
 As the limitations of traditional manufacturing methods become increasingly apparent in terms of design flexibility, prototyping speed, and production waste, 3D printing technology has emerged as a new additive manufacturing method. 3D printing meets the growing demand for customized solutions in industries such as aerospace, medical, and consumer goods by constructing objects layer by layer. However, most 3D printing technologies are limited by material compatibility and lack of multi-material processing capabilities.Material extrusion technology, especially Direct Ink Writing (DIW), has become an important development direction in the field of 3D printing due to its wide material applicability and versatility. DIW technology can handle a variety of materials, from biomaterials to metals, and achieves complex material combinations and structural designs through advanced nozzle designs, providing crucial support for the further development of 3D printing technology.This article is a review of multi-material extrusion 3D printing printheads, titled “Multimaterial extrusion 3D printing printheads,” summarized by the team of Jochen Mueller from Johns Hopkins University, published in Nature Reviews Materials.The core content of the article focuses on nozzle technology in 3D printing, particularly the latest advancements, classifications, applications, and future development directions of multi-material extrusion 3D printing printheads.
As the limitations of traditional manufacturing methods become increasingly apparent in terms of design flexibility, prototyping speed, and production waste, 3D printing technology has emerged as a new additive manufacturing method. 3D printing meets the growing demand for customized solutions in industries such as aerospace, medical, and consumer goods by constructing objects layer by layer. However, most 3D printing technologies are limited by material compatibility and lack of multi-material processing capabilities.Material extrusion technology, especially Direct Ink Writing (DIW), has become an important development direction in the field of 3D printing due to its wide material applicability and versatility. DIW technology can handle a variety of materials, from biomaterials to metals, and achieves complex material combinations and structural designs through advanced nozzle designs, providing crucial support for the further development of 3D printing technology.This article is a review of multi-material extrusion 3D printing printheads, titled “Multimaterial extrusion 3D printing printheads,” summarized by the team of Jochen Mueller from Johns Hopkins University, published in Nature Reviews Materials.The core content of the article focuses on nozzle technology in 3D printing, particularly the latest advancements, classifications, applications, and future development directions of multi-material extrusion 3D printing printheads. 【Main Content】
【Main Content】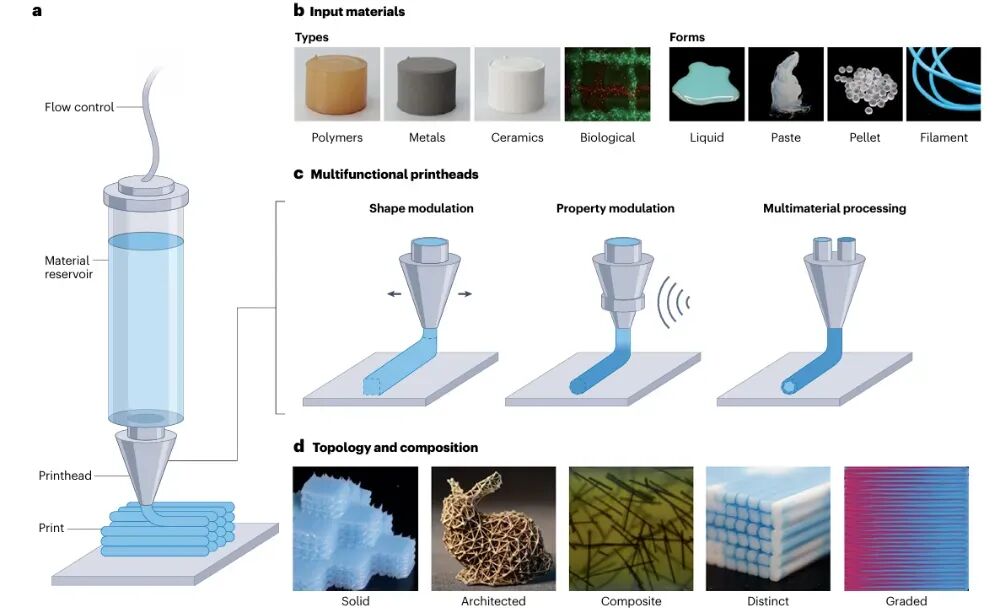
Figure 1 Multi-material extrusion additive manufacturing printheads are the core of material extrusion 3D printing systems, connecting material input and output, determining the type of printing material and the forming effect. The article classifies nozzles into three categories: shape-modulating nozzles (fixed, adaptive, and multi-output), property-modulating nozzles (motion and stimulation), and multi-material processing nozzles (switching, mixing, and co-extrusion), and introduces their key roles in material design and manufacturing.
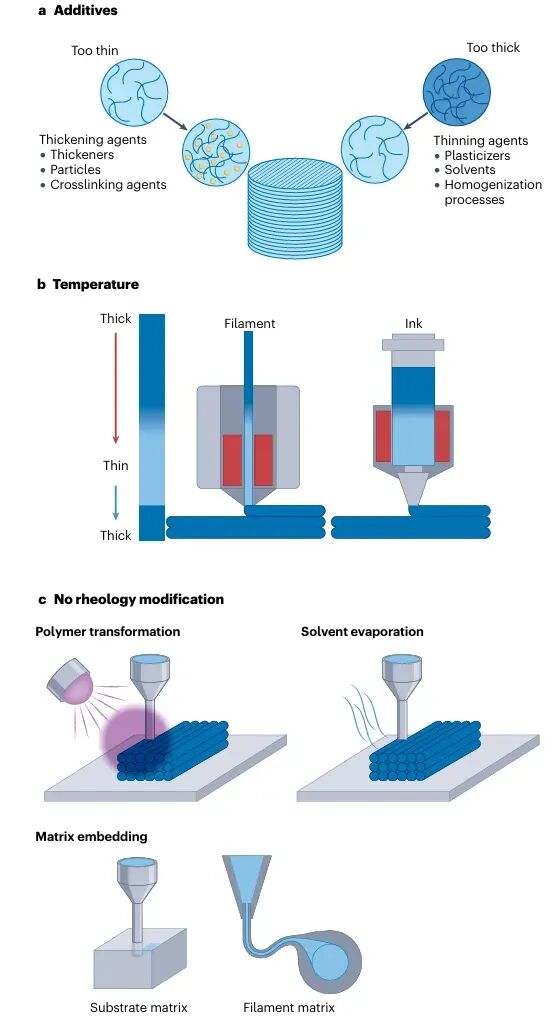
Figure 2 Printability and modifiability of materialsFurther discussion explores the impact of the rheological properties (flow characteristics) of materials on 3D printing. To ensure good printability, the viscosity, shear-thinning behavior, and yield stress of materials need to be adjusted through the addition of thickeners, diluents, crosslinkers, or temperature control. These adjustments not only improve the printability of materials but also provide a theoretical basis for developing new printing materials.
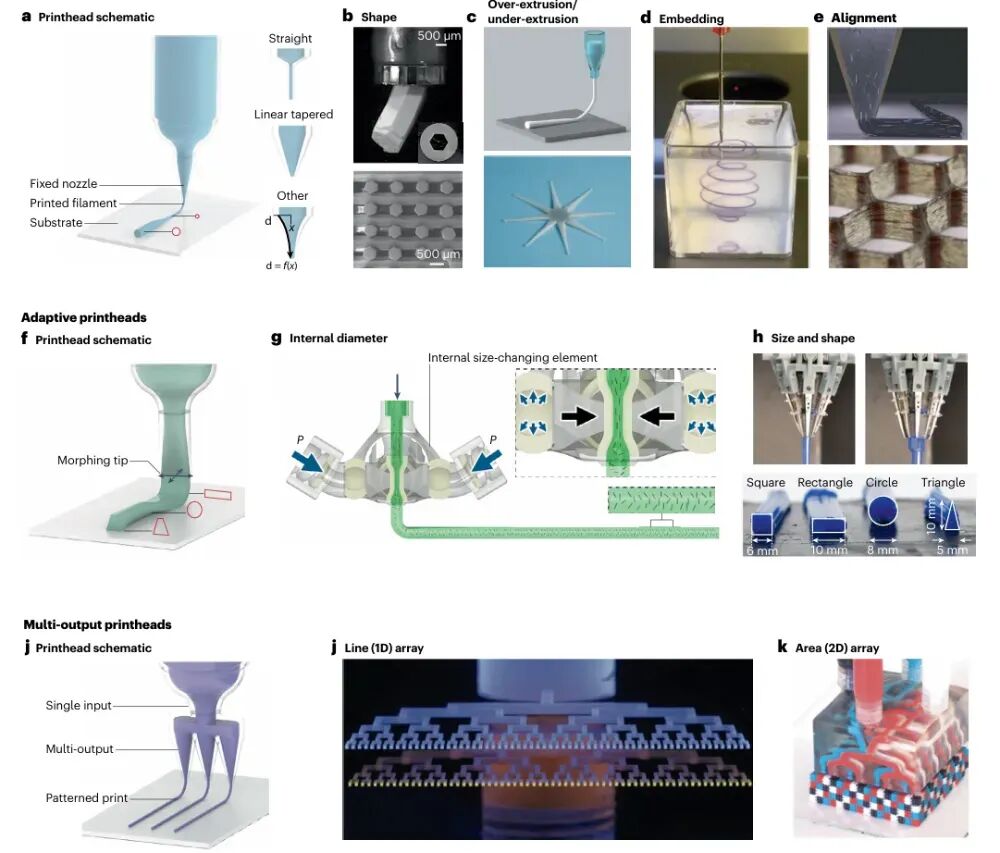
Figure 3 Shape-modulating nozzlesThe figure shows three types of shape-modulating nozzles: fixed nozzles, adaptive nozzles, and multi-output nozzles. Fixed nozzles are the most basic type, while adaptive nozzles can dynamically adjust the size or shape of the nozzle to meet different printing needs, thereby improving print quality and efficiency. Multi-output nozzles significantly increase printing speed by extruding materials through multiple nozzles simultaneously. These nozzles have broad application prospects in fields such as construction and aerospace.
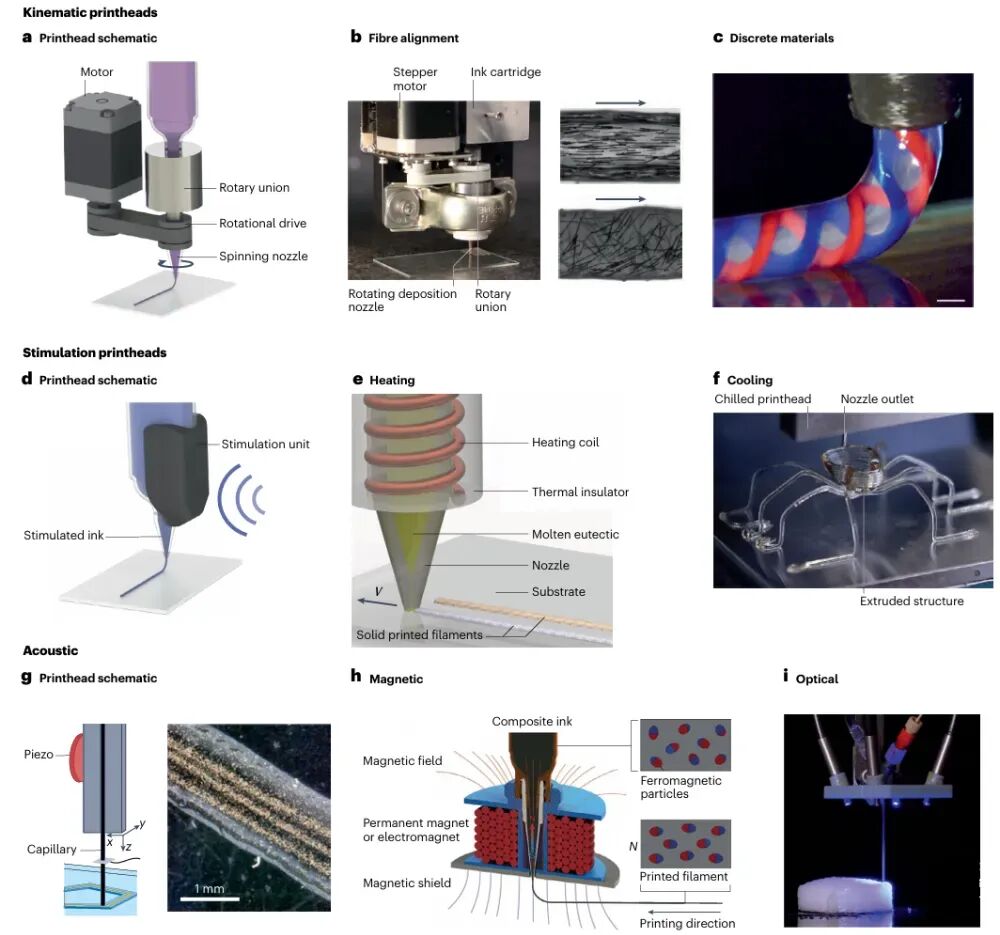
Figure 4 Property-modulating nozzlesThe figure introduces two types of property-modulating nozzles: motion nozzles and stimulation nozzles. Motion nozzles adjust the fiber arrangement or flow characteristics of materials through rotation or vibration, while stimulation nozzles change the physical properties of materials through external stimuli (such as magnetic fields or temperature). These nozzle technologies have broad application prospects in composite material manufacturing, biomedicine, and electronics manufacturing.
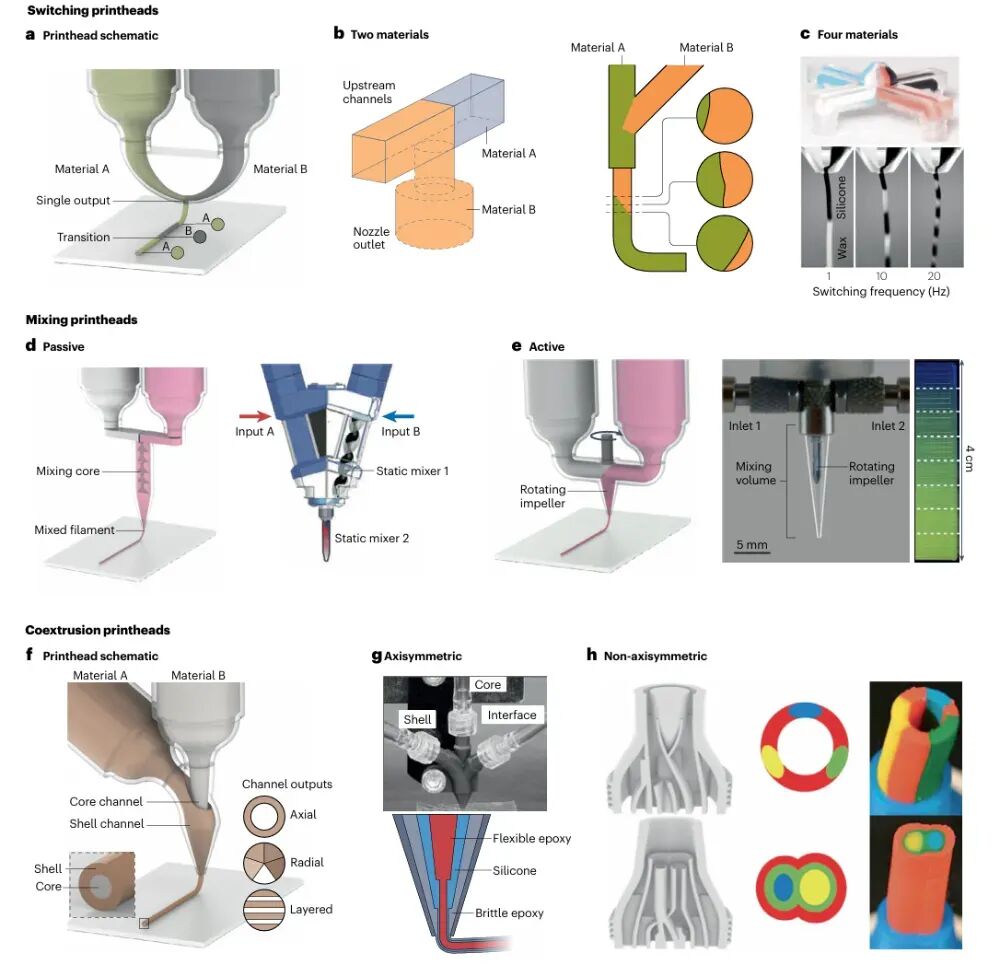
Figure 5 Multi-material nozzlesThe figure shows three types of multi-material processing nozzles: material switching nozzles, mixing nozzles, and co-extrusion nozzles. These nozzles can switch, mix, and co-extrude multiple materials within a single nozzle, achieving complex material combinations and performance gradients. This technology has significant application value in biomedicine, electronics manufacturing, and soft robotics.

Figure 6 Mixing nozzlesThe figure discusses the concept of mixing nozzles, which integrate multiple nozzle functions to achieve more complex printing tasks. Mixing nozzles can achieve more efficient and flexible printing effects by combining different types of nozzles (such as multi-output nozzles with switching mechanisms, rotating nozzles with co-extrusion nozzles). This design provides more possibilities for the future development of 3D printing technology.

Figure 7 Emerging applications of material extrusion additive manufacturing The figure showcases the applications of 3D printing technology in several emerging fields, including mechanical metamaterials, soft robotics, 4D printing, and biomedicine. These applications demonstrate the powerful potential of 3D printing technology, such as mechanical metamaterials achieved through multi-material printing that possess unique mechanical properties, soft robots that can achieve more flexible movements by integrating sensors and actuators, and 4D printing that can change shape after printing through external stimuli. These innovations provide new ideas for future manufacturing and innovation.【Full Summary】This article reviews the latest advancements in multi-material extrusion 3D printing printheads, emphasizing the core role of nozzle technology in achieving complex material designs and improving printing efficiency. The article introduces eight categories of prototype nozzles and their mixed types, exploring their roles in material design, ability to overcome processing limitations, and impact on emerging applications. Advances in nozzle technology have made shape modulation, property modulation, and multi-material processing possible, thereby promoting application development in aerospace, medical, consumer goods, and other fields. Nevertheless, 3D printing technology still faces challenges such as material compatibility, production speed, and precision. In the future, nozzle technology needs to further integrate more advanced functional materials, improve production speed without sacrificing precision, and enhance repeatability and predictability to fully realize its potential in manufacturing.
Source: BioMed Technology
Translation: Deng Zhichuan
Review: Wang Chunrong
Recommended Reading↓
Implementation difficulties! Why is UHPC difficult to apply on a large scale?
How to reduce the application cost of UHPC?
Costing ten times that of ordinary concrete, why is UHPC still a future trend?
The “stimulant” of concrete revealed! A spoonful of “white powder” can increase strength by 50%?
Innovative directions for ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC): breakthroughs in lightweight and sprayable technologies


Statement: All original works of this public account are copyrighted by this magazine. Without authorization from this magazine, no industry, website, or media (including but not limited to newspapers, Weibo, WeChat public accounts, etc.) may reproduce, excerpt, or use the original articles of this public account in any other way. If you need to reproduce, excerpt, or use in other ways, you must obtain consent from this magazine and pay remuneration, and indicate “Source: Concrete and Cement Products Magazine” (personal WeChat forwarding and sharing are not restricted but may not be used for commercial purposes). Those who violate the above statement will be held legally responsible by this magazine. In the interest of timely dissemination, this public account will reprint some exciting content. The copyright of reprinted content belongs to the original author, and some content may not have been able to contact the original author when pushed, or the original author could not be contacted, please understand, and the original author is requested to contact this public account in a timely manner, and this public account will pay remuneration according to relevant regulations.