

In 1979, Schneider Electric established the Modbus protocol, a bus protocol used for industrial sites. Many industrial applications using RS485 communication adopt the Modbus protocol, so today we will explore RS485 communication and the Modbus communication protocol.
【1】/ Introduction
In industrial control, power communication, and intelligent instruments, serial communication is typically used for data exchange. The initial method used was the RS232 interface, but due to the complexity of industrial sites, various electrical devices generate significant electromagnetic interference, which can lead to signal transmission errors.
In 1979, Schneider Electric established the Modbus protocol for industrial sites. Many industrial applications using RS485 communication adopt the Modbus protocol, so today we will explore RS485 communication and the Modbus communication protocol.
【2】/ RS485 Communication
1. In fact, RS232 was already born before RS485, but RS232 has its drawbacks:
1) The signal voltage level of the interface is relatively high, reaching several volts, which can easily damage the interface circuit chip and is not compatible with TTL levels. Therefore, when connecting to microcontroller circuits, a conversion circuit must be added.
2) The signal lines used by the interface form a common ground communication with other devices. This common ground mode of transmission is prone to interference and has weak anti-interference performance.
3) The transmission distance and speed are limited, with a maximum communication distance of only several tens of meters; communication can only occur between two points, and multi-machine networking is not possible.
2. To address the shortcomings of the RS232 interface, new interface standards like RS485 have emerged. RS485 has the following characteristics:
1) Logic “1” is represented by a voltage difference of + (2—6)V between the two wires; logic “0” is represented by a voltage difference of – (2—6)V. The signal voltage levels of the interface are lower than those of RS232, making it less likely to damage circuit chips, and this level is compatible with TTL levels, allowing for easy connection with TTL circuits.
2) RS485 communication is fast, with a maximum data transmission rate of over 10Mbps. Its internal physical structure uses a combination of balanced drivers and differential receivers, greatly enhancing its anti-interference capability.
3) The maximum transmission distance can reach about 1200 meters, but the transmission speed and distance are inversely proportional. To achieve the maximum communication distance, the transmission speed must be below 100KB/s. If longer distances are required, repeaters can be used.
4) Multiple devices can be connected on the bus for multi-machine communication, allowing multiple transceivers to be connected on the bus. Existing RS485 chips can support 32, 64, 128, 256, and other different numbers of devices.
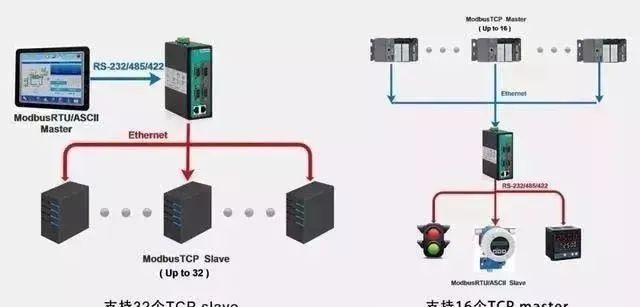
3. RS485 has two-wire and four-wire systems. The four-wire system only allows point-to-point communication and is rarely used now. The two-wire system is a bus topology structure, allowing a maximum of 32 nodes on the same bus. In RS485 communication networks, a master-slave communication method is generally used, with one master device controlling multiple slave devices.
4. In many cases, when connecting RS-485 communication links, a simple twisted pair is used to connect the “A” and “B” ends of each interface, while ignoring the connection of the signal ground. This connection method can work normally in many situations, but it poses significant risks for two reasons:
1) Common mode interference: The RS-485 interface uses a differential method to transmit signals and does not require detection relative to a reference point; the system only needs to detect the potential difference between the two wires. However, people often overlook that the transceiver has a certain common mode voltage range. The common mode voltage range for RS-485 transceivers is -7 to +12V. Only when this condition is met can the entire network operate normally. When the common mode voltage exceeds this range, it can affect the stability and reliability of communication and even damage the interface.
2) EMI issues: The common mode portion of the signal output from the driver requires a return path. If there is no low-resistance return channel (signal ground), it will return to the source in the form of radiation, making the entire bus act like a large antenna radiating electromagnetic waves.
5. Since PCs typically only come with RS232 interfaces, the following methods can be used to obtain RS485 circuits on PC host computers:
1) Use an RS232/RS485 conversion circuit to convert the PC’s RS232 signal into an RS485 signal. In complex industrial environments, it is best to choose surge-protected products with isolation.
2) Use a PCI multi-serial port card that directly outputs RS485 type signals.
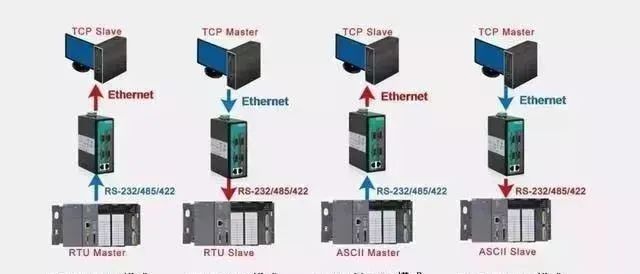
【3】/ Modbus Communication Protocol
Modbus is a universal language used in electronic controllers. Through this protocol, controllers can communicate with each other and with devices over networks (such as Ethernet). It has become a common industrial standard. With it, control devices produced by different manufacturers can be connected into an industrial network for centralized monitoring.
This protocol defines a message structure that a controller can recognize, describes the process of a controller requesting access to other devices, how to respond to requests from other devices, and how to detect and log errors. It establishes a common format for message domain patterns and content.
1. Modbus has the following characteristics:
1) Standard and open, users can freely and confidently use the Modbus protocol without paying licensing fees or infringing on intellectual property rights. Currently, there are over 400 manufacturers supporting Modbus and over 600 products that support it.
2) Modbus can support multiple electrical interfaces, such as RS-232, RS-485, and can also transmit over various media such as twisted pair, fiber optics, and wireless.
3) The frame format of Modbus is simple and compact, easy to understand. It is user-friendly and easy for manufacturers to develop.
2. Types of Modbus Registers
1) Coil status: Output port, can set the output status of the port and read the output status of that bit;
2) Discrete input status: Input port, changes input status through external settings, readable but not writable;
3) Holding register: Certain parameters set during the operation of the controller, readable and writable;
4) Input register: Certain parameters obtained from external devices during the operation of the controller, readable but not writable.
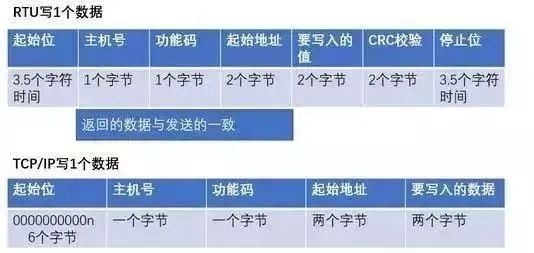
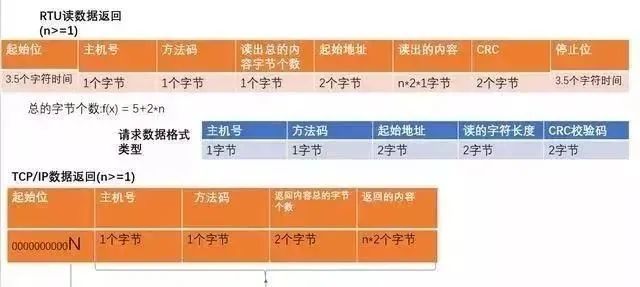
3. Modbus Communication Data Format
1) Single write:
2) Multiple writes:
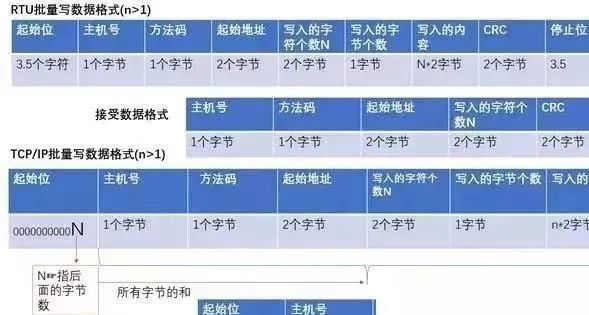
3) Read:
4. Overview of Modbus Function Codes
Function codes can be divided into bit operations and byte operations. The smallest unit of bit operations is Bit, while the smallest unit of byte operations is 2 bytes (Byte).
(1) Bit operation instructions: Read coil status 01H, read discrete input status 02H, write single coil 05H, write multiple coils 0FH.
(2) Byte operation instructions: Read holding register 03H, read input register 04H, write single holding register 06H, write multiple holding registers 10H.
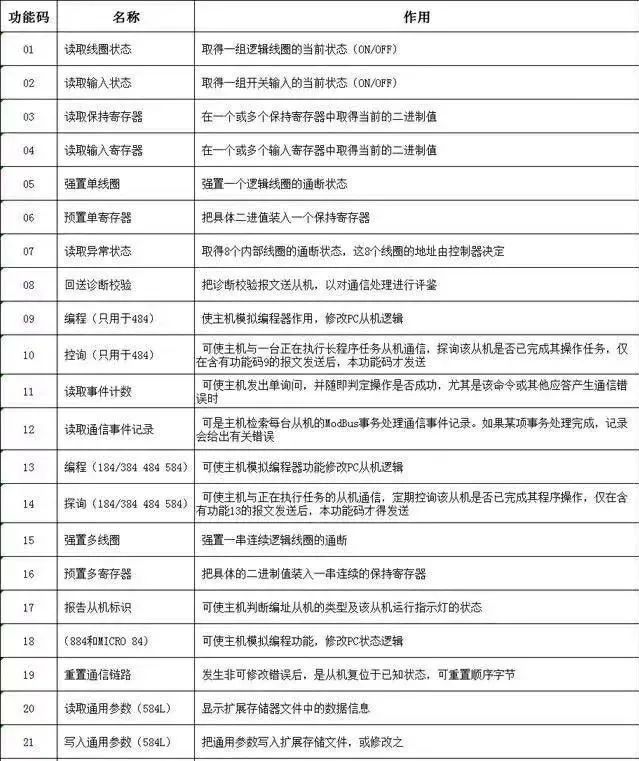
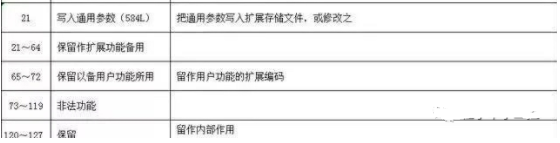
5. Modbus Function Codes
Complete Question Bank for 2021 Electrician Beginner Exam (with Answers)
Trouble with Inverter Fault Checking? Just One Click!
One Click to Brush Through All Electrical Exam Questions, Do You Not Have This Tool Yet?
Five Major Electrical Drawing Software (CAD, Eplan, CADe_simu…), Which One Do You Pick?
Latest Electrical Version CAD Drawing Software, with Super Detailed Installation Tutorial!
Latest Electrical Drawing Software EPLAN, with Super Detailed Installation Tutorial!
Common Issues for Beginners Using S7-200 SMART Programming Software (with Download Link)
Comprehensive Electrical Calculation EXCEL Sheets, Automatically Generated! No Need to Ask for Electrical Calculations!
Bluetooth Headphones, Electrical/PLC Introductory Books Given Away? Come and Get Your Electrical Gifts!
PLC Programming Basics: Ladder Diagrams and Control Circuits (with 1164 Practical Mitsubishi PLC Cases)
Still Can’t Understand Electrical Diagrams? Take Away Basic Electrical Diagram Reading Skills and Simulation Software, Quickly Get Started with Theory and Practice!
12 Free Electrician Video Courses, 10GB Software/Ebook Resources, 30 Days of Free Electrician Live Courses Given Away!

