Click the blue text / to follow us
 Serial Communication and Parallel Communication
Serial Communication and Parallel Communication
In communication and computer science, serial communication is a general concept that refers to all serial communication protocols, such as RS232, RS422, RS485, USB, I2C, SPI, etc.
Serial communication refers to a communication method that transmits data bit by bit using only one receiving line and one sending line. Although serial communication is slower than parallel communication, which transmits data by bytes, it can achieve data transmission using only two wires.
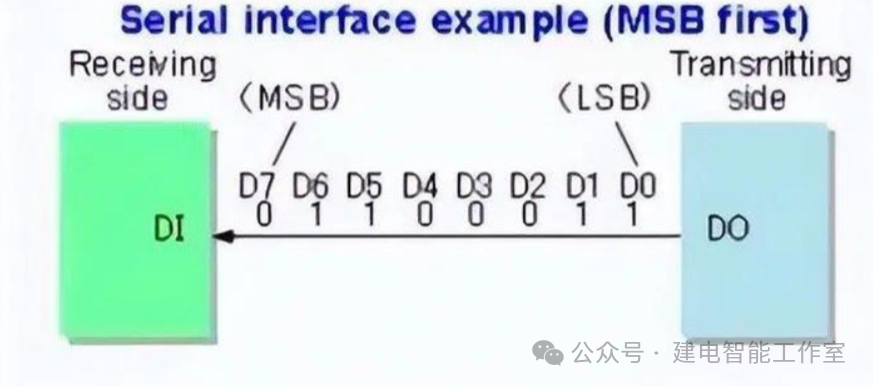
 Serial Communication Modes
Serial Communication Modes
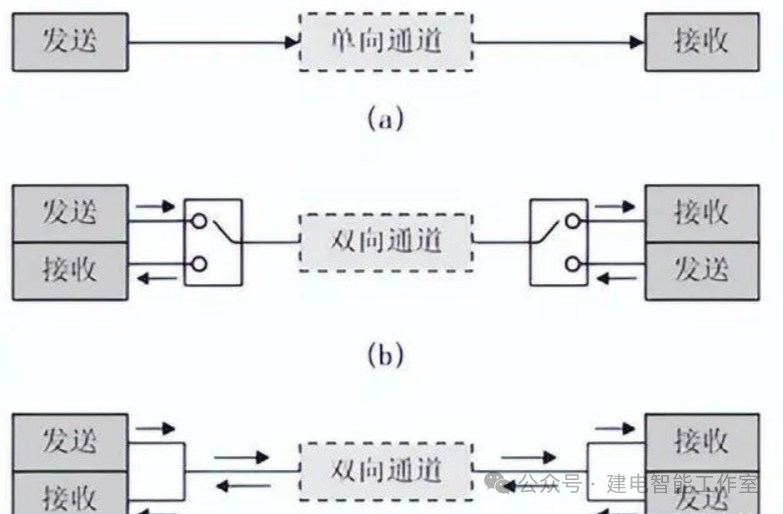
Serial communication modes include simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. In simplex mode, data transmission only supports data flow in one direction. Half-duplex mode allows data to flow in both directions, but only one direction at a time, effectively functioning as a switched direction simplex communication, which does not require separate receiving and sending ends; both can be combined into one port. See the diagram below:
 Serial Communication Protocols
Serial Communication Protocols
Initially, data was output as analog signals for simple process quantities. Later, the RS232 interface emerged, which allows point-to-point communication. However, this method does not support networking, leading to the development of RS422 and RS485.
We know that the data transmission in serial communication consists of 0s and 1s. In single bus, I2C, and UART, the logic 1 or logic 0 is determined by the high and low levels of a single wire. However, when the ground of this signal line is shared with other devices, it forms a common ground communication mode, which is prone to interference and has weak anti-interference performance. Therefore, differential communication, which supports multi-device communication and has strong anti-interference capabilities, such as RS422 and RS485, is widely used.
The main features of RS422 and RS485 communication are that the maximum transmission speed can reach over 10Mb/s, and the maximum transmission distance exceeds 1000 meters. It is important to note that although both RS485 has a high maximum speed and long maximum transmission distance, the transmission speed will decrease as the distance increases, so both cannot be achieved simultaneously.
 Detailed Introduction to RS232
Detailed Introduction to RS232
1. Basic Characteristics of RS232
RS-232 is a serial data interface standard established and published by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) to ensure compatibility between products from different manufacturers.
2. Physical Characteristics of RS232
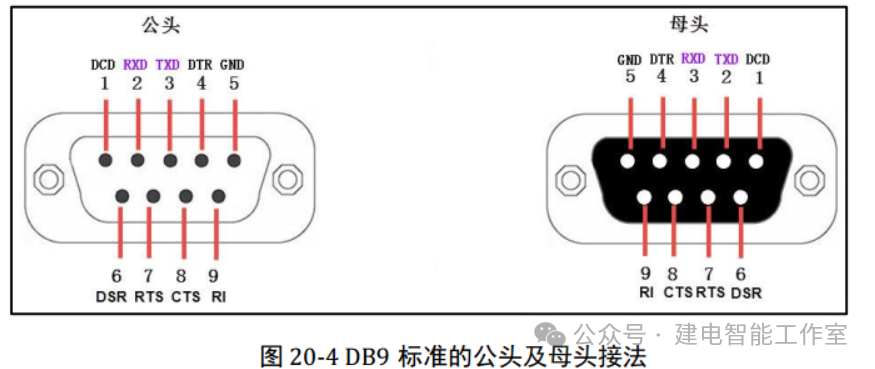
In RS232 communication, the “DB9 interface” between two communication devices is connected through serial signal lines, using the “RS-232 standard” to transmit data signals. The original numbering system of the D-type or D-subminiature (D-shaped subminiature) connector uses D as a prefix (naming it as a series), and then selects A, B, C, D, or E based on the shell size, with the last digit indicating the number of pins. See the diagram below:

3. Communication Protocol of RS232
RS232 generally uses the DB9 interface. Since the receiving and transmitting signals (RXD and TXD) between two communication devices should be cross-connected, the connection of the receiving and transmitting signals at the DB9 female connector on the modem side is generally opposite to that of the male connector. See the diagram of DB9 male and female connectors below.
4. Baud Rate of RS232
In a channel, the signal unit carrying data information is called a symbol, and the number of symbols transmitted through the channel in a unit time is called the symbol transmission rate, abbreviated as baud rate (Baud Rate), with the unit being baud (Baud, symbol/s). The typical baud rates for RS232 are
300/1200/2400/9600/19200/38400/115200/230400, etc.
5. Data Structure of RS232
A complete serial data frame, or character frame, includes a start bit, data bits, stop bits, and parity bits. The data bits are preceded and followed by frame headers and frame tails, which contain some necessary control information. Among them, MSB (Most Significant Bit) refers to the highest significant byte stored at the lowest address, while LSB (Least Significant Bit) refers to the lowest significant byte stored at the lowest address.
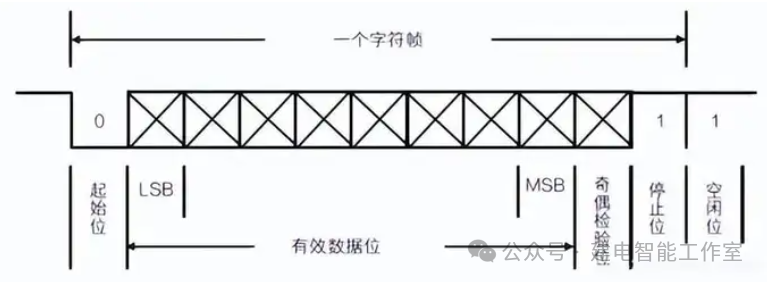
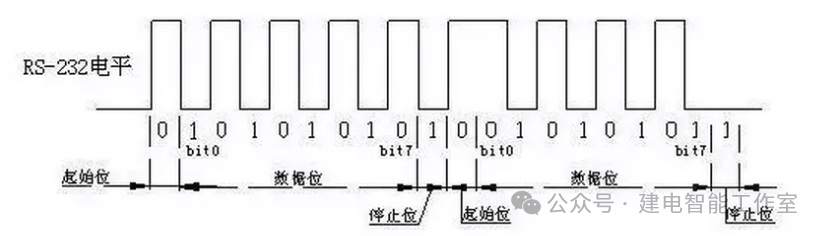
The start bit: The start bit must be a logic 0 level that lasts for one bit time, marking the beginning of the transmission of a character, allowing the receiver to synchronize its receiving clock with the data from the sender.
The data bits: The data bits immediately follow the start bit and contain the actual valid information in the communication. The number of data bits can be agreed upon by both communicating parties. When transmitting data, the low bits of the character are sent first, followed by the high bits.
The parity bit: The parity bit occupies only one bit and is used for odd or even parity. The parity bit is not mandatory. If it is odd parity, the total number of logic high bits transmitted must be odd; if it is even parity, the total number of logic high bits transmitted must be even.
The stop bit: The stop bit can be 1 bit, 1.5 bits, or 2 bits, and can be set by software. It must be a logic 1 level, marking the end of the transmission of a character.
The idle bit: The idle bit refers to the state from the end of one character’s stop bit to the beginning of the next character’s start bit, indicating that the line is in an idle state, which must be filled with a high level.
6. RS232 and RS232 (TTL)
The signal of the RS-232 level standard cannot be directly recognized by the controller, so these signals are converted through a “level conversion chip” into a “TTL calibrated” level signal that the controller can recognize to achieve communication.
TTL stands for Transistor-Transistor Logic, and this serial communication corresponds to physical levels that are always between 0V and Vcc, where common Vcc values are 5V or 3.3V. TTL high level 1 is >=2.4V, and low level 0 is <=0.5V (for 5V or 3.3V power supply voltage), which is positive logic.
The signal of the RS-232 level standard cannot be directly recognized by the controller, so these signals are converted through a “level conversion chip” into a “TTL” level signal that the controller can recognize to achieve communication.
 Detailed Introduction to RS422
Detailed Introduction to RS422
The RS-422 bus standard specifies the electrical characteristics of the bus interface. The sending end: positive level is between +2V and +6V, indicating logic state “1”; negative level is between -2V and -6V, indicating logic state “0”; the receiver: (V+) – (V-) ≥0.2V indicates signal “0”; (V+) – (V-) ≤0.2V indicates signal “1”.
RS-422 uses full-duplex communication mode, with 4 signal lines, separating receiving and transmitting, allowing simultaneous receiving and transmitting. It is suitable for communication between two stations, such as star networks, ring networks, etc., and cannot be used for bus networks.
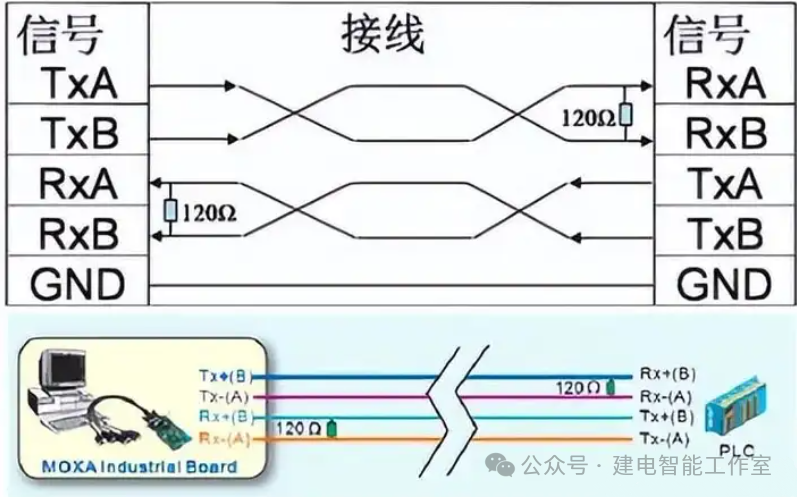
 Detailed Introduction to RS485
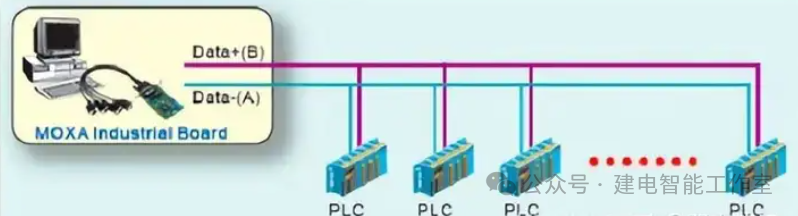
Detailed Introduction to RS485
The electrical characteristics of RS-485 are basically the same as those of RS-422. It uses half-duplex communication mode, with 2 signal lines, operating in half-duplex mode, commonly used in bus networks. The specific wiring method is shown in the diagram below:
 END
END
This issue was edited by: Luo Wanling
 Scan to follow us
Scan to follow us