
Background Introduction
With the development of high power and miniaturization of flexible electronic devices, their power density has increased dramatically, leading to severe heat accumulation issues. There is an urgent need for flexible high thermal conductivity materials to dissipate heat quickly and efficiently, ensuring the operational stability of electronic devices. Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is widely used as a substrate material for flexible electronic devices due to its softness, strong weather resistance, and wide temperature range. However, the intrinsic thermal conductivity of PDMS (λ) is extremely low (approximately 0.2 W/(m·K)), which cannot meet the urgent demand for high thermal conductivity materials in flexible electronic devices.
Results Summary
This work employs an “in-situ growth-high temperature carbonization” process to prepare magnetic responsive “point-surface” heterostructure BNNS@Ni thermal fillers. By magnetic field orientation, we fabricated H-BNNS@Ni/PDMS thermal composites with BNNS@Ni distributed orderly in-plane. When the mass ratio of BNNS to Ni in BNNS@Ni is 8:1 and the mass fraction of BNNS@Ni is 50 wt%, the in-plane thermal conductivity (λ∥) of H-BNNS@Ni/PDMS thermal composites reaches 5.50 W/(m·K), which is about 27.8 times that of pure PDMS λ∥(0.19 W/(m·K)). It is also significantly higher than that of R-BNNS@Ni/PDMS thermal composites with the same mass fraction of BNNS@Ni randomly distributed in the PDMS matrix (4.76 W/(m·K)). When used for CPU heat dissipation, H-BNNS@Ni/PDMS thermal composites can reduce the full power operating temperature by 19.2℃ compared to pure PDMS. Additionally, H-BNNS@Ni/PDMS thermal composites exhibit excellent thermal stability (thermal index of 248.0℃), photo-thermal conversion performance (surface temperature reaches 199.8℃ after 30 seconds of NIR (808 nm) irradiation at 1.31 W·cm-2), and hydrophobicity (water contact angle of 119.3°). Through practical heat dissipation tests and finite element simulations, H-BNNS@Ni/PDMS thermal composites demonstrate excellent thermal management capabilities, showing great application prospects in the field of next-generation flexible electronic devices.
Illustrated Guide
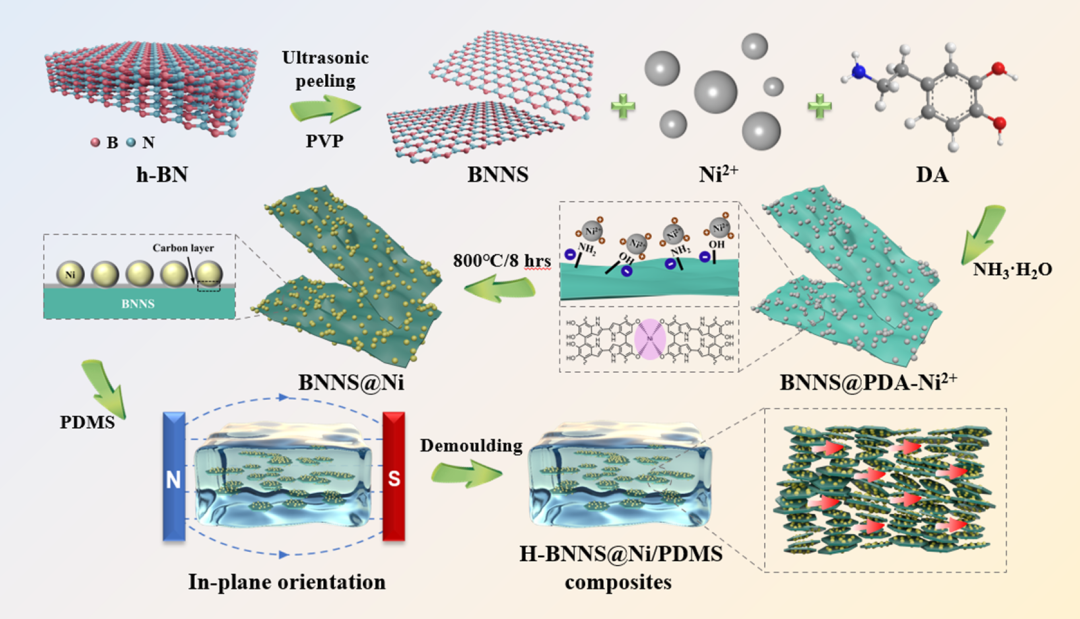
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the preparation of H-BNNS@Ni/PDMS thermal composites
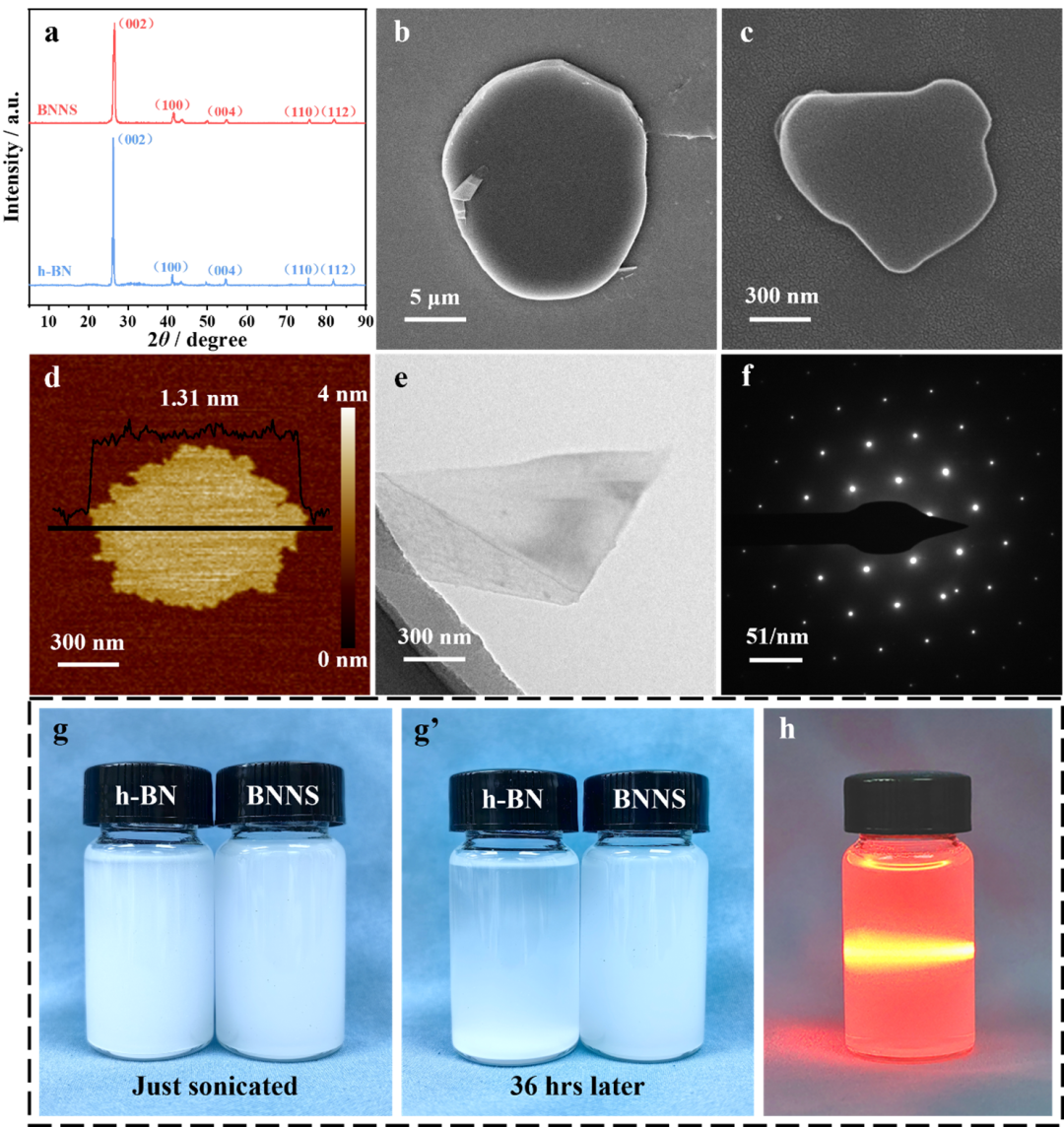
Figure 2 XRD spectra of h-BN and BNNS (a), SEM images of h-BN (b), SEM (c), AFM (d), TEM (e), and SAED (f) images of BNNS, optical images of h-BN and BNNS water dispersions (g-g’), and Tyndall effect of BNNS (h)
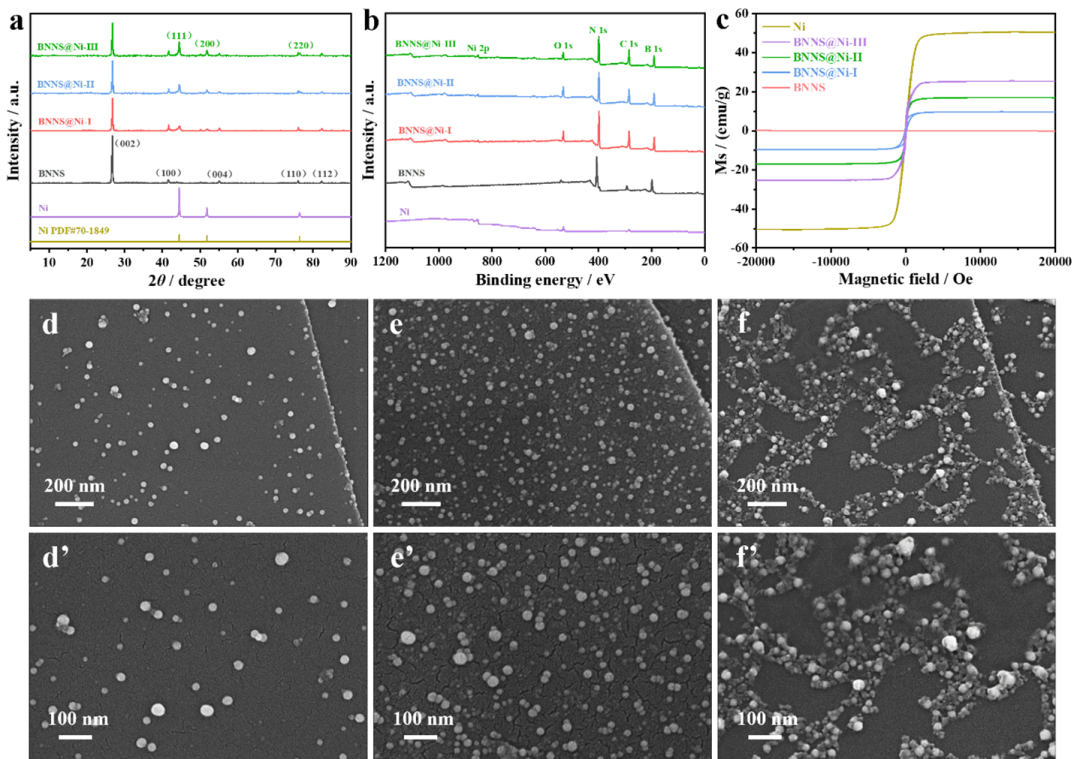
Figure 3 XRD spectra of BNNS, Ni, and BNNS@Ni thermal fillers (a), XPS spectra (b), hysteresis loops of BNNS, Ni, and BNNS@Ni thermal fillers (c), SEM images of BNNS@Ni-I (d-d’), BNNS@Ni-II (e-e’), and BNNS@Ni-III (f-f’)
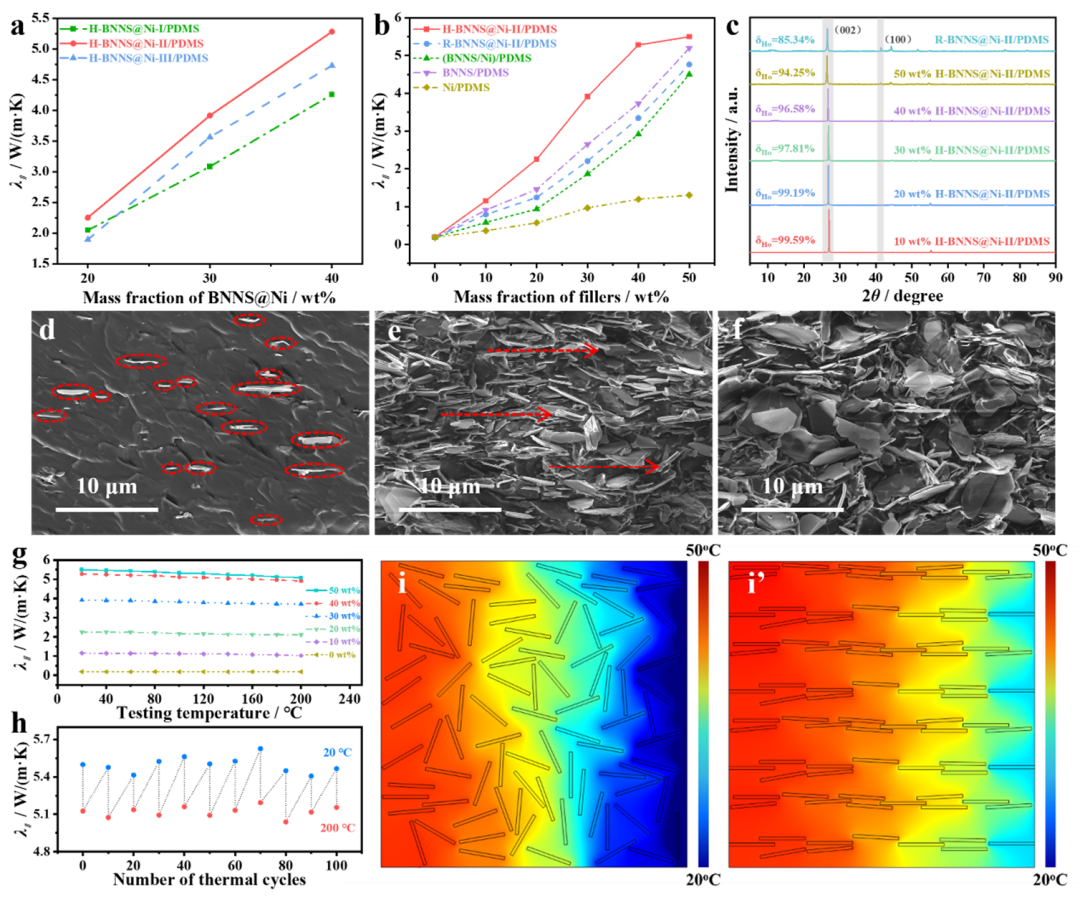
Figure 4 Effects of three types of BNNS@Ni on the thermal conductivity of H-BNNS@Ni/PDMS compositesλ∥ (a), effects of different amounts of thermal fillers on the thermal conductivity of PDMS compositesλ∥ (b), XRD spectra of H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS composites (c), SEM images of 10 wt% H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS composites (d), 50 wt% H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS composites (e), and 50 wt% R-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS composites (f), effects of temperature on the thermal conductivity of H-BNNS@Ni/PDMS compositesλ∥ (g) and thermal conductivity of 50 wt% H-BNNS@Ni/PDMS composites after repeated heating and cooling in the range of 20~200°C (h), thermal conduction simulations of R-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS (i), H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS (i’)
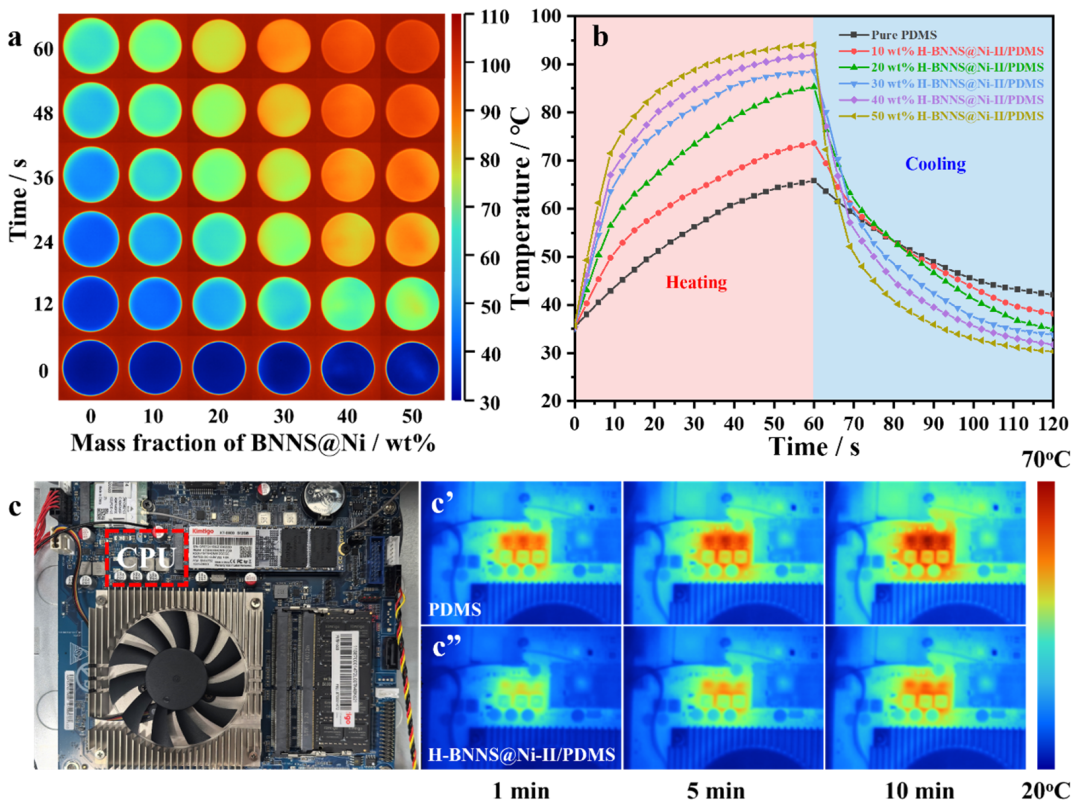
Figure 5 Infrared thermal imaging photos of pure PDMS and H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites on a constant temperature heating platform (a), temperature-time relationship during heating and cooling processes of pure PDMS and H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites (b), digital photos of an exposed computer motherboard (c) and infrared thermal imaging photos of a computer CPU working with pure PDMS (c’) and 50 wt% H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites (c”)
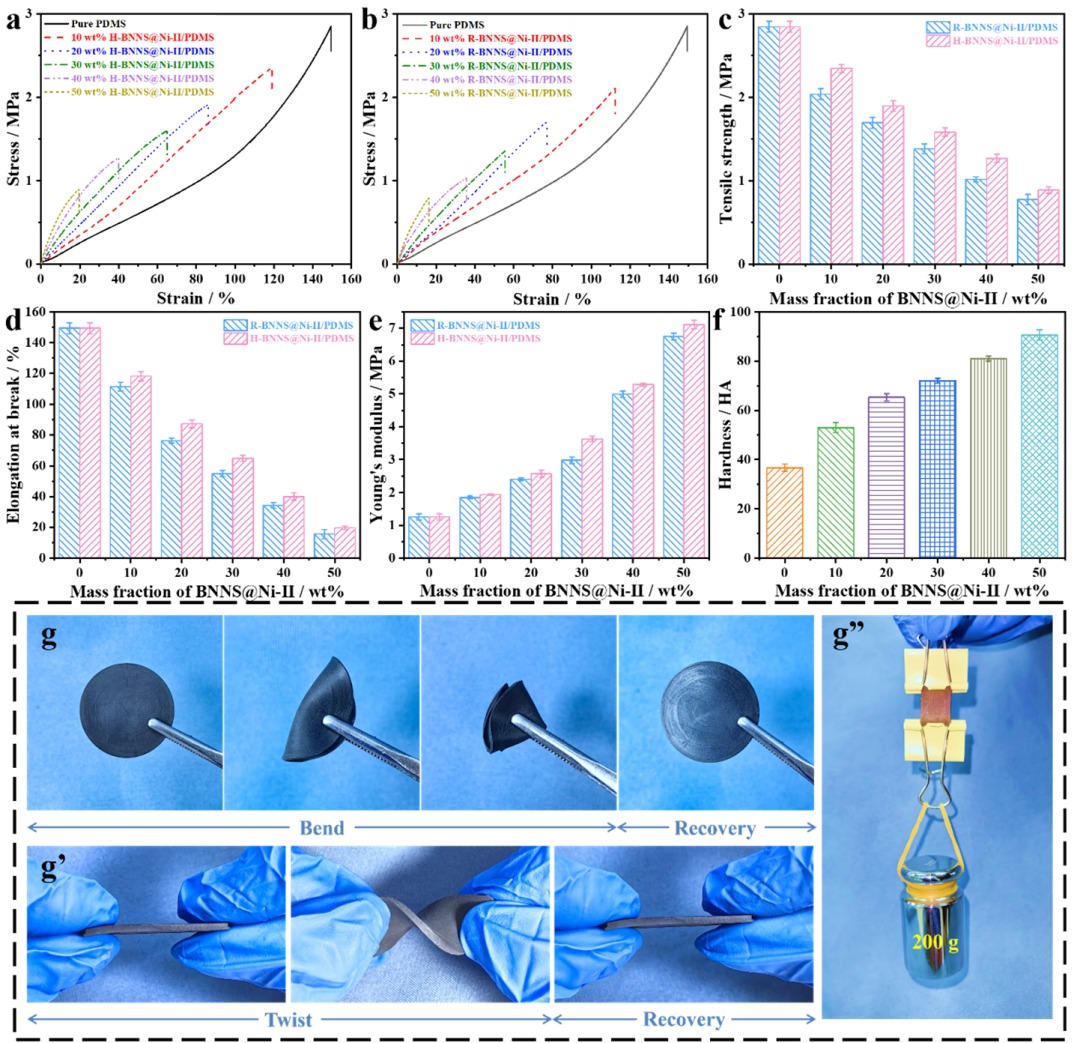
Figure 6 Stress-strain curves of H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS (a) and R-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS (b) thermal composites, tensile strength (c), elongation at break (d), and Young’s modulus (e) of H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS and R-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites, Shore hardness (f) of pure PDMS and H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites, flexibility (g), bendability (g’), and load-bearing capacity (200 g) (g”)
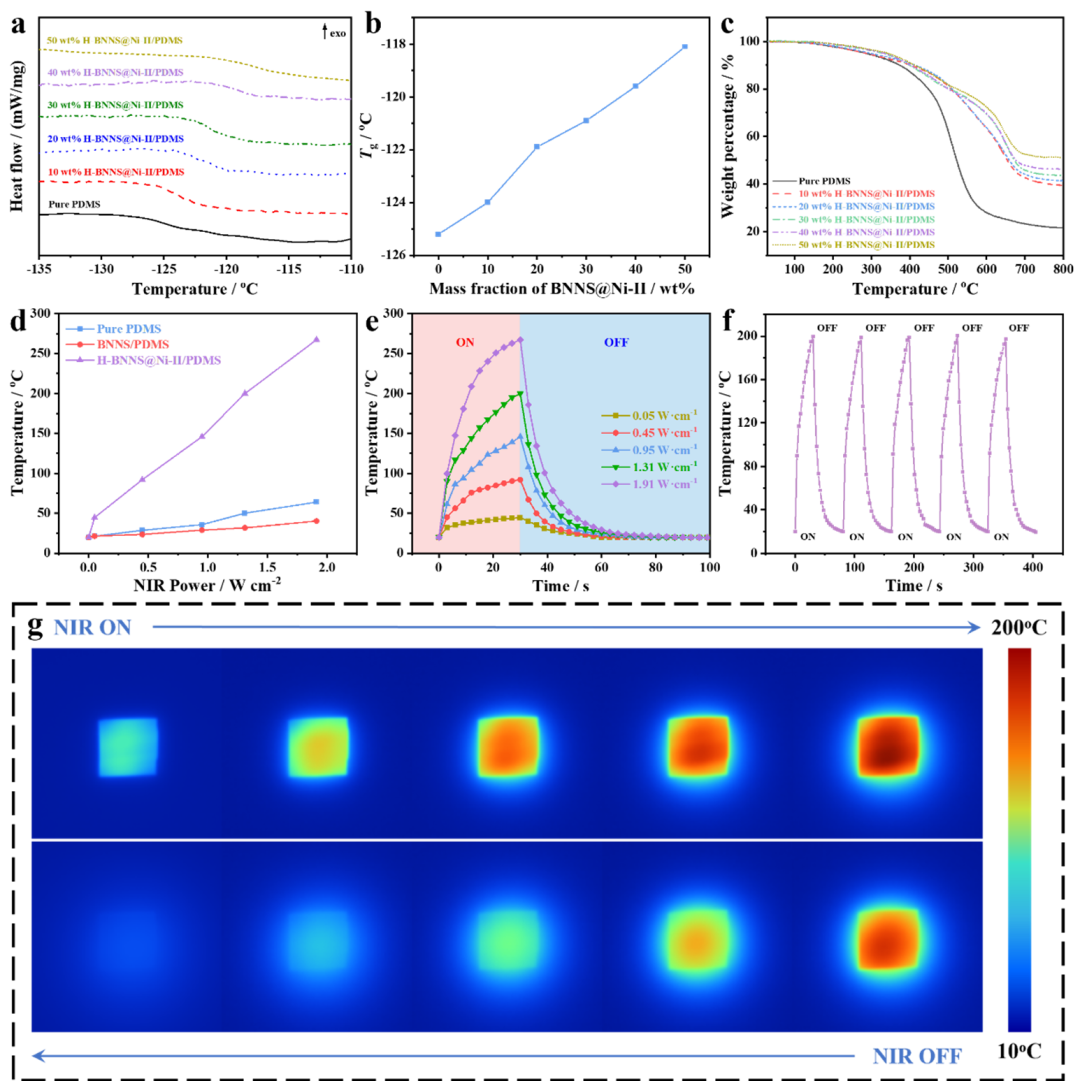
Figure 7 DSC curve of H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites (a),Tg (b) and TGA curve (c), surface temperatures of pure PDMS, BNNS/PDMS, and H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites under different NIR (808 nm) power densities (d), surface temperature change curves of H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites under different NIR (808 nm) power densities (e), heating stability and repeatability of H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites under repeated NIR (808 nm) irradiation at a power density of 1.31 W·cm-2 (f), infrared thermal imaging photos of H-BNNS@Ni-II/PDMS thermal composites during “on” and “off” states under NIR (808 nm) at a power density of 1.31 W·cm-2 (g)
Author Introduction

Song Ping, Associate Professor and Master’s Supervisor at the School of Printing, Packaging and Digital Media, Xi’an University of Technology. Mainly engaged in the microstructure design, performance regulation, and mechanism research of functional (electromagnetic shielding, thermal conductivity) polymer composites. Selected as one of the top 2% of scientists globally for the 2022-2024 impact list. Principal investigator of the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Science Fund project, and the Shaanxi Province Youth Talent Program project. Published 8 high-level academic papers as the first author or corresponding author in journals such as Nano-Micro Lett, J Mater Sci Technol, and Compos Sci Technol, with one paper selected as an excellent scientific paper by the China Association for Science and Technology. Holds 6 authorized national invention patents.

Gu Junwei, Dean of the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Northwestern Polytechnical University, Professor, Doctoral Supervisor, National-level Leading Talent, recipient of the Shaanxi Province Outstanding Youth Science Fund, and leader of the Shaanxi Province Science and Technology Innovation Team. Elected Fellow of the Royal Society of Chemistry, Fellow of the Royal Aeronautical Society, and Fellow of the Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining. Selected as an excellent mentor by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Clarivate Analytics’ “Highly Cited Researchers”, and Elsevier’s “China Highly Cited Scholars”. Currently serves as the Deputy Secretary-General/Director of the China Composites Society, Director of the Talent Evaluation Working Committee, and Executive Deputy Director of the Thermal Composite Materials Committee. Mainly engaged in the design, preparation, and molding processing research of functional polymer composites and fiber-reinforced advanced resin-based composites. Received five provincial and ministerial scientific research awards, including the first prize of the Technical Invention Award from the China National Light Industry Federation and the second prize of the Shaanxi Province Natural Science Award. Awarded the Morand Lambla Award from the International Polymer Processing Society, the Young Scientist Award from the China Composites Society, the Polymer Innovation Paper Award from the Chinese Chemical Society, and the “Emerging Innovation Award” for polymer molding processing and its industrial development. Principal investigator of over 30 provincial and ministerial projects, including key projects of the National Natural Science Foundation Joint Fund. Published over 210 academic papers as the first and/or corresponding author in journals such as Angew Chem Int Ed, Adv Mater, and Macromolecules. Four papers selected as “Top 100 Most Influential International Academic Papers in China”, and one paper selected as an excellent scientific paper by the China Association for Science and Technology. Authored or co-authored four English monographs. Holds 35 authorized national invention patents. Serves as an associate editor or editorial board member for several journals including Compos Sci Technol, Nano-Micro Lett, and Polymer Bulletin.
Article Information
Wang Y, Ruan K, Li M, et al. Horizontal array of BNNS@Ni for polydimethylsiloxane composites with high in-plane thermal conductivities and excellent photo-thermal performances. Nano Research, 2025, https://doi.org/10.26599/NR.2025.94907700.

Scan the QR code or click the bottom left corner “Read the original text” to access the full text
Follow us on Bilibili, Video Account, and our official website for more exciting content!

Bilibili

Video Account

Official Website