Multi-agent systems represent one of the most powerful capabilities in modern artificial intelligence architectures. Unlike relying on a single agent to handle complex tasks, you can create specialized agents that work together, each contributing unique expertise to solve complex problems.

Strands Agents support various multi-agent modes, each with different advantages and applicable scenarios:
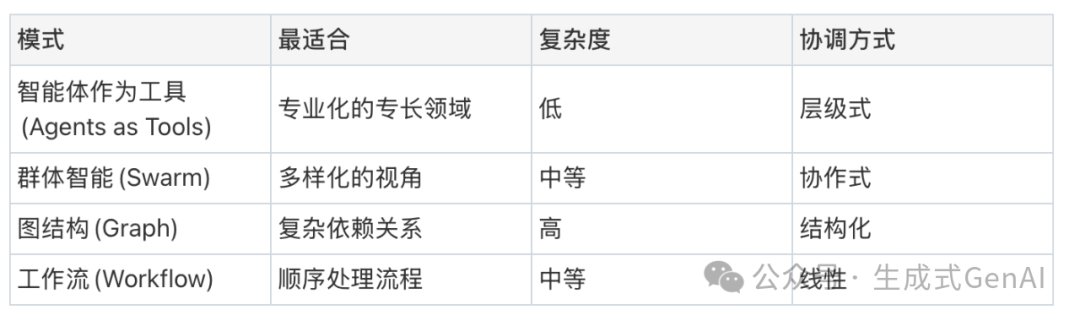
1. Tool Agents (Hierarchical Delegation)
Structure: A main “orchestrator” agent coordinates specialized “tool agents”
Best suited for: Complex workflows requiring different areas of expertise
Advantages: Clear separation of concerns, focused specialization, easy to understand and maintain
Example: Migration planning with architecture, cost analysis, and presentation experts
2. Collective Intelligence (Collaborative Processing)
Structure: Multiple agents work in parallel, sharing memory
Best suited for: Problems requiring diverse perspectives or parallel processing
Advantages: Collective intelligence, redundancy, faster processing through parallelization
Example: Market research with multiple analysts providing different viewpoints
3. Graph-Based Workflows (Structured Dependencies)
Structure: Agents connected in a directed graph with defined dependencies
Best suited for: Complex workflows with clear stepwise dependencies
Advantages: Precise control flow, conditional branching, error handling
Example: CI/CD pipeline with testing, building, and deployment agents
4. Workflow Orchestration (Sequential Processing)
Structure: A linear sequence of agents passing state between stages
Best suited for: Multi-stage processes with clear handoffs
Advantages: Predictable execution, easy debugging, clear audit trails
Example: Document processing pipeline with extraction, analysis, and formatting stages