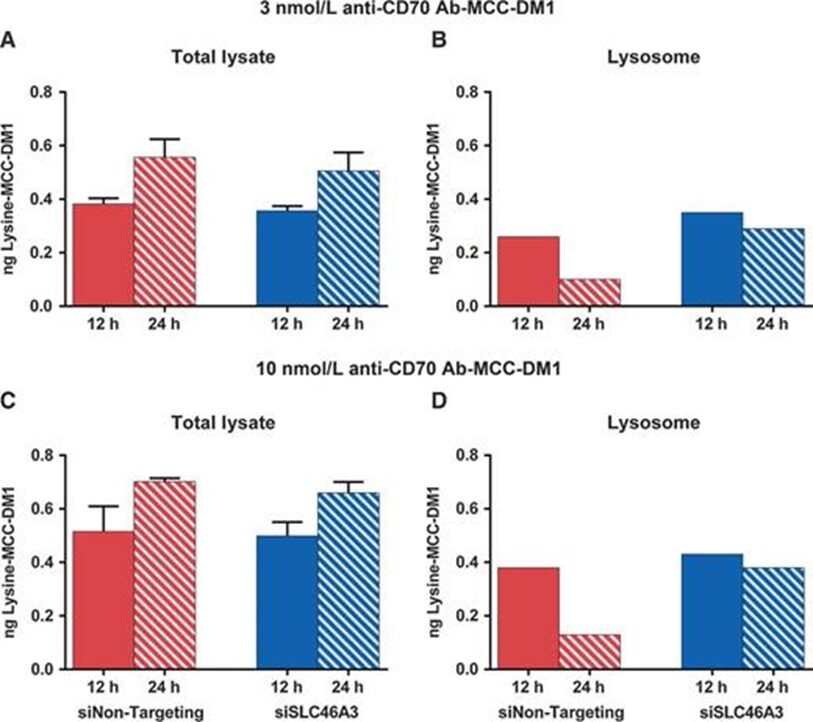
Image source: SLC46A3 Is Required to Transport Catabolites of Non-cleavable Antibody Maytansine Conjugates from the Lysosome to the Cytoplasm. Cancer Res. 2015 Dec 15;75(24):5329-40. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1610. Epub 2015 Dec 2. PMID: 26631267.

Due to overexpression of ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC), drugs are expelled from cells, inhibiting the cytotoxic effects of anticancer agents, which is a major cause of multidrug resistance (MDR) in human malignancies. These drug efflux pumps may also lead to resistance to ADCs, as many cytotoxic agents are substrates for ABC transporters.
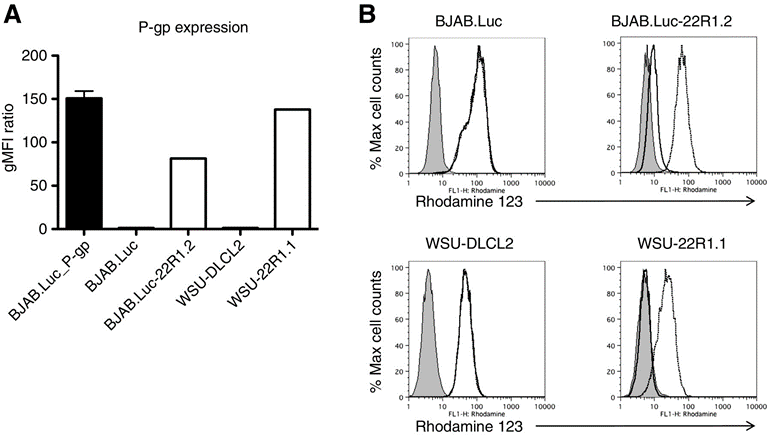
Image source: A Novel Anti-CD22 Anthracycline-Based Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) That Overcomes Resistance to Auristatin-Based ADCs. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jul 15;21(14):3298-306. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-2035. Epub 2015 Apr 3. PMID: 25840969.

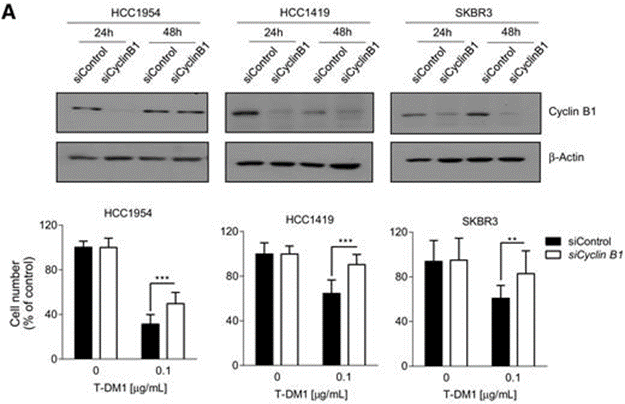
Cyclin B is a cyclin involved in the G2-M transition, and silencing cyclin B leads to drug resistance. Studies have observed that in HER2+ breast cancer cells sensitive to T-DM1, the drug increases cyclin B, while this increase is not observed in cells that develop resistance to T-DM1. Researchers transfected cell lines with siRNA targeting cyclin B1 mRNA, finding that cyclin B1 levels were significantly lower than in si control; assessing cell viability revealed that silencing cyclin B1 induced significant resistance to T-DM1 in all three parental cell lines (Figure A).

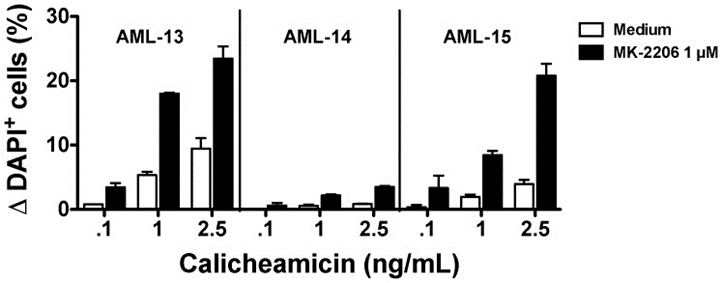
Activated PI3K/AKT signaling may generate ADC resistance. The small molecule allosteric inhibitor AKT MK-2206 makes resistant cells sensitive to gemtuzumab ozogamicin (GO) or free calicheamicin. A clinical study is currently exploring the safety and early signs of efficacy of T-DM1 in combination with PI3K inhibitors (NCT02038010)

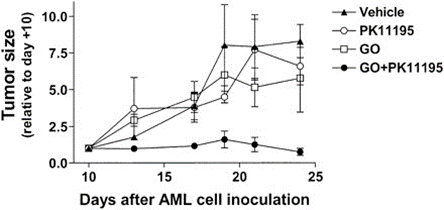
Changes in apoptosis may also regulate sensitivity to ADC. Overexpression of anti-apoptotic proteins BCL-2 and BCL-X is associated with gemtuzumab ozogamicin (GO) resistance, and studies have shown that PK11195 can increase the expression of anti-apoptotic proteins and drug transporters in AML cells, enhancing GO cytotoxicity. It has been found that PK11195 can safely increase the anti-leukemia activity of GO in mouse models; additionally, Oblimersen selectively targets Bcl-2 mRNA, which has been shown in preclinical studies to enhance the apoptotic activity of various anti-leukemia drugs (including GO); in NHL cell lines, Dornan and colleagues found that the expression level of BCL-XL was associated with reduced sensitivity to anti-CD79b-valine-citrulline-MMAE. In vivo data show that the BCL-2 family inhibitor ABT-263 enhances the activity of ADCs.

10. Summary
Editor: 💧Transparent
This post is used to convey knowledge. If there are any copyright issues, please contact us within 30 days of publication.
Original content is prohibited from being reproduced on other platforms without authorization.
If you have questions, you can email [email protected] for more information.
©2021 Medical Overview All rights reserved


Scan the mini-program below

