↑ Click on the above
“Smart Manufacturing Home”
Follow us
Introduction
Hello everyone, I am Alic, a friend of the owner Xiaozhi~
Industrial communication is an unavoidable topic in our field control, and we have introduced many aspects before, such as redundant networks, VLAN, PROFINET, etc.~
The main content of this communication discussion includes:
01 Overview of Communication
02 Communication under SIMATIC NET
03 What Can Save You from Confusion
01 Overview
Prerequisite for reading:
In previous articles:
The Two Layers and Three Levels of Industrial Networks – From PLM to MES, and then to SCADA and PLC connections
From this, we know that generally, the enterprise communication network can be divided into three levels: enterprise level, workshop level, and field level.
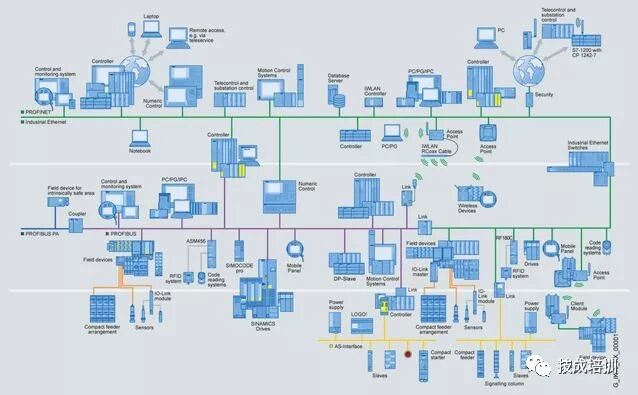
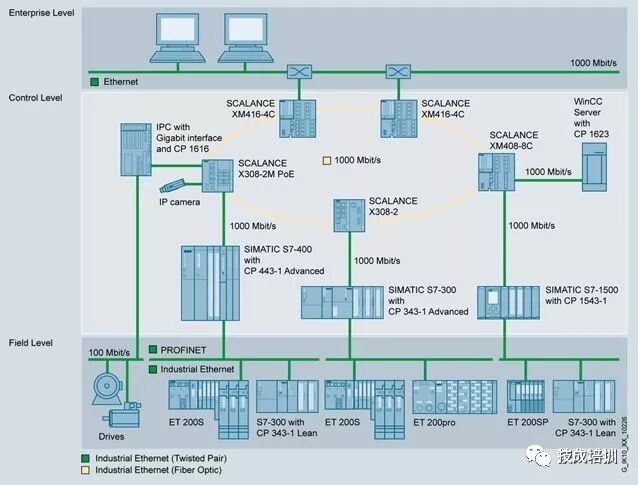
Within the scope of Siemens industrial communication network solutions, many communication technologies are used. In communication, configuration, and programming, in addition to the industrial Ethernet and PROFIBUS mentioned above, other communication technologies are also required.
02 Communication under SIMATIC NET
Below is a brief introduction to SIMATIC NET.
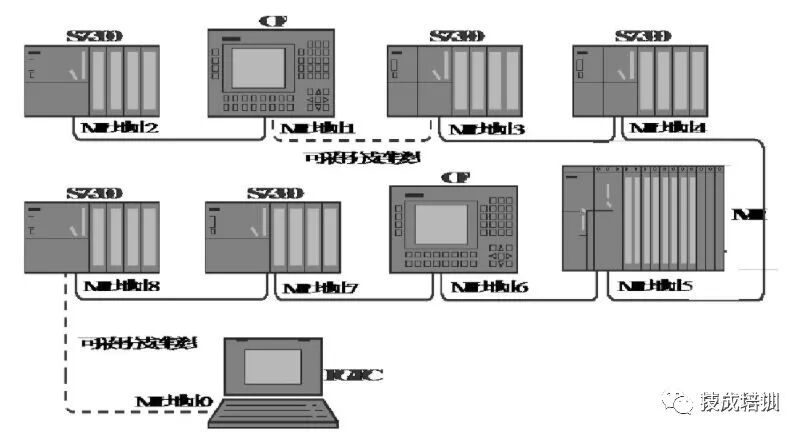
1) MPI (Multi-Point Interface) Protocol
MPI communication is used for small-scale, low-point field-level communication. MPI is a multi-point interface provided for S7/M7 and C7 PLC systems, designed for interfacing programmable devices and can also be used to transfer small amounts of data between a few CPUs.
1. MPI Network
MPI stands for Multi Point Interface, and the first communication interface of each SIMATIC CPU integrates the MPI communication protocol.
The physical layer of MPI is RS485, with a maximum transmission rate of 12 Mbit/s and a default transmission rate of 187.5 kbit/s. PLCs can connect to programming devices/computers (PGPC), human-machine interfaces (HM), SIMATIC S7, M7, and C7 simultaneously through MPI. The total number of MPI connections available for each CPU depends on the model, ranging from 6 to 64, for example, CPU312 has 6, and CPU417 has 64.
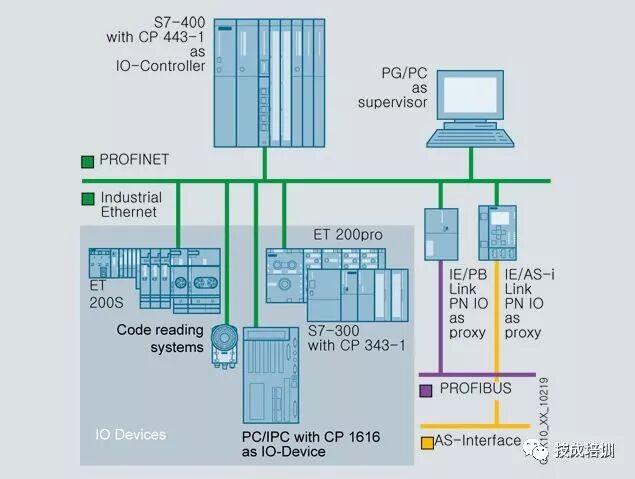
2) PROFIBUS
PROFIBUS complies with the international standard IEC6158 and is one of the internationally recognized fieldbus standards. With its unique technical characteristics, strict certification specifications, open standards, extensive vendor support, and continuously evolving application regulations, it has become the optimal solution for field-level communication networks, with network node counts exceeding 10 million, leading the fieldbus domain.
The PROFIBUS protocol mainly consists of three parts: PROFIBUS-DP, PROFIBUS-PA, and PROFIBUS-FMS.
1. PROFIBUS-DP
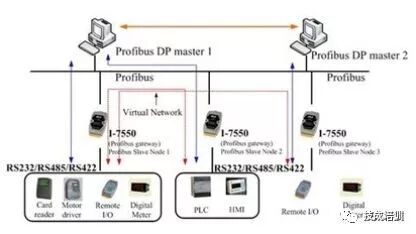
DP stands for Decentralized Periphery, and PROFIBUS-DP (abbreviated as DP) is mainly used for unit-level and field-level communication in manufacturing automation systems, particularly suitable for fast cyclic data exchange between PLCs and field-level distributed I/O devices. DP is the most widely used communication method in PROFIBUS.
PROFIBUS-DP is used to connect the following devices: PLCs, PCs, and HM devices; distributed field devices such as SIMATIC ET200 and inverters. PROFIBUS-DP has a fast response time, making it suitable for use in manufacturing.
As part of PLC hardware configuration, distributed I/O (e.g., ET200) is configured using STEP7. Other manufacturers’ slave devices can be configured into the network using GSD files provided by the supplier through STEP7.
Some S7-300/400 CPUs are equipped with integrated DP interfaces, and S7-200/300/400 can also connect to PROFIBUS-DP via communication processors (CP).
2. PROFIBUS-PA
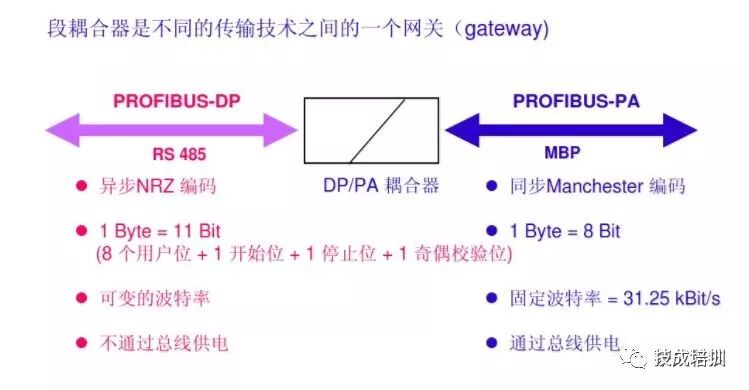
PA stands for Process Automation, and PROFIBUS-PA is used for low-speed data transmission between PLCs and intrinsically safe field sensors and actuators in process automation, particularly suitable for process industries. PROFIBUS-PA functionality is integrated into field devices such as starting actuators, solenoid valves, and measuring transmitters.
PROFIBUS-PA, adhering to the IEC1582 standard, ensures intrinsic safety and data transmission and power supply through shielded twisted pair cables, making it suitable for communication between sensors, actuators, and central control systems in explosion-proof areas.
PA devices can operate in the following explosion-proof zones:
Zone 0: Areas where hazardous gas is frequently present for long periods.
Zone 1: Areas where hazardous gas may be present during normal operation.
Zone 2: Areas where hazardous gas should not be present during normal operation.
Sensors/actuators are installed in the production field, while couplers and control devices are installed in the control room. Even if devices on the bus are not in hazardous areas, their intrinsic safety features must be ensured through appropriate structures. Using DP/PA couplers and DP/PA connectors, PROFIBUS-PA devices can be easily integrated into the PROFIBUS-DP network.
3. PROFIBUS-FMS
FMS stands for Field Message Specification, used for exchanging process data between automation systems from different vendors at the system and workshop levels, handling unit-level (PLC and PC) multi-master communication.
According to PROFIBUS-FMS, the communication model between masters is defined, utilizing the OSI seven-layer model’s layers 1, 2, and 7. S7-300/400 uses communication FB to implement FMS services, configuring static connections for FMS to send and receive data using STEP7. PROFIBUS-FMS has largely been replaced by Ethernet communication and is now rarely used.
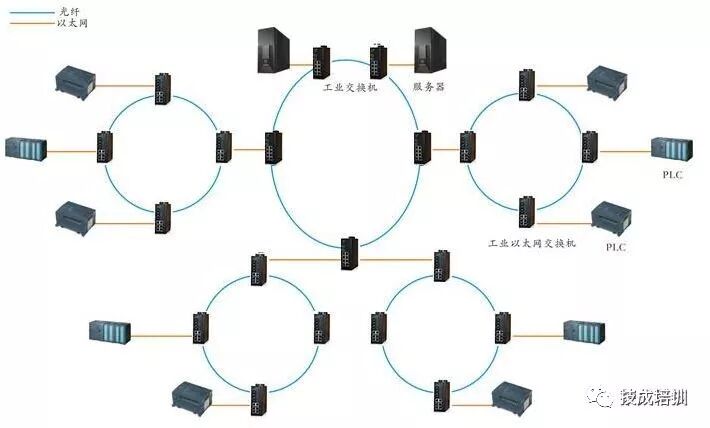
3) Industrial Ethernet
Industrial Ethernet is specifically designed for industrial applications, adhering to the IE802.3 international standard as an open, multi-vendor, high-performance regional and unit-level network. Industrial Ethernet connects various workstations of automation systems while also connecting computers, making it a high-speed open network. Industrial Ethernet is currently the most popular network technology in the industrial control field, providing SIMATIC NET with seamless integration into the multimedia world.
What factors should be considered when selecting the right industrial Ethernet? In simple terms, considerations include industrial Ethernet communication protocols, power supply, communication rates, industrial environment certifications, installation methods, the impact of housing on heat dissipation, simple communication functions, and communication management functions, as well as considerations for electrical or optical ports. Signal strength, port settings, error alarms, serial port usage, trunking redundancy, ring network redundancy, quality of service (QoS), virtual local area networks (VLAN), simple network management protocol (SNMP), port mirroring, and other functions that can be provided by industrial Ethernet managed switches.
From Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP), ring network redundancy (RapidRingTM) to trunk redundancy (TrunkingTM), industrial Ethernet devices include several important components.
Industrial Ethernet hubs
Industrial Ethernet unmanaged switches
Industrial Ethernet managed switches
Industrial Ethernet managed redundant switches
Advanced managed redundant switches offer special features, particularly optimized for redundancy systems with strict stability and security requirements. The main methods for constructing redundant networks include STP, RSTP; ring network redundancy RapidRingTM, and Trunking.
1. Industrial Ethernet STP and RSTP
STP (Spanning Tree Protocol, IEEE 802.1D) is a link layer protocol that provides path redundancy and prevents network loops. It keeps backup data paths in a blocked state. If a path fails, the topology can reconfigure and reconstruct links by activating the backup path. The network interruption recovery time is between 30-60 seconds. RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol, IEEE 802.1w) is an upgrade of STP, reducing the network interruption recovery time to 1-2 seconds. The spanning tree algorithm offers flexible network structures but has the drawback of slow recovery speed.
2. Industrial Ethernet Ring Network Redundancy
To meet the real-time characteristics of industrial control networks, RapidRing was born. This technology provides high-speed redundancy using a ring network in industrial Ethernet networks. It allows the network to self-recover within 300 ms after an interruption. Users can be alerted to network disconnection through error relay connections, status indicator lights, and SNMP settings on industrial Ethernet switches. These can help diagnose where the ring network has disconnected.
RapidRingTM also supports two interconnected ring networks, making the network topology more flexible and diverse. The two rings are connected through dual channels, which can be redundant, avoiding issues caused by a single cable failure.
3. Industrial Ethernet Trunk Redundancy
By setting multiple ports of different switches as Trunking trunk ports and establishing connections, these industrial Ethernet switches can form a high-speed backbone link. This not only multiplies the network bandwidth of the backbone link, enhancing network throughput, but also provides redundancy. If a backbone link in the network fails, data will be transmitted through the remaining links, ensuring normal network communication.
Trunking backbone networks adopt bus and star network structures, with theoretical communication distances potentially unlimited. This technology, using hardware detection and data balancing methods, has achieved a new height in network interruption recovery time, generally below 10 ms.
4) Point-to-Point Connection Strictly speaking, point-to-point connection is not a network technology. In SIMATIC, point-to-point connections are achieved through serial communication modules. The typical serial communication standards are RS232 and RS485, which define voltage, impedance, etc., but do not define software protocols. Unlike RS232, RS485 has the following characteristics:
1. Electrical characteristics of RS-485: Logic “1” is represented by a voltage difference of + (2-6)V between the two wires; Logic “0” is represented by a voltage difference of – (2-6)V between the two wires. The signal level of the interface is lower than that of RS-232-C, making it less likely to damage the interface circuit chips, and this level is compatible with TTL levels, facilitating connections with TTL circuits.
2. The maximum data transmission rate of RS-485 is 10 Mbps.
3. RS-485 interfaces are robust, with good noise immunity.
4. The maximum transmission distance standard for RS-485 interfaces is 4000 feet, practically reaching 3000 meters (theoretical data, in actual operation, the limit distance is only about 1200 meters). In contrast, RS-232-C interfaces only allow one transceiver to be connected on the bus, i.e., single-station capability. RS-485 interfaces allow up to 128 transceivers on the bus, providing multi-station capability, allowing users to easily establish a device network using a single RS-485 interface.
Due to the advantages of RS-485 interfaces, such as good noise immunity, long transmission distances, and multi-station capability, it has become the preferred serial interface. Since half-duplex networks composed of RS-485 interfaces generally require only two wires, RS-485 interfaces use shielded twisted pair transmission. RS-485 connectors use DB-9 9-pin plugs, with smart terminal RS-485 interfaces using DB-9 (socket), and keyboard connection RS-485 interfaces using DB-9 (pin).
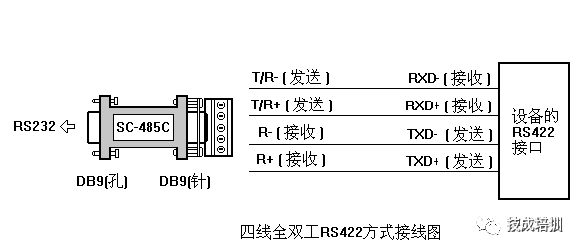
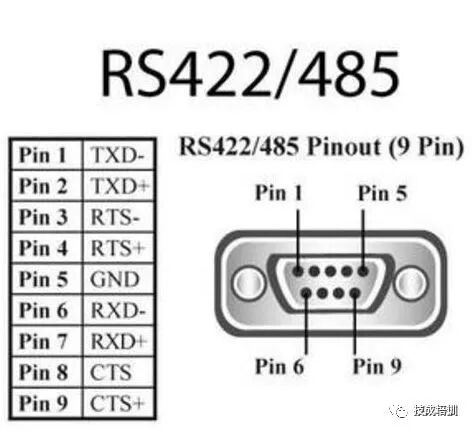
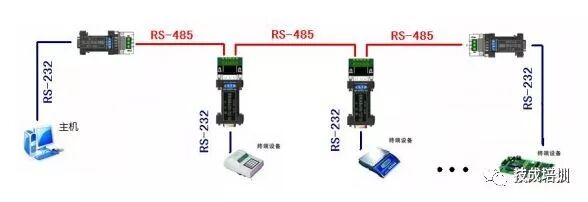
5) AS-Interface
Also known as the sensor/actuator interface, it is the communication network at the lowest level of automation systems. It is specifically designed to connect binary sensors and actuators, with a maximum data capacity of 4 bits for each slave.
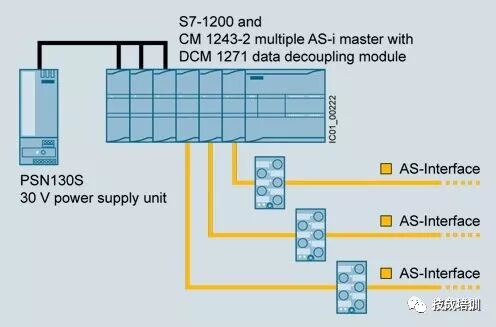
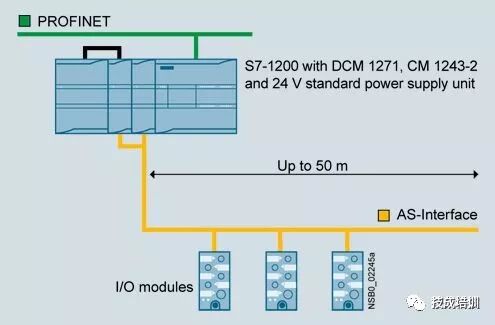
03 What Can Save You from Confusion
Many friends, especially beginners, often feel overwhelmed by various concepts and knowledge, unsure of where to start, or feel that there is too much to learn and cannot keep up. Indeed, this is an era of information explosion; we are encountering the best of times and the worst of times.
1. In the previous popular article by Xiaozhi: Automation is no longer the automation of the past, why are you still the same you?
It mentioned the importance of foundational thinking. Many people do not pay much attention to the underlying principles and technologies during their learning process, so when faced with many similar things, they do not recognize the commonalities~
2. Not cultivating independent thinking. After signing up for PMP with me, Xiaozhi wrote an article: Remembering my 16-day PMP preparation, discussing confusion in middle age, transformation, and reflection.
In it, he talked about deep thinking, which may be the ability that we technical personnel should possess~
Previous Recommendations
Introduction and Practice of Industrial Control System Security – Starting from the Five-Layer Architecture and Security Standards
Introduction and Practice of Industrial Control System Security – Analysis of Industrial Control Security Entry
Data Collection under MES and SCADA – Analysis of Siemens S7comm Protocol
PLC Attack Experiments Based on Step7 – Analysis of Siemens S7 Communication Process and Replay Attacks
Siemens S7 Series PLC Simulated Virus Attack Experiments – See if Your Industrial System is Really Safe
Confused about Modbus RTU, ASCII, TCP? This will be the most comprehensive analysis you have seen.
That’s all for today~ If you like it, please click the “Like” button in the lower right corner, or share and save it.(Don’t forget the surprise at the end of the article)
-
Disclaimer: The articles published by this public account are original or edited and organized based on online searches, and the copyright belongs to the original author. Due to numerous reprints, it is impossible to find the true source. If the source is incorrectly marked, or if there are any infringements regarding the images, materials, download links, etc. used in the article, please contact us for negotiation or deletion. Thank you!


We are a group of enthusiasts in smart manufacturing technology, eager to share, positive, and perhaps a bit introverted, but we are very loving, and we look forward to your joining us.
— Smart Manufacturing Home
Multiple Benefits
1. Learning alone without friends leads to ignorance,Reply in the WeChat public account:Join the group. Get the editor’s WeChat ID, add the editor’s WeChat and note “Industry + Name + City” (If the format is incorrect, you will not pass the friend verification, and will not be added to the group), join the 【Smart Manufacturing Home】 technical exchange group, and learn together with like-minded friends!
I knew you were “looking”