Xinge Corporation (headquartered in Nagoya, Aichi Prefecture, Japan) recently announced that non-clinical data for its novel antibody-drug conjugate (ADUC) K-679 will be officially presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2025, scheduled to take place from April 25 to 30, 2025, in Chicago, Illinois, USA.
K-679
K-679 is an antibody-drug conjugate (ADUC) that utilizes Xinge Corporation’s proprietary micelle technology. This drug integrates a large payload into a single-chain polymer by conjugating an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) antibody with the drug payload (DM1), achieving an ultra-high drug-antibody ratio (DAR), with each antibody averaging about 40 DM1 molecules, significantly higher than traditional antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).
In non-clinical studies, K-679 demonstrated strong anti-tumor effects in xenograft models, outperforming traditional ADCs. Notably, K-679 exhibited significant efficacy not only in EGFR-positive tumors but also showed good therapeutic effects in EGFR-negative heterogeneous tumors, with a remarkable bystander killing effect. This innovative drug is expected to provide a new and more effective treatment option for EGFR-expressing solid tumors.
Platform Patents
In 2022, Xinge Corporation applied for the platform patent, which is currently published in several countries, including Australia and South Korea, while still undergoing substantive examination in China.

According to the Chinese patent (CN 119698305), the core structure of the platform consists of a polymer divided into three parts: structural unit (A) functions as a hydrophilic unit, structural unit (B) serves as a hydrophobic unit, and structural unit (C) acts as a scaffold for binding active ingredients (drugs, physiologically active substances) with copolymer X or target-recognition copolymers.
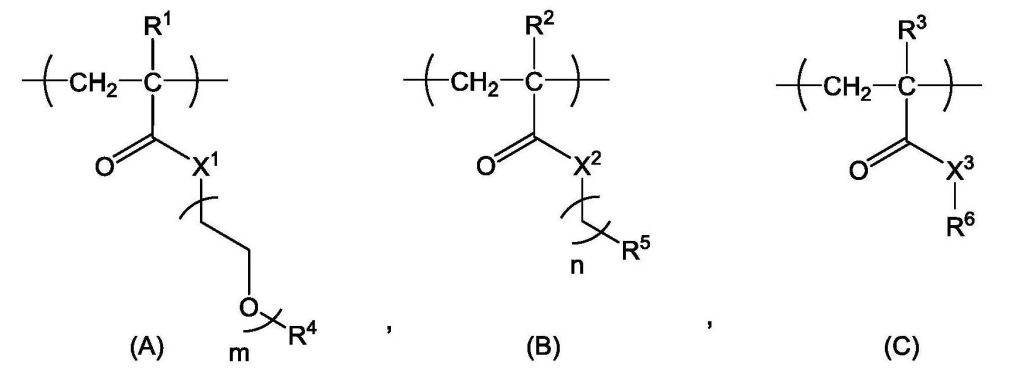
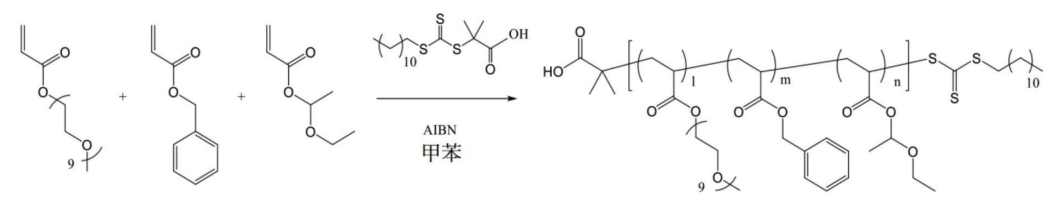
Copolymer synthesis is achieved through varying ratios of mPEGA, BnA, and EEA.
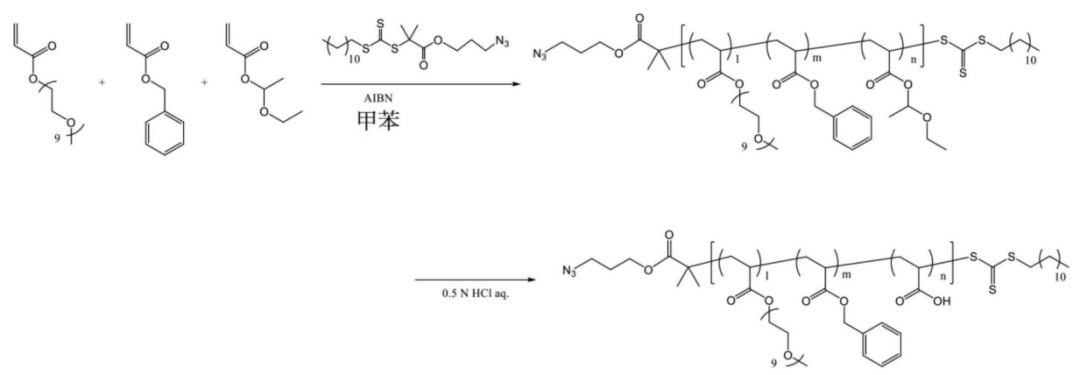
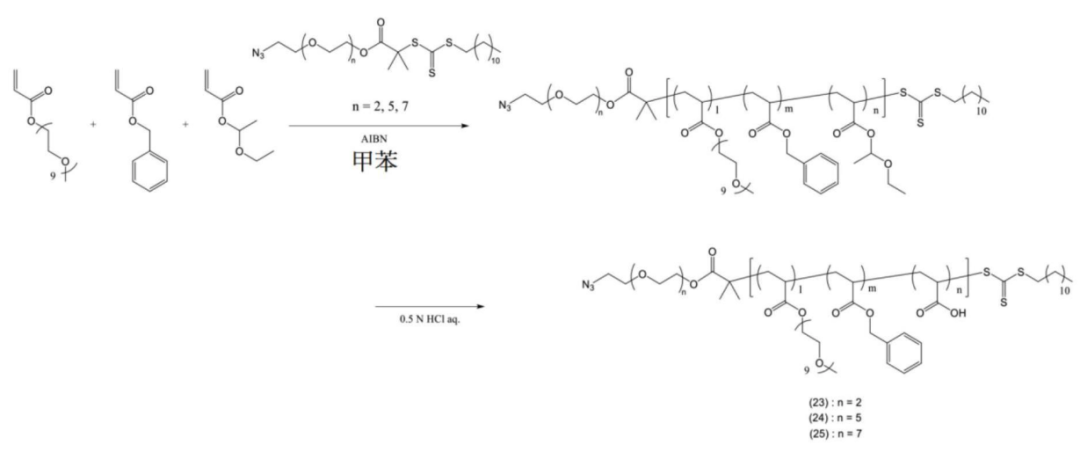
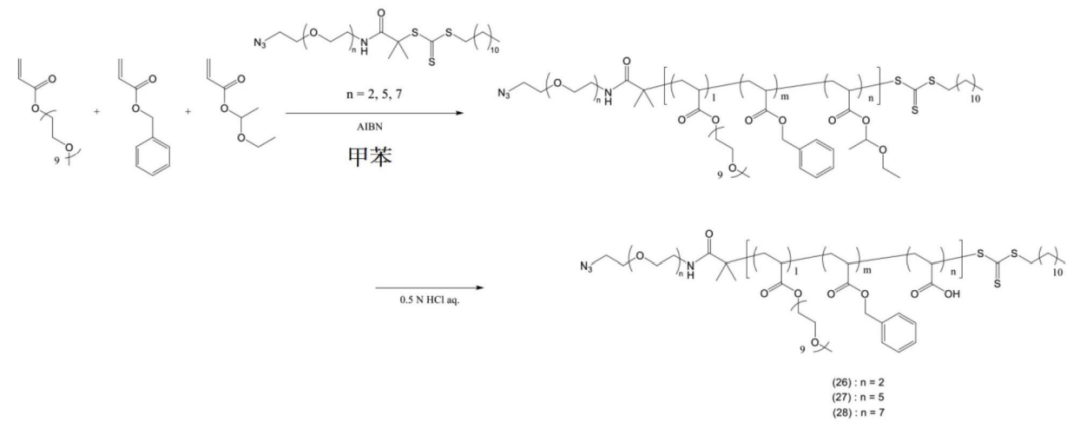
Some copolymers are further modified.
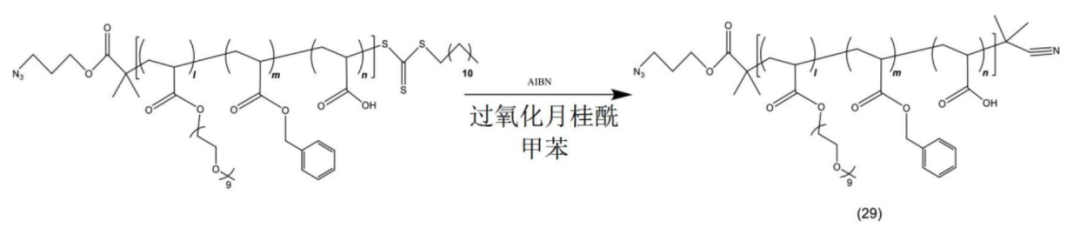
The copolymer is connected to the payload.
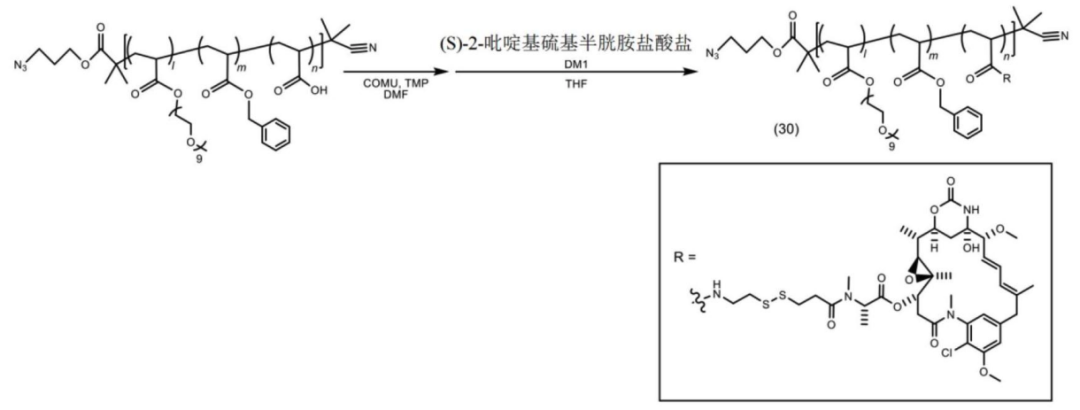
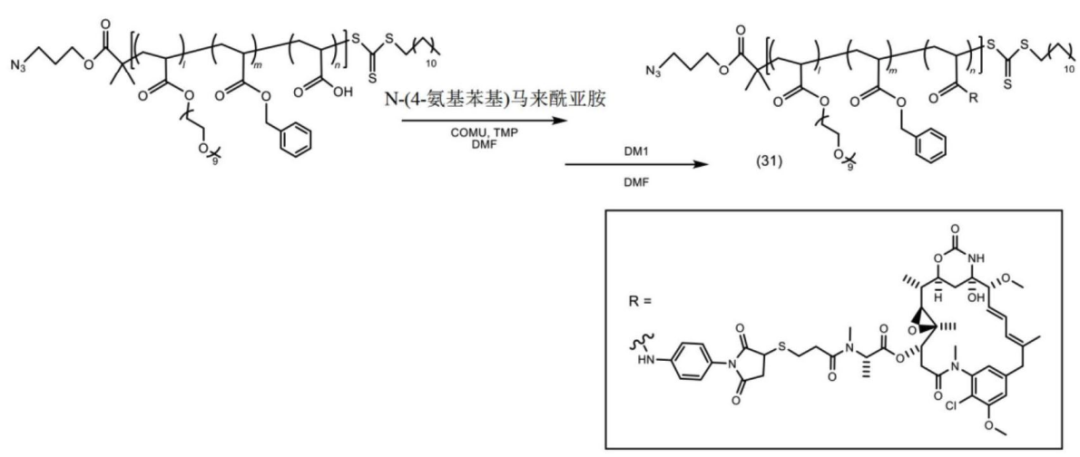
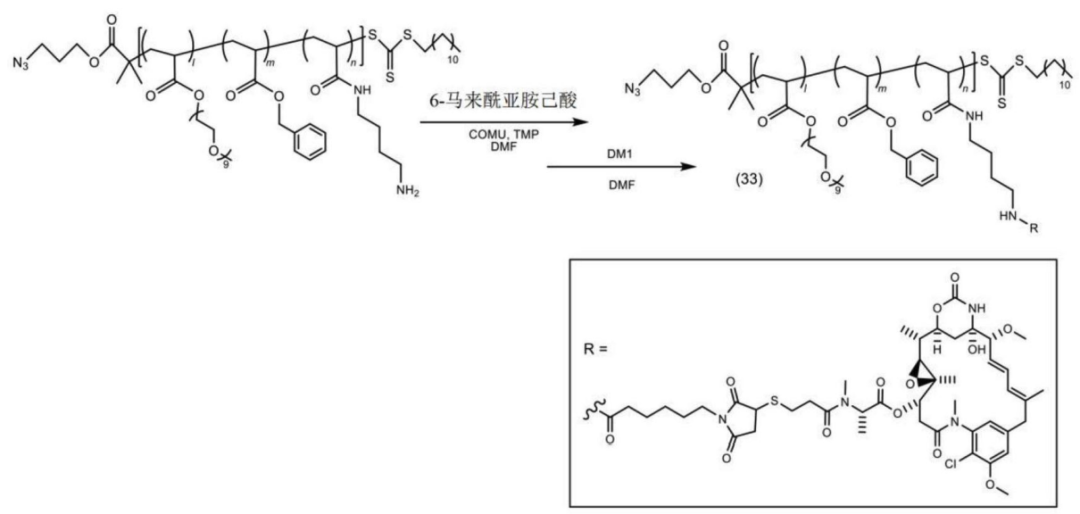
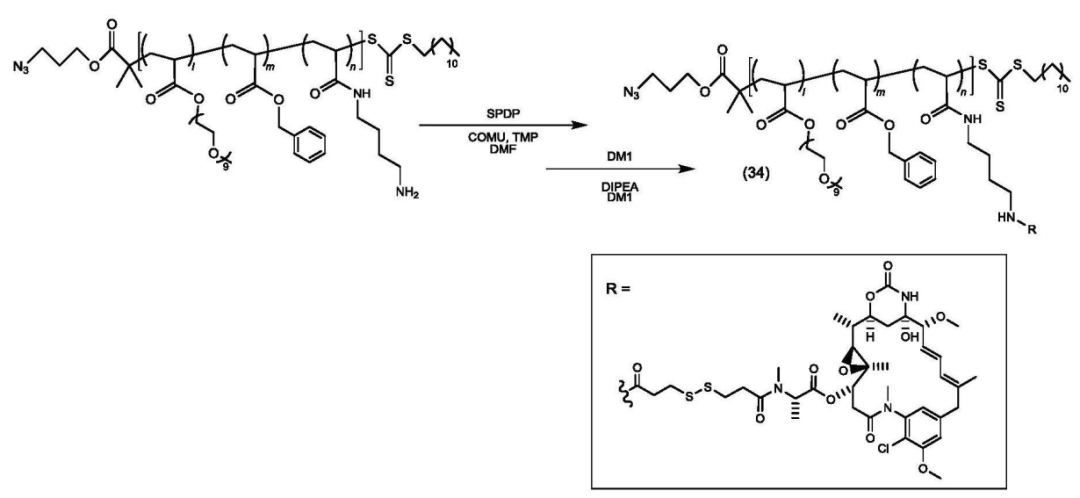
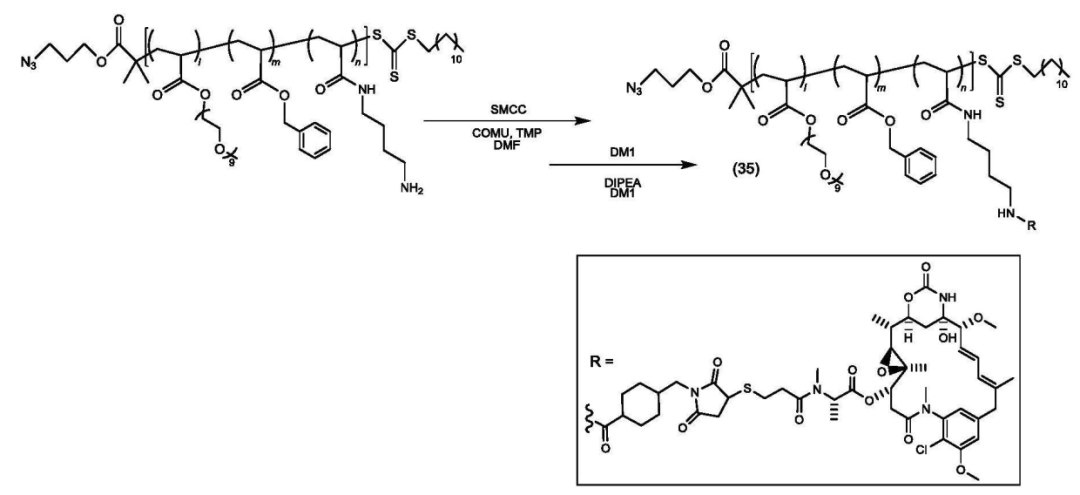
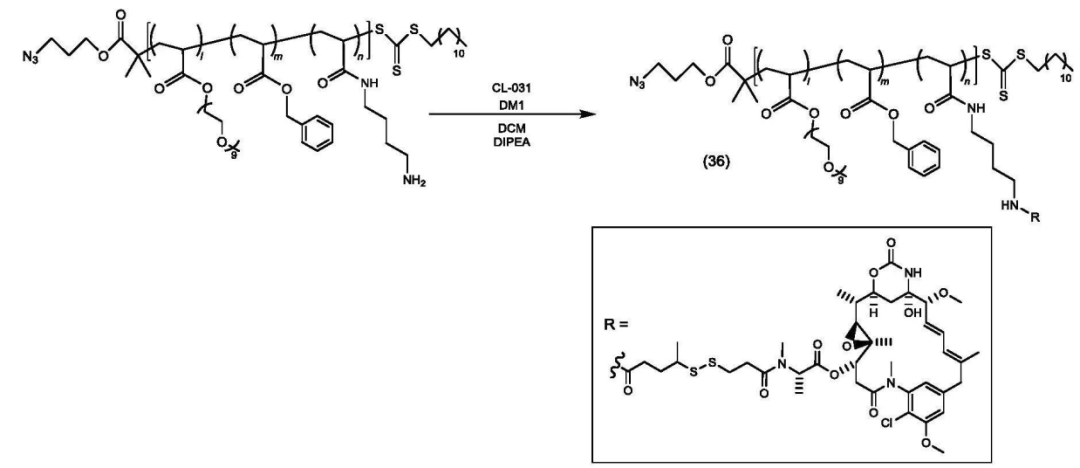
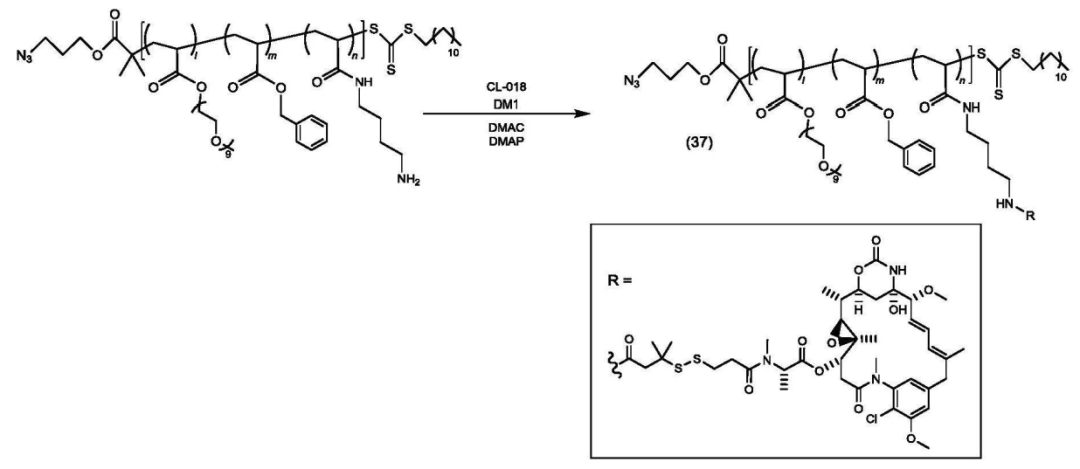
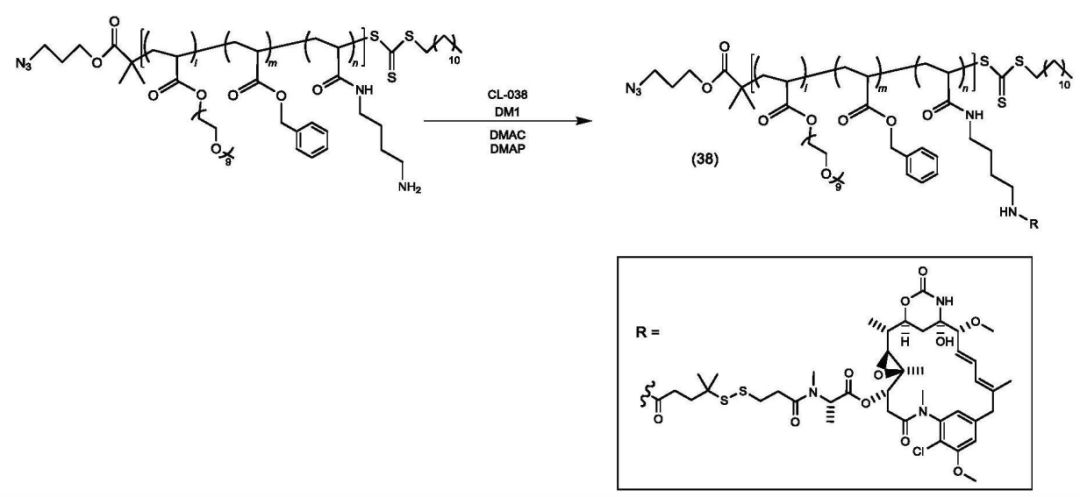
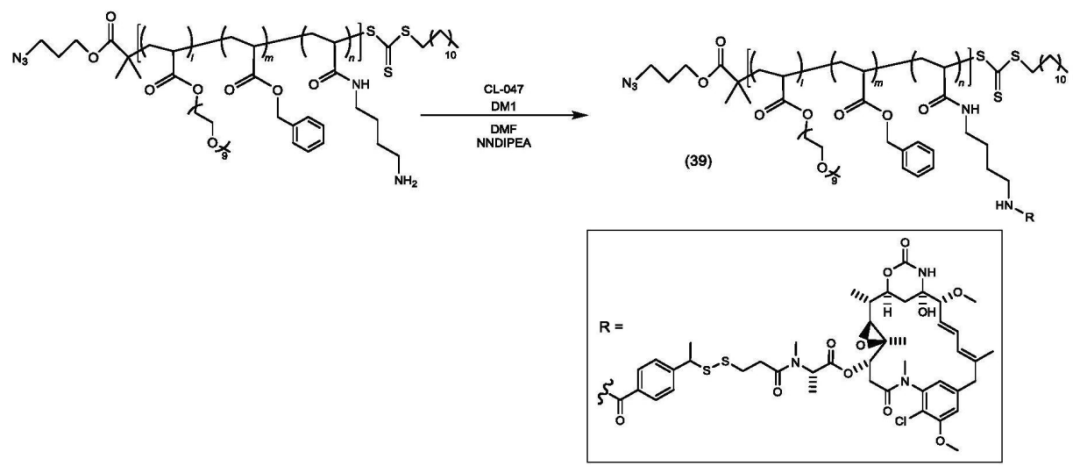
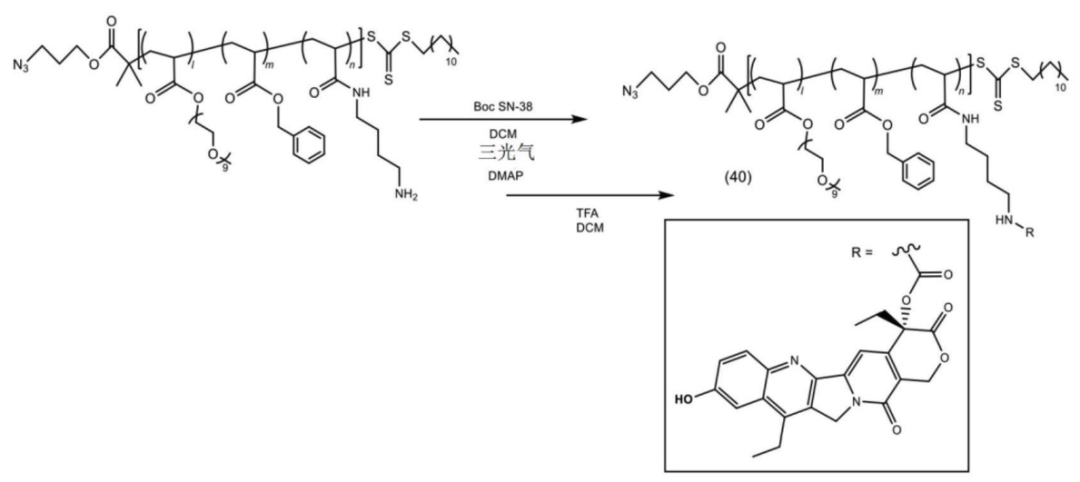
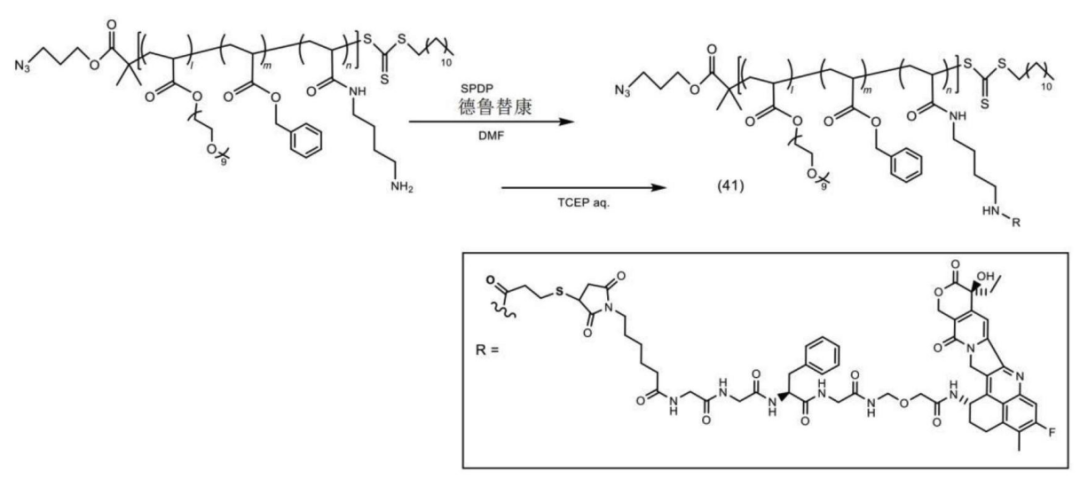
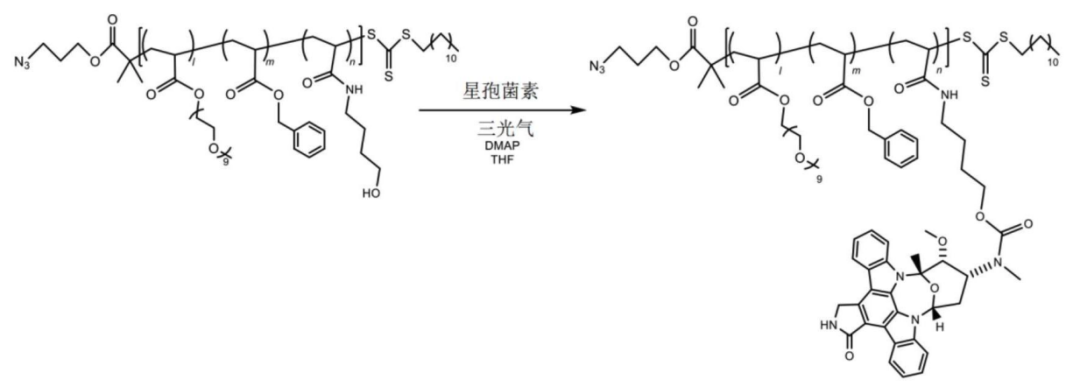
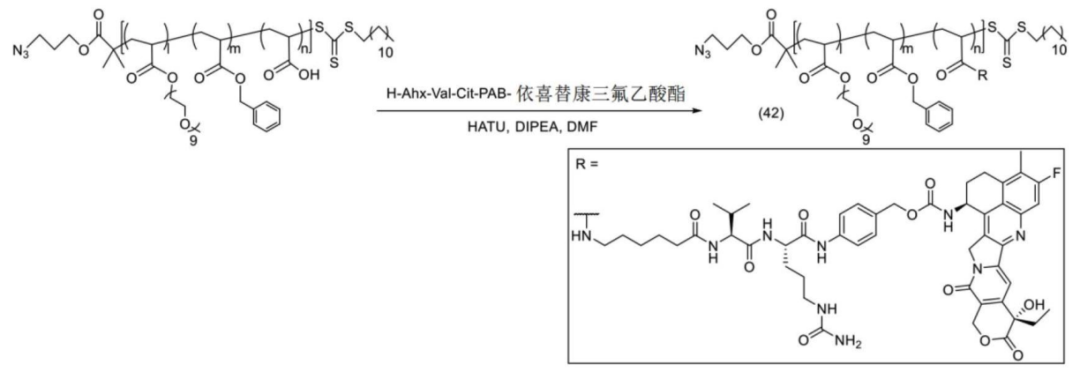
The polymer-payload complex is connected to the antibody.
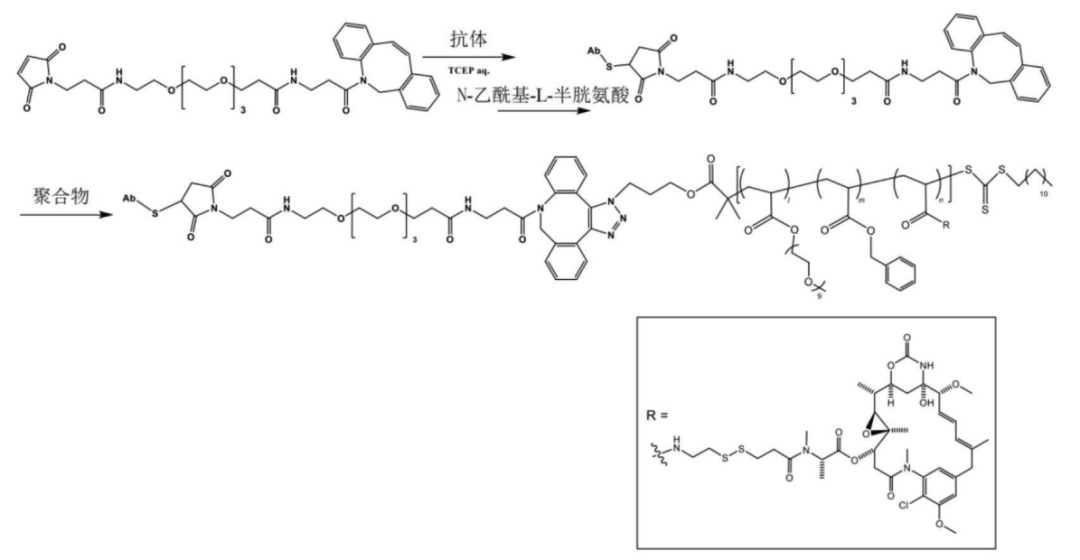
Based on this platform, the DAR value can reach an astonishing 85.
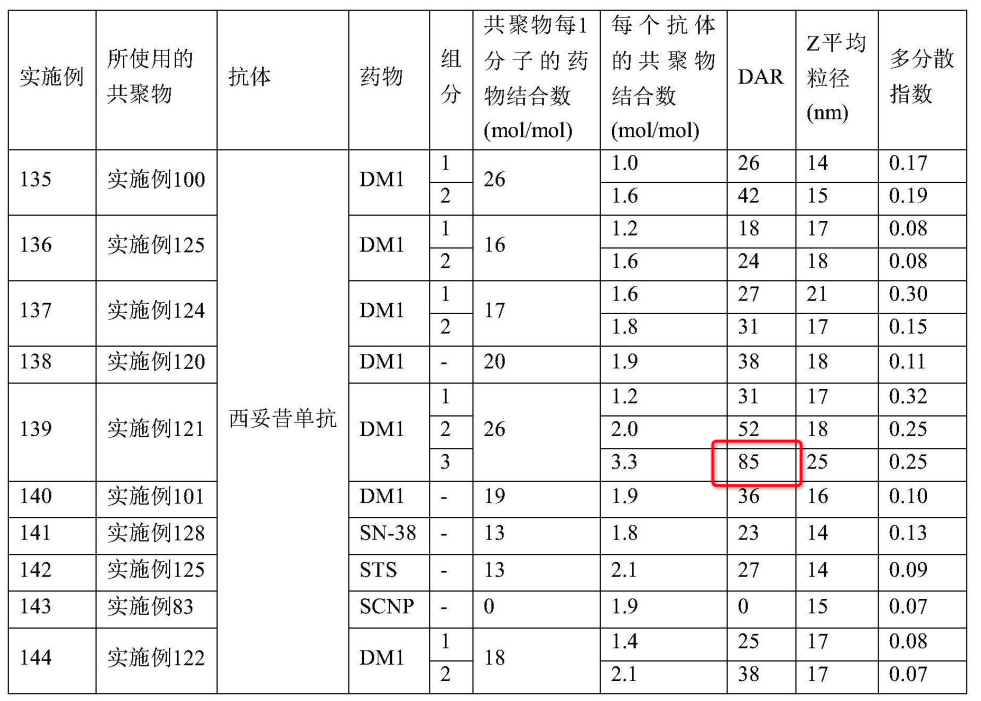
Examples of High DAR Value Efficacy Trials
Example 138
DAR = 38, Cetuximab + DM1
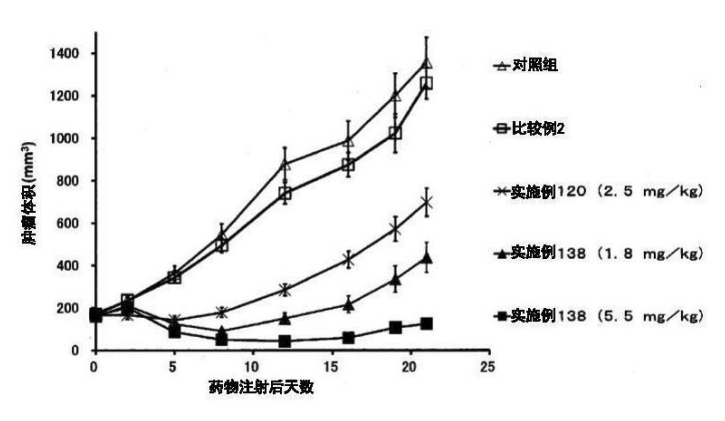
Example 161
DAR = 41, Cetuximab + DM1
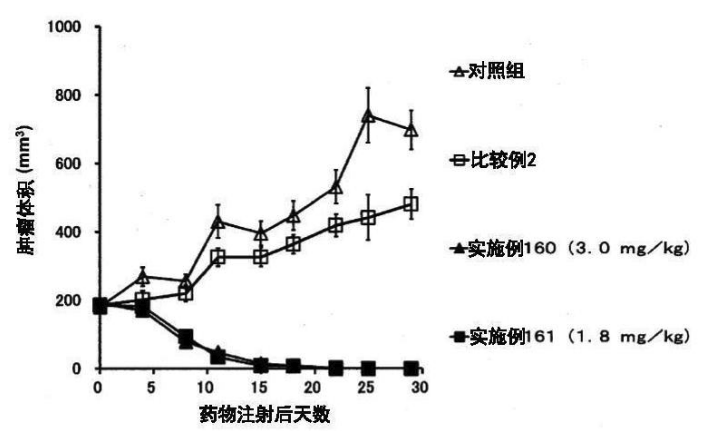
Example 163
DAR = 43, Cetuximab + DM1
Example 151
DAR = 40, Trastuzumab + DM1
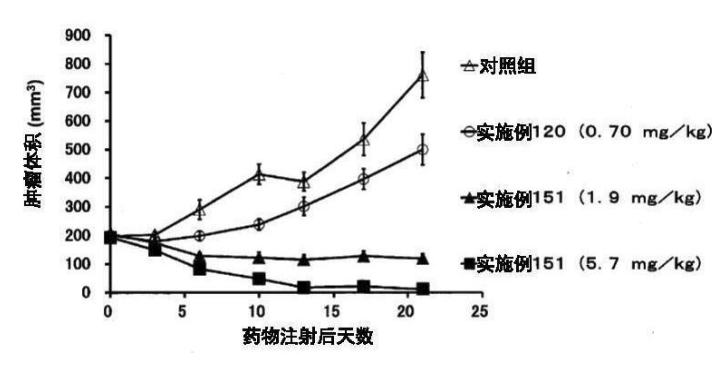
Conclusion
Traditionally, the optimal DAR for ADCs is considered to be between 4 and 8. Previously, Mersana Therapeutics attempted to develop some high DAR ADC projects (10-15), such as XMT-1536 and XMT-1522, but these projects failed, raising doubts about the feasibility of high DAR ADCs in the industry.
However, recent innovative attempts by Puzhong Company and Xinge Corporation have brought new hope for the development of high DAR ADCs. These two companies are reintroducing high DAR ADCs to the public eye and are committed to breaking traditional limitations through technological innovation, demonstrating the potential value of high DAR ADCs in drug development. Their efforts are expected to not only advance ADC technology but also provide more effective solutions for cancer treatment.