Main Content: The code primarily implements a distributed dispatch strategy for power systems, specifically a distributed economic dispatch method based on the multi-agent consensus algorithm, where the consensus variables are the incremental costs of generator units and the flexible load increments.
 The following text and example code are for reference only.
The following text and example code are for reference only.
Article Directory
- 📌 Problem Description: Distributed Economic Dispatch
- 🧠 Control Strategy: Consensus Algorithm
- Core Idea:
- Update Rule (Continuous Time):
- ✅ System Modeling Example (3 Units + Flexible Load)
- Cost Function (Quadratic Function):
- 🧮 MATLAB Code Implementation
- 📈 Explanation of Results
- 📦 Simulink Extension Suggestions (Optional)
- 🧪 Advanced Directions
The following is an implementation of the Distributed Economic Dispatch (DED) strategy for power systems based on MATLAB using the Consensus-based Distributed Economic Dispatch method. This approach is suitable for power systems with multiple generator units and flexible loads, achieving global cost minimization through local communication without relying on a centralized coordinator.
📌 Problem Description: Distributed Economic Dispatch
Objective Function:
Constraints:
- Power Balance:
∑ i = 1 N P i = P l o a d - Generator Power Limits:
P i m i n ≤ P i ≤ P i m a x
Where:
C i ( P i ) i P i i P l o a d
🧠 Control Strategy: Consensus Algorithm
Core Idea:
Each agent maintains an incremental cost λ_i, updating its value through communication with neighboring nodes, ultimately converging to the same λ value (i.e., the Lagrange multiplier in the global optimal solution).
Update Rule (Continuous Time):
In discrete time, it can be written as:
✅ System Modeling Example (3 Units + Flexible Load)
Cost Function (Quadratic Function):
The corresponding incremental cost is:
🧮 MATLAB Code Implementation
% Multi-Agent Consensus Algorithm for Distributed Economic Dispatch in Power Systems
clear; clc; close all;
% Define the number of units
N =3;
a =[0,0,0];% Fixed cost coefficients
b =[5.0,5.5,6.0];% Linear cost coefficients
c =[0.01,0.012,0.015];% Quadratic cost coefficients
P_min =[50,40,30];
P_max =[200,180,150];
% Initial power allocation
P =(P_min + P_max)/2;
lambda =zeros(N,1);
% Flexible load demand
P_load =sum(P)-50;% Assume load decreases by 50 MW
% Communication topology (adjacency matrix)
A =[011;
101;
110];
L =diag(sum(A))- A;% Laplacian matrix
% Control parameters
alpha =0.1;
iter =500;
dt =0.01;
% Storage variables
lambda_hist =zeros(N, iter);
P_hist =zeros(N, iter);
for k =1:iter
% Calculate incremental cost gradient
grad_C = b"+2* c".* P";
% Consensus update
lambda = lambda - alpha * dt *(L * lambda + grad_C");
% Update power allocation
fori=1:N
P(i)=max(P_min(i),min((lambda(i)-b(i))/(2*c(i)),P_max(i)));
end
% Power balance adjustment (only do one projection)
ifmod(k,50)==0
total_P =sum(P);
delta_P = total_P - P_load;
P = P - delta_P / N *ones(N,1);
end
% Store historical data
lambda_hist(:, k)= lambda;
P_hist(:, k)= P;
end
% Result display
figure;
plot(lambda_hist");
legend('Agent 1','Agent 2','Agent 3');
title('Incremental Cost Consensus');
xlabel('Iteration');ylabel('\lambda');
figure;
bar(P_hist(:,end)');
set(gca,'XTickLabel',{'G1','G2','G3'});
title('Final Power Allocation');
ylabel('Power (MW)');
📈 Explanation of Results
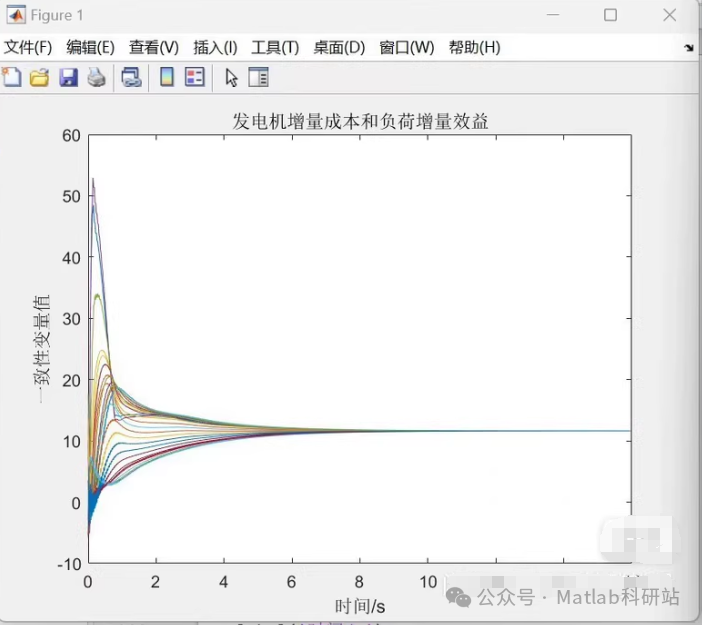
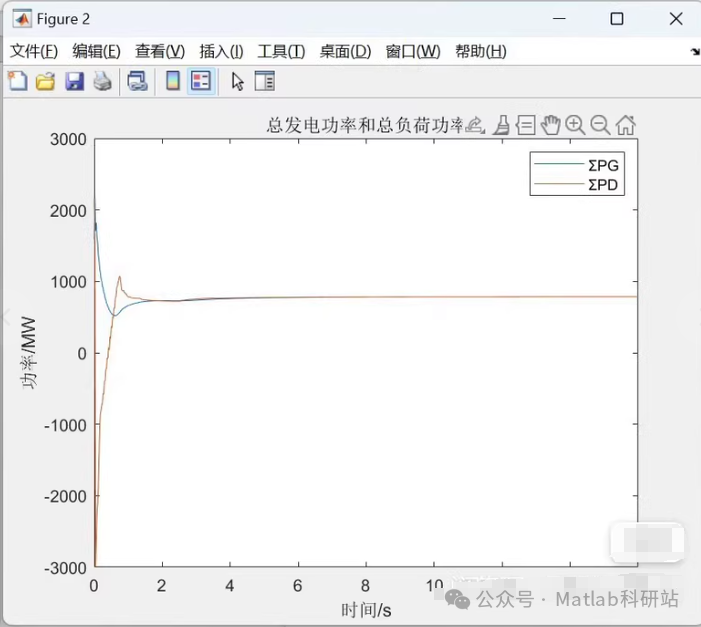
<span>lambda</span>curves will converge, indicating consensus among agents.- The final power allocation meets power balance and complies with unit constraints.
- The cost minimization objective is achieved.
📦 Simulink Extension Suggestions (Optional)
You can also use Simulink to build a multi-agent communication structure, with each agent implementing the consensus update logic using Stateflow or MATLAB Function Block, and simulating real communication networks through TCP/IP, UDP, or CAN bus.
🧪 Advanced Directions
- Consider dynamic load variations
- Introduce communication delays or packet loss mechanisms
- Incorporate energy storage systems (ESS) into the dispatch
- Combine game theory for market bidding analysis
- Apply to microgrids/virtual power plants (VPP)