✅ Author Introduction: A research enthusiast and MATLAB simulation developer, skilled in data processing, modeling simulation, program design, complete code acquisition, paper reproduction, and research simulation.
🍎 Previous Review: Follow my personal homepage:MATLAB Research Studio
🍊 Personal Motto: Investigate to gain knowledge, complete MATLAB code and simulation consultation available via private message.
🔥 Content Introduction
Robot path planning is a core issue in the field of robotics, aimed at finding an optimal collision-free path for robots from a starting point to a target point within a given environment. With the rapid development of robotic technology, path planning has shown immeasurable value in various fields such as automated production, intelligent transportation, space exploration, and military applications. Simulation technology, as an important means of path planning research, provides an economical, efficient, and safe platform for the development, verification, and optimization of algorithms.
The path planning problem can typically be abstracted as a search for the optimal path within an environment. The environment can be a two-dimensional plane or a three-dimensional space, containing obstacles, traversable areas, as well as starting and target points. The definition of the optimal path can vary based on specific application requirements, with common optimization objectives including the shortest path, shortest time, lowest energy consumption, or smoothest path. Depending on the completeness of environmental information, path planning can be divided into global path planning and local path planning. Global path planning assumes that the robot has complete knowledge of the environmental information and can compute the complete path during the planning phase; while local path planning is suitable for situations where environmental information is incomplete or dynamically changing, requiring the robot to perceive the environment in real-time and adjust its path accordingly.
In terms of path planning algorithms, numerous classic methods have emerged, such as the A* algorithm, Dijkstra’s algorithm, RRT (Rapidly-exploring Random Tree) algorithm, PRM (Probabilistic Roadmap) algorithm, and sampling-based algorithms. The A* algorithm and Dijkstra’s algorithm are classic graph search algorithms that can find globally optimal paths, but they have a high computational load, especially in complex environments where efficiency may be low. RRT and PRM algorithms are sampling-based planning algorithms suitable for high-dimensional spaces and complex environments, generating nodes through random sampling and constructing search trees or roadmaps to find feasible paths. In recent years, with the development of artificial intelligence technologies, emerging techniques such as reinforcement learning and deep learning have also been applied in the field of path planning, aiming to improve planning efficiency and robustness by learning environmental features and experiences.
Robot path planning simulation provides an indispensable platform for the development and verification of algorithms. Through simulation, researchers can test the performance of different algorithms in a virtual environment, evaluating their robustness, efficiency, and safety under various conditions. The simulation environment can accurately simulate the physical characteristics, sensor data, and robot dynamics models found in the real world, thus providing strong support for the actual deployment of algorithms. For example, in the field of autonomous driving, simulation platforms can simulate various traffic scenarios, weather conditions, and emergency events, helping to test the path planning and decision-making capabilities of autonomous vehicles, thereby enhancing their safety and reliability on actual roads.
During the simulation process, it is often necessary to construct detailed environmental models, including the shapes, positions, and sizes of obstacles, as well as the definitions of traversable areas. Additionally, accurate robot models must be established, including kinematic and dynamic parameters, as well as sensor models, to realistically simulate the robot’s behavior. Commonly used simulation software includes Gazebo, V-REP, Webots, and MATLAB/Simulink. These software provide rich modeling tools, physics engines, and visualization capabilities, making it easy for users to build simulation environments, load robot models, and run path planning algorithms. Through simulation, researchers can intuitively observe the robot’s motion trajectories, obstacle avoidance effects, and the path planning process, allowing for in-depth analysis and optimization of algorithms.
However, robot path planning simulation also faces several challenges. Firstly, there are certain discrepancies between the simulation environment and the real environment, which may lead to simulation results that do not match actual performance. For instance, factors such as sensor noise, actuator errors, and environmental uncertainties can all affect the robot’s actual movement. Secondly, high-precision simulation requires substantial computational resources and time, especially in complex environments and multi-robot systems, where simulation efficiency may become a bottleneck. Furthermore, the validity of simulation results also depends on the accuracy of the environmental and robot models; any errors in the models can impact the reliability of the simulation results.
Despite these challenges, robot path planning simulation remains an indispensable tool in robotics research. In the future, with the continuous development of simulation technology, computational capabilities, and artificial intelligence algorithms, robot path planning simulation will become more precise, efficient, and intelligent. Researchers will be able to construct more realistic simulation environments, develop more advanced robot models, and implement adaptive path planning by integrating machine learning techniques. Through the close integration of simulation and actual deployment, robots will unleash their immense potential across broader application fields, bringing more convenience and progress to human society.
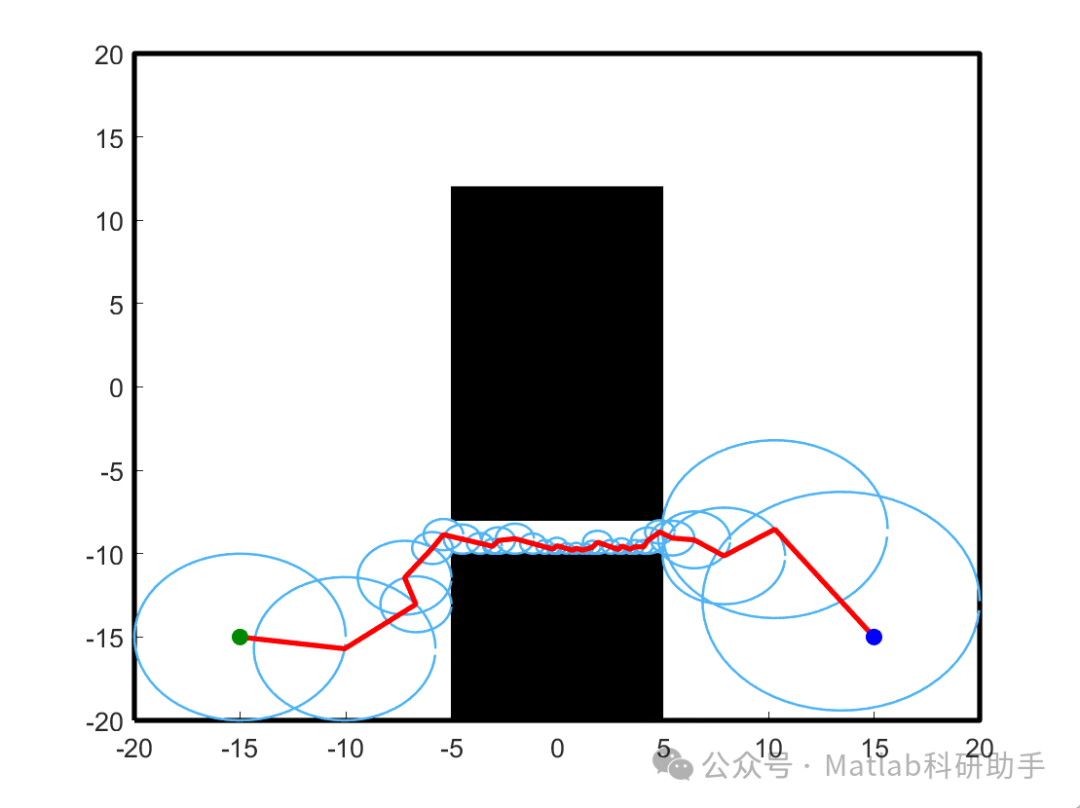
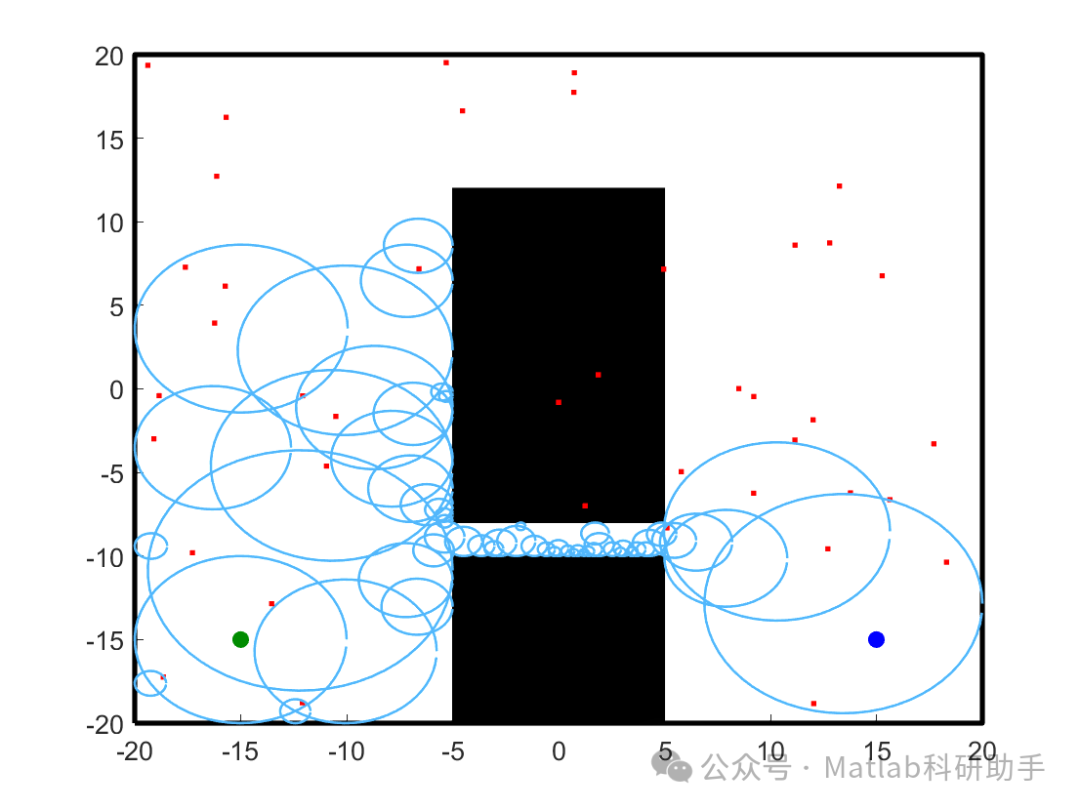
⛳️ Simulation Results
🔗 References
[1] Liu Jinkun. Design and MATLAB Simulation of Robot Control Systems [M]. Tsinghua University Press, 2008.
[2] Shi Tiefeng. Application of Improved Genetic Algorithm in Mobile Robot Path Planning [J]. Computer Simulation, 2011, 28(4):4. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2011.04.048.
[3] Liu Jinkun. Design and MATLAB Simulation of Robot Control Systems [M]. Tsinghua University Press, 2008.
📣 Partial Code
🎈 Some theoretical references are from online literature; please contact the author for removal if there is any infringement.
👇 Follow me to receive a wealth of MATLAB e-books and mathematical modeling materials
🏆 Our team specializes in guiding customized MATLAB simulations in various research fields, helping to realize research dreams:
🌈 Various intelligent optimization algorithm improvements and applications
Production scheduling, economic scheduling, assembly line scheduling, charging optimization, workshop scheduling, departure optimization, reservoir scheduling, three-dimensional packing, logistics site selection, cargo location optimization, bus scheduling optimization, charging station layout optimization, workshop layout optimization, container ship loading optimization, pump combination optimization, medical resource allocation optimization, facility layout optimization, visual domain base station and drone site selection optimization, knapsack problem, wind farm layout, time slot allocation optimization, optimal distributed generation unit allocation, multi-stage pipeline maintenance, factory-center-demand point three-level site selection problem, emergency life material distribution center site selection, base station site selection, road lamp post arrangement, hub node deployment, transmission line typhoon monitoring devices, container scheduling, unit optimization, investment optimization portfolio, cloud server combination optimization, antenna linear array distribution optimization, CVRP problem, VRPPD problem, multi-center VRP problem, multi-layer network VRP problem, multi-center multi-vehicle VRP problem, dynamic VRP problem, two-layer vehicle path planning (2E-VRP), electric vehicle path planning (EVRP), hybrid vehicle path planning, hybrid flow shop problem, order splitting scheduling problem, bus scheduling optimization problem, flight shuttle vehicle scheduling problem, site selection path planning problem, port scheduling, port bridge scheduling, parking space allocation, airport flight scheduling, leak source localization.
🌈 Time series, regression, classification, clustering, and dimensionality reduction in machine learning and deep learning
2.1 BP time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.2 ENS voice neural network time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.3 SVM/CNN-SVM/LSSVM/RVM support vector machine series time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.4 CNN|TCN|GCN convolutional neural network series time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.5 ELM/KELM/RELM/DELM extreme learning machine series time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.6 GRU/Bi-GRU/CNN-GRU/CNN-BiGRU gated neural network time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.7 Elman recurrent neural network time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.8 LSTM/BiLSTM/CNN-LSTM/CNN-BiLSTM long short-term memory neural network series time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.9 RBF radial basis function neural network time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.10 DBN deep belief network time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.11 FNN fuzzy neural network time series, regression prediction
2.12 RF random forest time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.13 BLS broad learning time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.14 PNN pulse neural network classification
2.15 Fuzzy wavelet neural network prediction and classification
2.16 Time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.17 Time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.18 XGBOOST ensemble learning time series, regression prediction, and classification
2.19 Transform various combinations time series, regression prediction, and classification
Directions cover wind power prediction, photovoltaic prediction, battery life prediction, radiation source identification, traffic flow prediction, load forecasting, stock price prediction, PM2.5 concentration prediction, battery health status prediction, electricity consumption prediction, water body optical parameter inversion, NLOS signal identification, precise prediction of subway stops, transformer fault diagnosis.
🌈 In image processing
Image recognition, image segmentation, image detection, image hiding, image registration, image stitching, image fusion, image enhancement, image compressed sensing.
🌈 In path planning
Traveling salesman problem (TSP), vehicle routing problem (VRP, MVRP, CVRP, VRPTW, etc.), three-dimensional path planning for drones, drone collaboration, drone formation, robot path planning, grid map path planning, multimodal transport problems, electric vehicle path planning (EVRP), two-layer vehicle path planning (2E-VRP), hybrid vehicle path planning, ship trajectory planning, full path planning, warehouse patrol.
🌈 In drone applications
Drone path planning, drone control, drone formation, drone collaboration, drone task allocation, online optimization of drone safety communication trajectories, vehicle collaborative drone path planning.
🌈 In communication
Sensor deployment optimization, communication protocol optimization, routing optimization, target localization optimization, Dv-Hop localization optimization, Leach protocol optimization, WSN coverage optimization, multicast optimization, RSSI localization optimization, underwater communication, communication upload and download allocation.
🌈 In signal processing
Signal recognition, signal encryption, signal denoising, signal enhancement, radar signal processing, signal watermark embedding and extraction, EMG signals, EEG signals, signal timing optimization, ECG signals, DOA estimation, encoding and decoding, variational mode decomposition, pipeline leakage, filters, digital signal processing + transmission + analysis + denoising, digital signal modulation, bit error rate, signal estimation, DTMF, signal detection.
🌈 In power systems
Microgrid optimization, reactive power optimization, distribution network reconstruction, energy storage configuration, orderly charging, MPPT optimization, household electricity.
🌈 In cellular automata
Traffic flow, crowd evacuation, virus spread, crystal growth, metal corrosion.
🌈 In radar
Kalman filter tracking, trajectory association, trajectory fusion, SOC estimation, array optimization, NLOS identification.
🌈 In workshop scheduling
Zero-wait flow shop scheduling problem (NWFSP), permutation flow shop scheduling problem (PFSP), hybrid flow shop scheduling problem (HFSP), zero idle flow shop scheduling problem (NIFSP), distributed permutation flow shop scheduling problem (DPFSP), blocking flow shop scheduling problem (BFSP).
👇