Many people have such questions: what are the differences between HMI, touch screens, and PLCs? In many cases, these three are even confused with each other. Today, ‘Smart Medicine Life’ will introduce the differences between them.
The Human Machine Interface (HMI), also known as a touch screen monitor, is an intelligent operation control and display device. When the screen is touched, the resistance and voltage on the resistive network change, and the software calculates the touch position.

(Image from the internet)
The Human Machine Interface (HMI) is also referred to as the ‘human-machine interface.’ Its main role is to help establish a connection between humans and computers, serving as an input/output device interface for exchanging information. These devices include keyboards, monitors, printers, mice, etc.
So, what is the difference between HMI and touch screens?
There is an essential difference between the two. The ‘touch screen’ is merely a hardware component that may be used in HMI products. It acts as an input device that replaces some functions of a mouse and keyboard, installed at the front of the display, such as the touch screens commonly used in mobile phones today.
On the other hand, the Human Machine Interface (HMI) is an interactive device that includes both hardware and software. In the industrial field, people sometimes inaccurately refer to HMI products with touch input functions as ‘touch screens.’
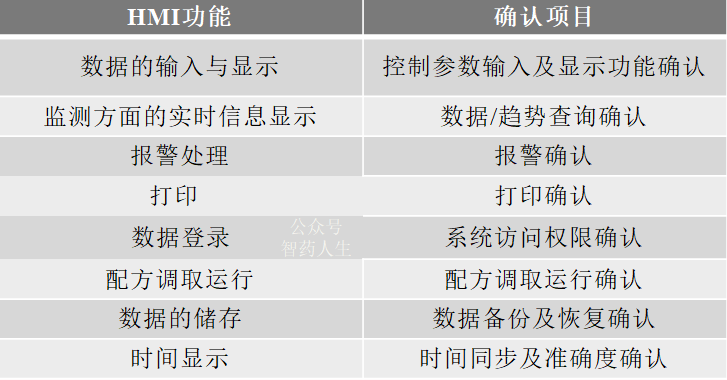
Many HMIs have been in use for a long time and frequently malfunction, leading many companies to inevitably replace their HMIs. When replacing an HMI, the principal confirmation activities that should at least be conducted based on the main functions and risks of the HMI include:
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a digital computation controller with a microprocessor used for automation control. It can store and execute control instructions in memory at any time.
PLC consists of a CPU, instruction and data memory, input/output interfaces, power supply, and various functional units such as digital-analog conversion.
The communication methods between HMI and PLC are numerous, with the most common being Ethernet and serial communication.
So, what is the relationship between HMI and PLC?
They are actually ‘arch-enemies.’ HMI is the ‘little guy,’ while PLC is the ‘nice guy.’
Because PLC tirelessly collects information from the field [captured by field sensors and converted into signals recognizable by PLC, such as 4~20mA current signals], calculated results with great effort.
However, HMI takes this data away through data cables [Ethernet or serial data cables] from the PLC’s communication port. Moreover, HMI also commands PLC to perform various tasks.
Additionally, all the glamorous aspects are occupied by HMI [process control and display], while PLC sadly remains hidden in the dark box [control cabinet] out of sight.
Previous original articles recommended
A Small Secret About Data Backup
Six Stages and Twenty Tasks of Equipment Lifecycle Management
Cleaning Validation Execution Strategies in Co-Production
Is the Access Control System Related to GMP? How to Validate?
Difficulty Analysis – Sampling of Cleaning Validation Rinse Water
ISPE Commissioning and Qualification (Second Edition) Full Interpretation.PPT