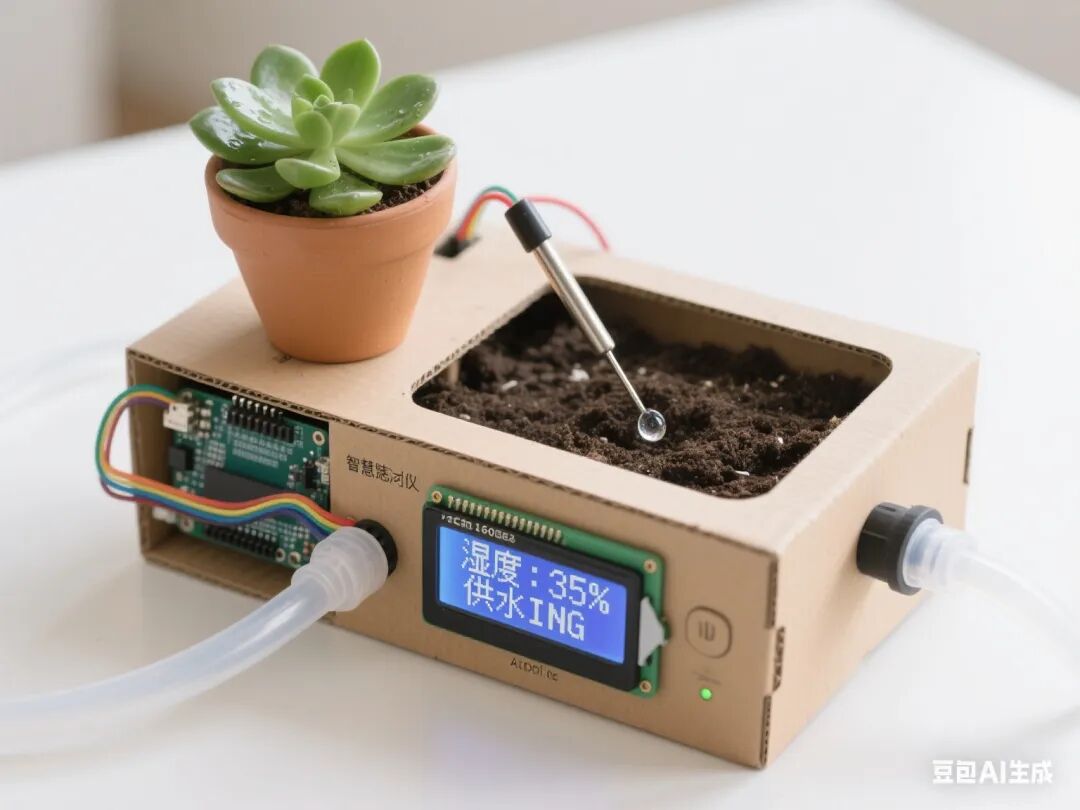
1. Project Overview
This project is driven by the need to solve the automatic watering problem for plants. Students will utilize Mind+ graphical programming, the Arduino hardware platform, and various sensor/actuator modules to achieve functions such as soil moisture detection, critical value setting, and automatic irrigation control through phased tasks. The project deeply integrates the Doubao Classroom Assistant AI, providing students with real-time learning support and personalized guidance, fostering interdisciplinary engineering practice skills and awareness of sustainable development.
 2. Overall Project Goals
2. Overall Project Goals
1. Knowledge and Skills Objectives
◦ Master the analog signal acquisition and calibration methods of soil moisture sensors
◦ Understand the principle of analog-to-digital conversion of potentiometers and the logic of critical value setting
◦ Learn the circuit design for controlling the water pump with a relay
◦ Achieve real-time data visualization on an OLED screen
2. Process and Method Objectives
◦ Cultivate system thinking through the engineering process of “demand analysis – prototype design – testing iteration”
◦ Learn to use the serial monitor and AI for debugging
3. Emotional Attitude and Values Objectives
◦ Appreciate the application value of intelligent technology in ecological protection
◦ Enhance awareness of water conservation and scientific planting responsibilities
3. Required Hardware
1. Arduino Nano + Expansion Board
2. Soil Moisture Sensor (Analog Signal Type)
3. 0.96-inch OLED Screen (I2C Interface)
4. Relay Module
5. Mini DC Water Pump (DC 5V)
6. Potentiometer (10kΩ)
7. Water Pipe and Connectors
8. Corrugated Cardboard Box and Auxiliary Materials
9. Battery Holder (4 AA Batteries)
10. Dupont Wires, Zip Ties, Hot Melt Glue, and other tools
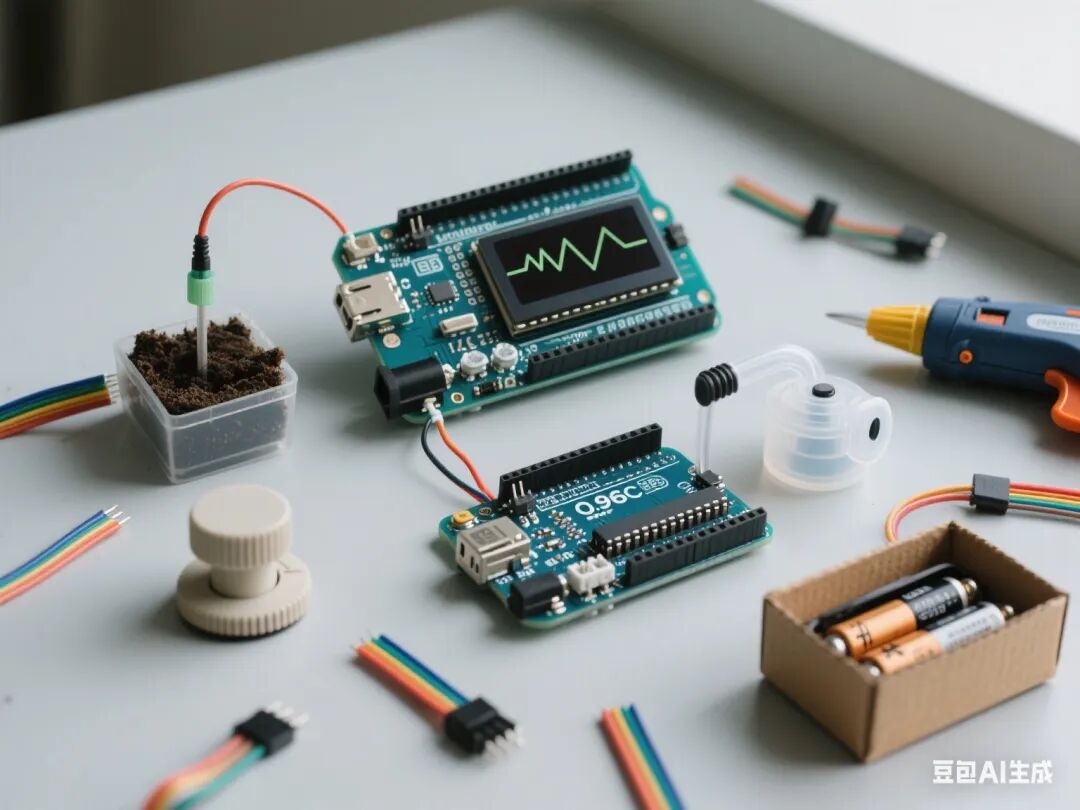
4. Class Schedule and Lesson Design
First Lesson: Soil Moisture Detection System
1. Learning Objectives
◦ Master the working principle and calibration method of soil moisture sensors
◦ Display real-time humidity values on the OLED screen

2. Teaching Key Points
◦ Key Point: Connection of the sensor to the Arduino’s analog signal
◦ Difficulty: Calibration of the relationship between humidity values and soil conditions
3. Teaching Steps
◦ Introduction (5 minutes): Show a video of the difficulties faced by plants in arid regions, leading to the need for irrigation
◦ Knowledge Explanation (15 minutes):
◦ Sensor pin functions (VCC/GND/AO)
◦ Reading analog signals in Mind+ and displaying on OLED
◦ Hardware Practice (20 minutes):
◦ Connect the sensor to pin A0, OLED to SDA/SCL
◦ Write code: Read humidity values and display (0-100%)
◦ Calibration Experiment (10 minutes):
◦ Test the value range for dry/wet soil
◦ Establish a reference table for humidity values and soil states
◦ AI Interaction: Doubao provides calibration parameter suggestions and answers sensor anomaly questions
Second Lesson: Critical Value Setting System
1. Learning Objectives
◦ Master the analog-to-digital conversion and value mapping of the potentiometer
◦ Implement human-computer interaction for setting irrigation thresholds
2. Teaching Key Points
◦ Key Point: Signal acquisition from the potentiometer and application of the map() function
◦ Difficulty: Matching threshold ranges with irrigation logic,

3. Teaching Steps
◦ Review Introduction (5 minutes): Review the humidity detection function, leading to the need for automatic irrigation
◦ Knowledge Explanation (15 minutes):
◦ Signal acquisition from the potentiometer and principles of analog-to-digital conversion
◦ Use of variables and comparison operators in Mind+
◦ Hardware Practice (20 minutes):
◦ Connect the potentiometer to pin A1
◦ Write code: Rotate the potentiometer to set the irrigation threshold (30%-70%)
◦ Logic Design (10 minutes):
◦ Add threshold over-limit judgment (if statement)
◦ Display current threshold and humidity comparison on OLED
◦ AI Interaction: Doubao provides code optimization suggestions and demonstrates threshold setting logic
Third Lesson: Relay Water Pump Control System
1. Learning Objectives
◦ Master the circuit design for controlling the water pump with a relay
◦ Implement automatic irrigation logic triggered by thresholds
2. Teaching Key Points
◦ Key Point: High-voltage circuit connection between the relay and water pump
◦ Difficulty: Timing control for multi-module collaborative work
3. Teaching Steps
◦ Problem Introduction (5 minutes): Discuss the risks of directly driving the water pump, leading to the relay solution
◦ Knowledge Explanation (15 minutes):
◦ Relay pin definitions and control logic
◦ Correspondence between water pump operation and relay status
◦ Hardware Practice (20 minutes):
◦ Connect the relay to pin D2, water pump to the normally open terminal of the relay
◦ Write code: Start the water pump when humidity is below the threshold
◦ Safety Testing (10 minutes):
◦ Test relay response under no-load/load conditions
◦ Add overload protection (delay shutdown)
◦ AI Interaction: Doubao demonstrates circuit connection standards and reminds of high-voltage circuit safety matters
Fourth Lesson: System Function Integration Testing
1. Learning Objectives
◦ Achieve programming logic for multi-module collaborative work
◦ Master basic methods for system debugging
2. Teaching Key Points
◦ Key Point: Coordination of threshold triggering and irrigation duration
◦ Difficulty: Implementation of non-blocking delays
3. Teaching Steps
◦ Task Introduction (5 minutes): Clarify complete functional requirements (detection → judgment → irrigation → stop)
◦ Programming Practice (30 minutes):
◦ Integrate humidity detection, threshold judgment, and water pump control code
◦ Add irrigation duration control (automatically stop after 5 minutes)
◦ Debugging Optimization (15 minutes):
◦ Test response times under different humidity conditions
◦ Adjust code parameters (e.g., retry counts, interval times)
◦ Troubleshooting (10 minutes):
◦ Address common issues (water pump running dry, false triggering)
◦ Learn to use serial logs for debugging assistance
◦ AI Interaction: Doubao provides a debugging flowchart and analyzes common error causes
Fifth Lesson: Structural Optimization and Project Presentation
1. Learning Objectives
◦ Complete the mechanical structure building and beautification of the irrigation device
◦ Enhance the aesthetics and practicality of engineering design
2. Teaching Key Points
◦ Key Point: Design of water pump fixation and water pipe layout
◦ Difficulty: Balancing waterproof performance and maintenance convenience
3. Teaching Steps
◦ Design Introduction (5 minutes): Show excellent structural design cases, emphasizing outdoor applicability
◦ Structural Building (30 minutes):
◦ Use corrugated cardboard to create the device shell and sensor bracket
◦ Install the water pump, water pipe, and battery holder
◦ Beautification (20 minutes):
◦ Draw humidity level indicators and operation instructions
◦ Add handles, waterproof eaves, and other practical structures
◦ Final Testing (15 minutes):
◦ Simulate testing under continuous drought conditions for 3 days
◦ Record leakage, circuit short circuit, and other issues
◦ AI Interaction: Doubao presents waterproof treatment solutions and provides structural improvement suggestions
5. Assessment Methods
1. Process Evaluation (40%)
◦ Norms of hardware connections (10%)
◦ Reasonableness of code logic (15%)
◦ Problem-solving ability (15%)
2. Summative Evaluation (60%)
◦ Completeness of functional implementation (30%)
◦ Innovation in structural design (20%)
◦ Presentation of project display (10%)
6. Safety Tips
1. Ensure correct connection of battery holder’s positive and negative terminals to avoid short circuits
2. Ensure the water pipe is unobstructed when the water pump is working to prevent motor blockage
3. Ensure proper waterproofing of circuits when used outdoors
7. Doubao AI Application Design
1. Real-time Guidance: Provide step-by-step voice prompts during hardware connections, code writing, and other stages
2. Error Diagnosis: Automatically identify code logic errors and provide modification suggestions
3. Resource Expansion: Push water-saving irrigation technology materials and ecological protection cases
4. Learning Archives: Record student debugging data and generate personalized ability analysis reports
8. Teaching Resources
1. Mind+ software and extension libraries
2. Technical documentation for each module
3. Engineering log templates
4. Reference table for soil moisture and plant water needs
