“If ARM is working well, why switch to RISC-V?”
“If the software that customers need cannot be installed, how can I promote it?”
“Porting and developing software on RISC-V chips requires investment; how can software development be profitable?”
Although the shipment of chips based on the RISC-V instruction set is expected to reach hundreds of billions by 2024, companies promoting RISC-V to downstream customers still face various issues related to cost, business models, compatibility, and toolchains. At the fifth RISC-V China Summit held on July 17, Bao Yungang, Deputy Director of the Institute of Computing Technology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Secretary-General of the RISC-V Open Instruction Ecosystem Alliance, and Chief Scientist at the Beijing Open Source Chip Research Institute, stated that a collaborative development model based on open source can structurally reduce chip development costs while producing high-quality designs and accelerating iteration and verification.

Bao Yungang pointed out that the current RISC-V industry urgently needs to address four issues. First, there is a lack of truly competitive products and solutions, leading to a situation where there is much noise but little action. Second, the toolbox is not rich enough, and it is necessary to quickly achieve a “diverse, fast, good, and economical” effect. For example, in OpenEuler (the open-source Euler operating system), there are over 30,000 software packages for X86 and ARM, while RISC-V has fewer than 3,000. Third, there is a shortage of talent at all levels in chip design, verification, solutions, and technical support, with teaching, materials, training, and certification needing improvement, requiring a large number of talents at various levels. Fourth, there are not enough comprehensive benchmark cases, such as a lack of high-end chip application cases in the server chip and AI chip fields.
To solve the above problems and accelerate the RISC-V industry’s implementation, several perceptions need to change.
First, if RISC-V is only used as a direct replacement for ARM, it will bury its true advantages and fail to leverage the openness and customizability of RISC-V.
Second, the openness of RISC-V enables open-source implementations and open-source toolchains, which can structurally reduce costs and foster new business models. In today’s software field, open-source software has become the norm, such as PC cluster solutions based on the Linux+RedHat model.
Third, RISC-V’s customizability means extreme optimization of hardware and software, combined with agile development to lower development barriers and foster new models. In the future, APP development teams may only need to add two or three chip designers to quickly customize chips based on application scenarios, providing integrated hardware and software solutions.
Fourth, the computational power demand for AI inference is showing new characteristics, and RISC-V+AI will become a new combination in the future. The close collaborative design of AI and CPU will present diverse demands for RISC-V.
Fifth, it is essential to enable software developers to profit. Currently, the profitability of the RISC-V industry is concentrated in chip companies, and ways must be found for software developers to profit.
How can the open-source model represented by RISC-V structurally reduce chip development costs? Taking the development of a 64-core server chip with a production target of 100,000 units as an example, the estimated development cost is about 750 million yuan, with IP licensing fees and royalties accounting for about 35% of the cost. Based on an open-source collaborative development model, the single licensing fee can be reduced to below 10 million yuan, and the proportion of IP costs can be reduced to 2%, saving companies 33% (about 250 million yuan) in R&D expenses. This means that companies can concentrate more funds on solution innovation, which is a new opportunity that RISC-V brings to the industry.
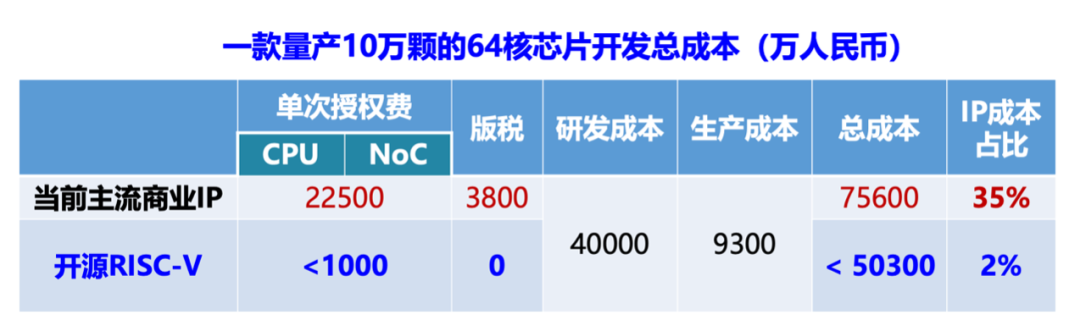
Source: Content from Bao Yungang’s presentation at the fifth RISC-V China Summit
In addition to “cost reduction,” RISC-V can also “increase efficiency”—the open-source collaborative development not only produces high-quality designs but also accelerates iteration and verification. Over the past year, the “Xiangshan” open-source RISC-V processor project has progressed from unit-level testing to integration testing and then to system-level testing, forming over 20,000 test cases, with users and companies contributing nearly 1,600 test cases. The Kunming Lake (the third generation of “Xiangshan”) V2 has completed 1,470 bug discoveries and 1,467 bug fixes, with partner companies participating in open-source collaborative development, submitting a total of 492 bugs.
Bao Yungang stated that in open-source software, 96% of software codebases contain open-source code, with the proportion of open-source code reaching 77%. In future chips, the proportion of open-source IP will surely break through zero, and the proportion of open-source IP will continue to increase. This improvement will lower the costs of the chip design industry, thereby enhancing the competitiveness of enterprises.
Further Reading:Major Changes in End Devices in the AI Era | Can AI Reshape Television Functions? Huang Renxun Answers Questions Today, the Transcript is Here!Author丨Zhang XinyiEditor丨Qiu JiangyongArt Editor丨MariaSupervisor丨Lian Xiaodong
 Click “View” to Stay Connected
Click “View” to Stay Connected