Recommended by the editor: Brilliance

Click the audio below to let your ears ‘feel’ the mechanics
The term “Bluetooth” is very familiar to us. More and more products relying on Bluetooth technology are appearing in our lives, such as Bluetooth headsets, Bluetooth speakers, Bluetooth mice, and Bluetooth watches. At first hearing “Bluetooth”, you might picture a blue tooth in your mind. So, why does such a good technology have this name? What story lies behind this naming, and what is its principle? Today, let’s unveil the mysterious veil of “Bluetooth”!

🔺Blue Tooth
Introduction and Origin of Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a method of short-range wireless communication between electronic devices using the power of radio waves. The origin of this name can be traced back to King Harald Blåtand of Denmark in the 10th century. King Harald ruled Denmark from around 958 to 986 AD, he was a great warrior who ended the Viking Age and unified the vast Nordic regions of present-day Norway, Sweden, and Denmark.

🔺King Harald Blåtand
The Danish word Blåtand translates to Bluetooth in English, so this king is also known as Harald Bluetooth. There are many versions regarding the origin of this name; one legend suggests that the king loved to eat blueberries, which stained his teeth blue; some historians speculate that one of the king’s teeth was decayed and appeared blue.

🔺A decayed tooth of the king that appeared blue
In the 1990s, Nordic communication technology was very strong, with giants like Ericsson and Nokia coming together to discuss how to establish a communication protocol to standardize wireless communication between mobile phones, computers, and wireless headsets. After the technology was developed, the Bluetooth development team needed to give this technology a catchy name,hoping that this technology could unify global short-range wireless communication solutions just like King Bluetooth conquered the vast Nordic regions, thus naming it “Bluetooth”.
Having discussed the origin of the name Bluetooth, let’s take a look at its logo. At first glance, it looks like a bow tie rotated 90° clockwise, or a mask at a masquerade. So, how did the Bluetooth team conceive this logo? In fact,the Bluetooth logo is a combination of runes, merging the rune letters H (ᚼ) and B (ᛒ) from the runic alphabet (a type of letter used by ancient Norse people, now extinct), and it is also the initials of King Harald’s name.
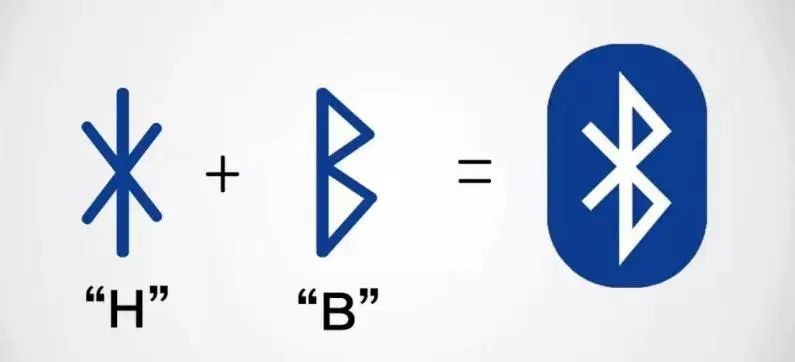
🔺Bluetooth Logo
Basic Working Principle of Bluetooth
Although people often understand Bluetooth as a type of device, in fact, Bluetooth is a wireless communication technology protocol that uses radio waves in the frequency range of 2.4GHz-2.4835GHz, enabling short-range digital communication exchanges between fixed devices, mobile devices, and buildings.
🔺Bluetooth enables short-range digital communication exchanges between various devices
When Bluetooth devices operate, they mainly utilize wireless modules, digital modules, and audio amplifiers.The wireless module completes the wireless communication between two devices, just like communication between two mobile phones. The wireless module transmits the digital signal from one device wirelessly to the other device, completing the work of the wireless module once the signal is received. After receiving the signal,the digital module decodes the signal and sends the code to the processing chip, converting the code into an audio signal, which can be heard after processing bythe audio amplifier.
What are the similarities and differences between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi?
As both are short-range communication technologies, Bluetooth inevitably gets compared with Wi-Fi technology. So what are the differences between them?

🔺Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are often compared
First, from theusage perspective, we often connect multiple devices to a singleWi-Fi to access the internet, which is aone-to-many connection method, whileBluetooth is a method of data transmission between two devices, which is apoint-to-point connection method. From this perspective,Bluetooth has higher data security. Secondly, although Bluetooth operates in the 2.4GHz frequency band, just like Wi-Fi, both are in the 2.4~2.4835GHz range, the difference is thatBluetooth divides this 83.5MHz bandwidth into 79 information channels, which meansit uses FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) to communicate, thus having stronginterference resistance.
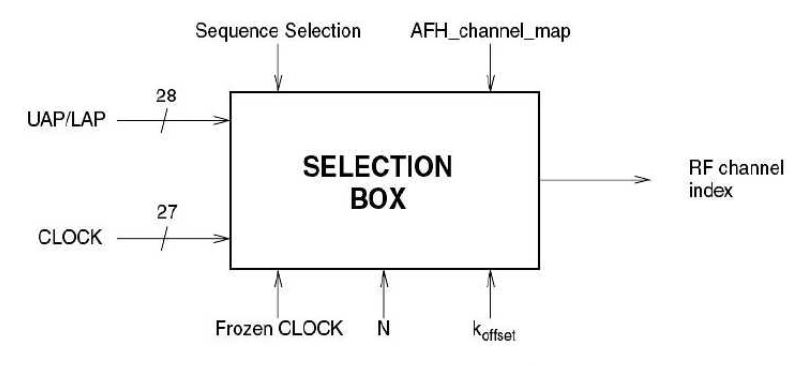
🔺General block diagram of Bluetooth frequency hopping selection scheme
Furthermore, sinceBluetooth uses microstrip antennas, which are small and easy to integrate into devices, and Bluetoothmodules are very low cost, the popularity of Bluetooth devices is very high; however, Wi-Fi devices require separate network cards and routing devices, which are costly and have higher power consumption. In some scenarios, Bluetooth is more suitable than Wi-Fi.
Applications of Bluetooth in Daily Life
01Code Scanning for Entry and Exit
Friends in Shanghai often use an app called “Metro Metropolis” when taking the subway. This app requires users to turn on Bluetooth for mutual verification between the gate and the phone, and only after verification will the gate open. This prevents passengers with poor network conditions from being unable to pass through the gate.

🔺Official Shanghai Metro APP
02Anti-Loss Device
Have you ever used an anti-loss device that supports Bluetooth connection? It is also very convenient to use; just turn on the phone’s Bluetooth to connect. Place the anti-loss device on your phone, elderly people, children, or pets, and as soon as it exceeds the set range, the anti-loss device will automatically alarm.
🔺Anti-loss device
03Bluetooth Mouse and Keyboard
Now many mice and keyboards support Bluetooth connections, and wireless mice and keyboards are becoming increasingly popular, providing great convenience for both carrying and working.

🔺Bluetooth mouse and keyboard
What other Bluetooth applications can you think of in daily life? Feel free to share in the comments!
References
[1]XU Fei. Research on Bluetooth Data Transmission Enhancement Technology and Its Baseband Chip Design Implementation[D]. Xi’an University of Electronic Science and Technology, 2013.
[2]ZHANG Qiqi. Exploring the Principles and Applications of Bluetooth Technology[J]. China New Communication, 2018, 20(23): 98-99.
[3]LIN Manshan. A Brief Discussion on the Current Status and Prospects of Bluetooth Technology[J]. Heilongjiang Science and Technology Information, 2016, (14): 165-165.
[4]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/PQzMZkMg4XUWKYPOc9J-VQ
[5]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Aw84ox4uF0hO5QaqjC3ssQ
[6]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/qDV54lKJYx3cu8moHQy-MA
[7]https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bRvcf6tJlkq3_BrB4GkGQQ

The reproduced content only represents the author’s views
It does not represent the position of the National Nano Center
