Note: This is a practical machine learning project (including data + code + documentation), if you need data + code + documentation you can directly obtain it at the end of the article.
1. Project Background
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women worldwide, and early diagnosis is crucial for improving cure rates and survival rates. Traditional diagnostic methods rely on the experience of doctors and pathological analysis, which are not only time-consuming but also susceptible to subjective factors. With the development of machine learning technologies, it has become possible to automatically classify and predict medical images and data using algorithms such as Support Vector Machines (SVM). This project aims to develop an efficient and accurate breast cancer classification method based on the MATLAB platform, by applying the SVM algorithm to train and test breast cancer-related datasets, achieving effective identification and classification of breast cancer. This system can not only assist doctors in making faster and more accurate diagnoses but also provide a reference for personalized treatment plans, thereby improving medical efficiency and patient satisfaction. Additionally, this project will explore the impact of different feature selection methods on model performance, with the goal of finding the optimal breast cancer classification strategy.
This project implements the application of SVM support vector machine for breast cancer classification based on MATLAB.
2. Data Acquisition
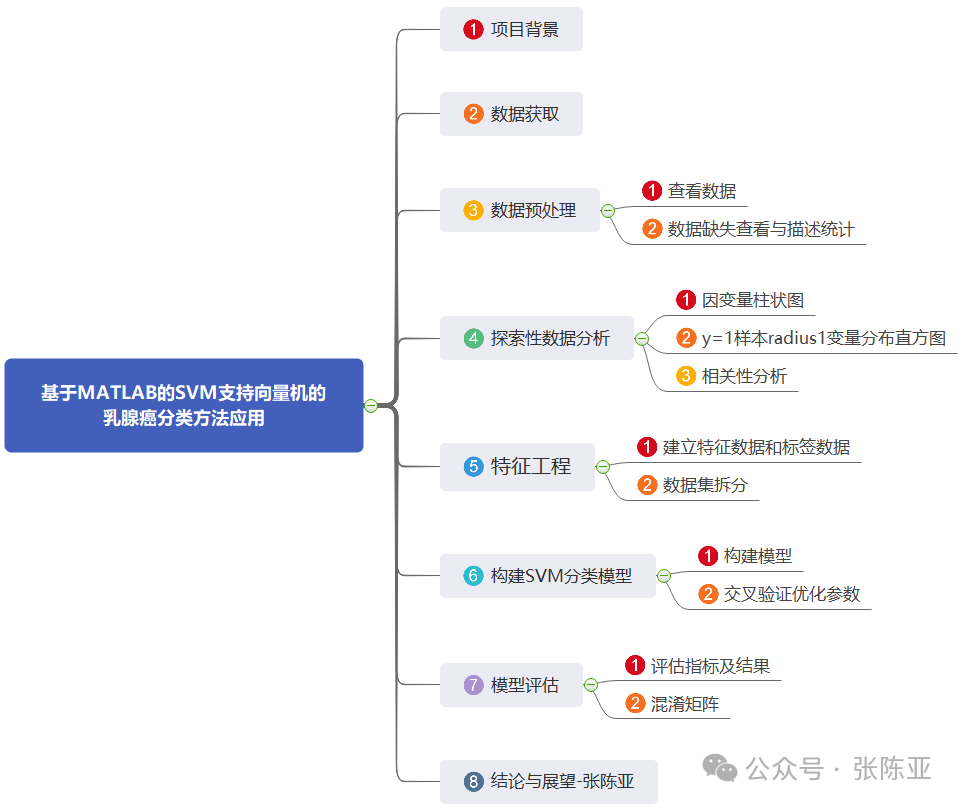
The modeling data is sourced from the internet (compiled by the author of this project), and the data items are summarized as follows:
|
No. |
Variable Name |
Description |
|
1 |
radius1 |
Mean radius |
|
2 |
texture1 |
Mean texture |
|
3 |
perimeter1 |
Mean perimeter |
|
4 |
area1 |
Mean area |
|
5 |
smoothness1 |
Mean smoothness |
|
6 |
compactness1 |
Mean compactness |
|
7 |
concavity1 |
Mean concavity |
|
8 |
concave_points1 |
Mean number of concave points |
|
9 |
symmetry1 |
Mean symmetry |
|
10 |
fractal_dimension1 |
Mean fractal dimension |
|
11 |
radius2 |
Standard error of radius |
|
12 |
texture2 |
Standard error of texture |
|
13 |
perimeter2 |
Standard error of perimeter |
|
14 |
area2 |
Standard error of area |
|
15 |
smoothness2 |
Standard error of smoothness |
|
16 |
compactness2 |
Standard error of compactness |
|
17 |
concavity2 |
Standard error of concavity |
|
18 |
concave_points2 |
Standard error of number of concave points |
|
19 |
symmetry2 |
Standard error of symmetry |
|
20 |
fractal_dimension2 |
Standard error of fractal dimension |
|
21 |
radius3 |
Mean of the maximum three radius values |
|
22 |
texture3 |
Mean of the maximum three texture values |
|
23 |
perimeter3 |
Mean of the maximum three perimeter values |
|
24 |
area3 |
Mean of the maximum three area values |
|
25 |
smoothness3 |
Mean of the maximum three smoothness values |
|
26 |
compactness3 |
Mean of the maximum three compactness values |
|
27 |
concavity3 |
Mean of the maximum three concavity values |
|
28 |
concave_points3 |
Mean of the maximum three number of concave points |
|
29 |
symmetry3 |
Mean of the maximum three symmetry values |
|
30 |
fractal_dimension3 |
Mean of the maximum three fractal dimension values |
|
31 |
y |
Whether the tumor is benign (0) or malignant (1) |
Data details are as follows (partial display):
3. Data Preprocessing
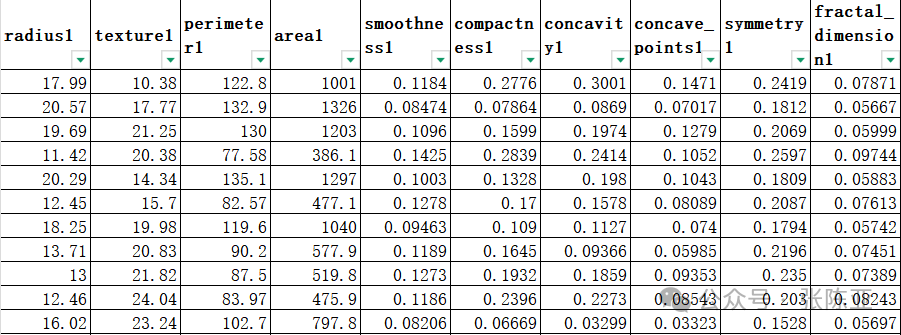
3.1 View Data
Use the head() method to view the first five rows of data:
Key code:

3.2 Check for Missing Data and Descriptive Statistics
Use the summary() method to view data information:
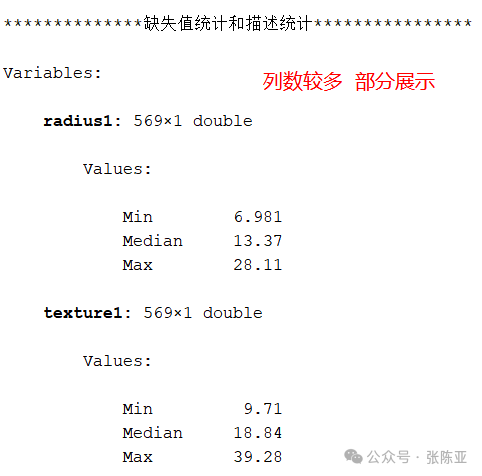
From the above figure, it can be seen that there are a total of 31 variables, with no missing values in the data, totaling 569 data entries.
Key code:

4. Exploratory Data Analysis
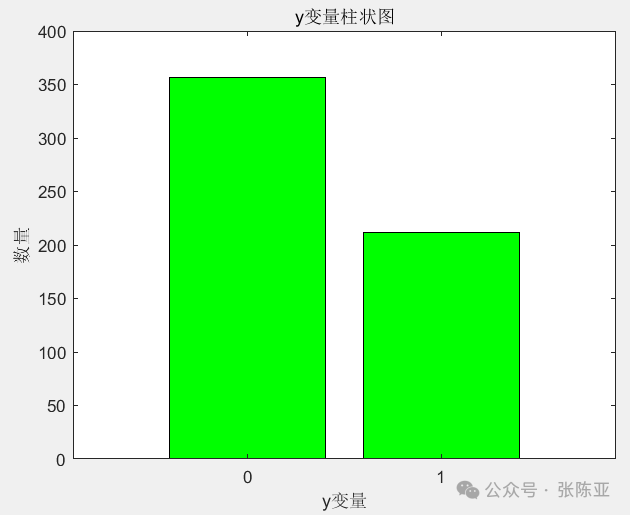
4.1 Bar Chart of Independent Variables
Use the bar() method to draw a bar chart:
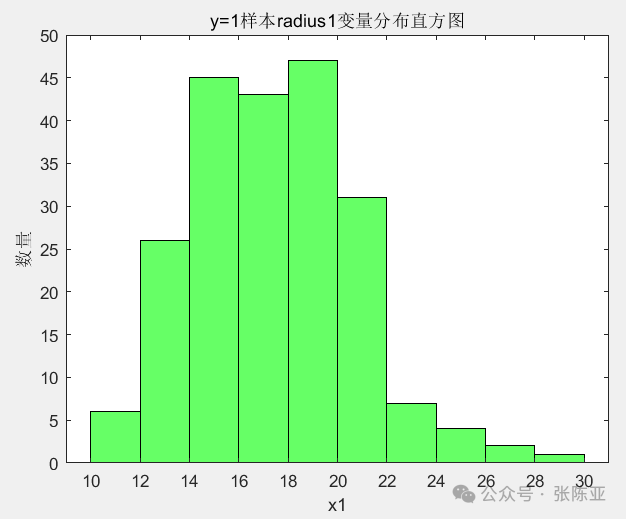
4.2 Histogram of radius1 Variable for y=1 Samples
Use the histogram() method to draw a histogram:
4.3 Correlation Analysis
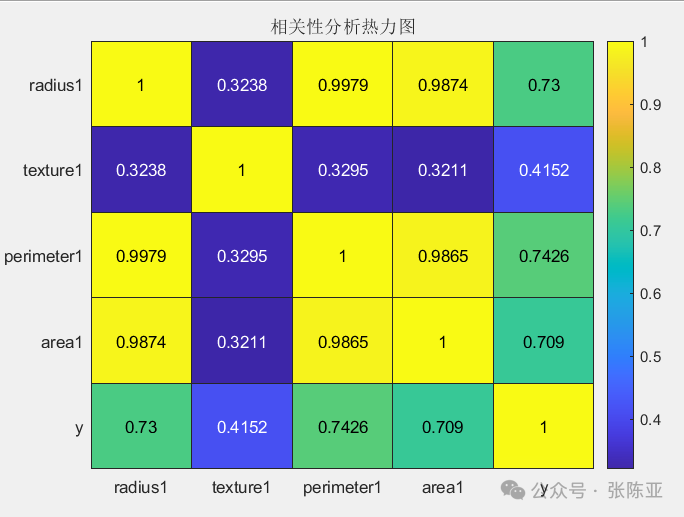
Correlation analysis of some data variables: From the above figure, it can be seen that the larger the value, the stronger the correlation; positive values indicate positive correlation, while negative values indicate negative correlation.
5. Feature Engineering
5.1 Establish Feature Data and Label Data
Key code is as follows:

5.2 Dataset Splitting
Split into 80% training set and 20% validation set, key code is as follows:

6. Build SVM Classification Model
Mainly implements the application of SVM support vector machine for breast cancer classification based on MATLAB..
6.1 Build Model
Build classification model.
|
Model Name |
Model Parameters |
|
SVM Classification Model |
‘KernelFunction’, ‘linear’ |
|
‘Standardize’, true |
|
|
‘ClassNames’, [0, 1] |
6.2 Cross-Validation to Optimize Parameters
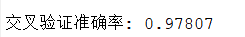
Key code:

7. Model Evaluation
7.1 Evaluation Metrics and Results
Evaluation metrics mainly include accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score, etc.
|
Model Name |
Metric Name |
Metric Value |
|
Test Set |
||
|
SVM Classification Model |
Accuracy |
0.9735 |
|
Precision |
1.0000 |
|
|
Recall |
0.9286 |
|
|
F1 Score |
0.9630 |
From the above table, it can be seen that the F1 score is 0.9630, indicating that the model performs well..
Key code is as follows:

7.2 Confusion Matrix
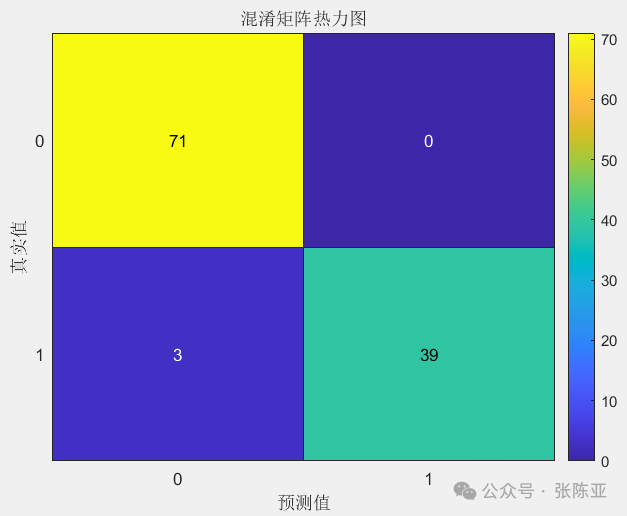
From the above figure, it can be seen that there are 0 samples predicted as not 0 when the actual value is 0, and 3 samples predicted as not 1 when the actual value is 1, indicating that the model performs well..
8. Conclusion and Outlook
In summary, this project implements the application of SVM support vector machine for breast cancer classification based on MATLAB, ultimately proving that the model we proposed performs well. This model can be used for daily product modeling work.
Project practical collection navigation:
https://docs.qq.com/sheet/DTVd0Y2NNQUlWcmd6?tab=BB08J2 | Python Project Collection |
| Graduation Project System |
| MATLAB Project Collection |
| Special Training Camp |
| Thesis Full Package, Half Package Services |
| Data Collection |
| Free Material Acquisition |
| R Project Collection |
——Welcome to follow our public account——