In the execution of real AI projects, a single agent is often insufficient to meet current demands, which is where multi-agent collaboration comes into play.
Multi-Agents vs. Single Agent
Generally, multi-agents can “play” multiple roles, greatly expanding their capabilities. They can achieve task planning and allocation, cooperate with each other, communicate, make distributed decisions, engage in competitive adversarial interactions, and perform reinforcement learning, collectively solving complex problems or tasks.
In contrast, a single agent requires long-term memory capabilities (which is currently reflected in the 100k-200k context window, significantly testing the performance of LLMs) to solve complex problems or tasks, while multi-agents do not need to focus heavily on this aspect, which is a significant advantage.
Multi-agents enhance the capabilities of AI agents through cooperation among agents, simulating human team collaboration. Building a multi-agent system is akin to forming a functional team, where each member (agent) takes on different roles to collectively complete predefined projects.
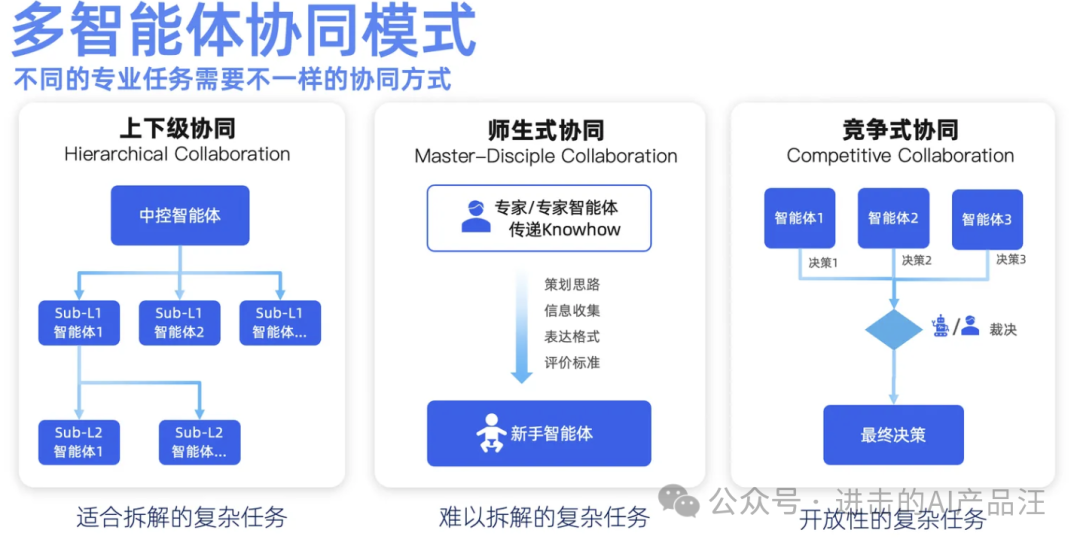
The core technical issue of multi-agents lies in how different agents can be organized together through reasonable collaboration patterns at various functional positions. As a team, multi-agents need to be more robust than directly using large models end-to-end or a single agent working alone from scratch, and the complexity of the organization should not make the overall system more fragile.
Current Domestic Agent Building Platforms[Partial List]
-
BanTouYan Intelligent Technology: BetterYeah “Founded by members of the DingTalk team”
-
ByteDance: Coze
-
Baidu Qianfan AgentBuilder: AgentBuilder
-
SkyAgents (Kunlun Wanwei): TianGong Open Platform
-
Aliyun MoDa: ModelScope
-
Xinghuo Large Model (iFLYTEK): Xinghuo Intelligent Agent Creation
Open Source Framework Comparison
| Features | AutoGen | CrewAI | LangGraph |
| Framework Type | Conversational Agent | Role Agent | Graph-based Agent |
| Autonomy | Highly Autonomous | Highly Autonomous | Conditionally Autonomous |
| Collaboration | Centralized Group Chat | Autonomous agents with roles and goals | Condition-based Cyclic Graph |
| Execution | Managed by dedicated agents | Dynamic delegation, but can define hierarchical processes | All agents can execute |
| Applicable Scenarios | Prototype Design | From Development to Production | Detailed Control Scenarios |
Scenario Examples
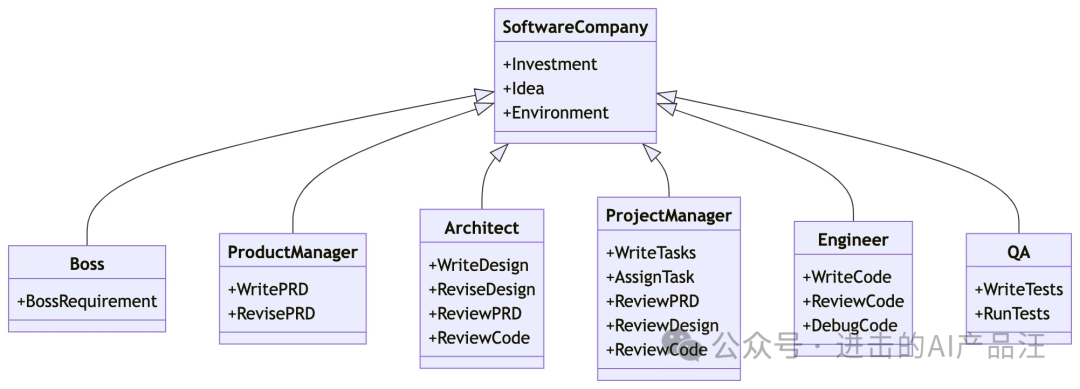
MetaGPT: Forming a Software Company with GPTs to Collaborate on More Complex Tasks
-
MetaGPT Input A one-sentence request from the boss, Output User Stories / Competitive Analysis / Requirements / Data Structures / APIs / Documents, etc.
-
MetaGPT includes Product Managers / Architects / Project Managers / Engineers, providing a complete process of a software company and a carefully coordinated SOP
-
<span>Code = SOP(Team)</span>is the core philosophy. We visualize SOP and apply it to teams composed of LLMs.
CrewAI
A Langchain-based agent framework with stronger customization, allowing for custom roles and collaboration methods.
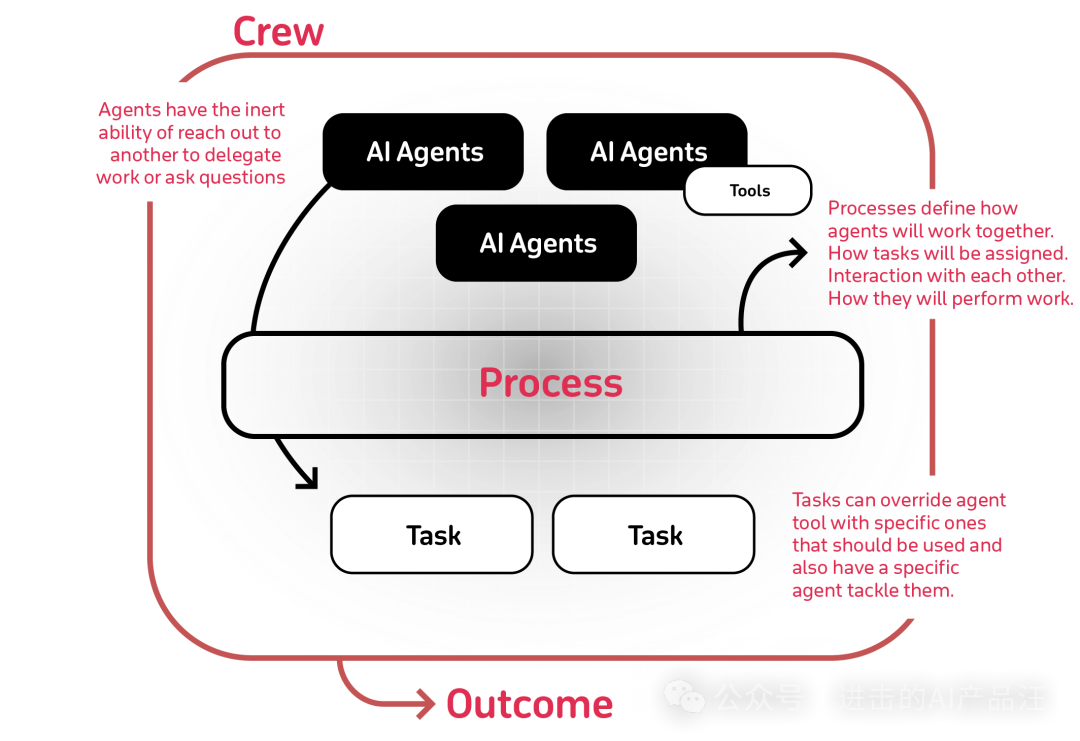
Role-playing agents: Agents can take on different roles and personalities to better understand and interact with complex systems. Autonomous decision-making: Agents can make decisions autonomously based on the given context and available tools. Seamless collaboration: Agents can work together seamlessly, sharing information and resources to achieve common goals. Complex task handling: CrewAI is designed to handle complex tasks such as multi-step workflows, decision-making, and problem-solving.Core Concepts
-
Tool: Tools are auxiliary means required for agents to perform specific tasks, such as search engines, document loaders, etc. CrewAI is built on LangChain, allowing developers to use existing tools provided by LangChain or customize new tools to meet different task requirements.
-
Task: A task is a specific work unit that agents need to perform. In CrewAI, each task is clearly defined and equipped with the necessary tools and resources. Agents select appropriate tools and methods to complete the work based on task requirements.
-
Agent: Agents are the core units in the CrewAI framework, playing the role of team members. Each agent has specific roles, backstories, goals, and memories. Agents in CrewAI are extended based on LangChain Agent, adding ReActSingleInputOutputParser to support more complex role-playing and contextual memory functions.
-
Crew: A crew consists of multiple agents working together to achieve specific goals. In CrewAI, the collaboration methods among team members are organized and managed through predefined processes or strategies, ensuring that tasks can be executed in an orderly and efficient manner.
-
Process: The process defines the strategies and methods for the team to complete tasks. The CrewAI framework provides three basic process strategies: Sequential Execution, Hierarchical Execution, and Consensual Process (in planning). These strategies allow developers to choose appropriate collaboration modes based on task characteristics and requirements.