
The 2025 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting grandly opened in Chicago on May 31, lasting for 4 days, with the theme “Driving Knowledge to Action: Building a Better Future,” focusing on the latest research progress and innovative translational achievements in the global cancer treatment field. ADC drugs remain a hot area of focus, with Chinese companies contributing 89 out of 184 selected abstracts and oral presentations (accounting for 48.4%). From early efficacy exploration to pivotal trials, China’s innovative forces are actively exploring new targets or combinations of targets, expanding immunotherapy combination strategies to advance treatment lines, and continuously breaking through indication boundaries, achieving significant progress and breakthroughs in multiple directions. This article will review the main highlights of this ASCO meeting regarding the clinical trial design and translational results of ADC drugs, deeply analyze their scientific value and clinical application potential, aiming to contribute more to the industry development in subsequent CRO work.
Total: 8879 words, 36 figures
Estimated reading time: 30 minutes
Introduction
The 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting once again highlights the important position of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) in the field of cancer treatment. The highlights focus on three dimensions:
-
The maturity and accelerated iteration of various ADC technology platforms, the flourishing of bispecific ADCs and new target ADCs, enhancing the efficacy of clinical precision treatment;
-
Breakthroughs in areas where traditional treatments face bottlenecks, exploring new strategies for difficult-to-treat brain metastases, platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer, and other challenges, with multiple ADCs attempting to expand “ADC+IO” combination therapies, actively extending approved drugs to first-line treatments and broadening indications;
-
The international breakthrough of Chinese innovation forces – among 40 oral presentations related to ADCs, China contributed 11 key studies, with several domestic companies showcasing related products and becoming important participants in the global ADC open wave.
This article will provide an overview of the ADC R&D projects at this conference, focusing on products in critical clinical stages, and systematically sorting out innovative products that have achieved target breakthroughs and completed concept validation. Based on industry frontier trends, focus on the safety characteristics of clinical efficacy data, emerging treatment strategies, and efficacy prediction methods. At the same time, it aims to provide references for colleagues engaged in non-clinical research to conduct translational research from clinical to non-clinical in a “beginning with the end in mind” manner.
★ Article Guide ★
|
01 |
ASCO 2025 – Overview of ADC Projects |
|
02 |
Analysis of ADC Projects in Critical Clinical Trial Stages |
|
03 |
Target Innovation and Concept Validation |
|
04 |
New Trends in ADC Treatment |
|
05 |
Conclusion |
01
ASCO 2025 – Overview of ADC Projects
This year’s ASCO meeting has become the core display platform for ADC R&D progress.
Among all drug categories, 432 oral presentations were made, with ADC-related research accounting for 9.25%, an increase of 48% compared to last year, reflecting unprecedented R&D vitality in this field. This section focuses on the progress of ADC products that are in the R&D stage and not yet on the market, categorized and summarized based on indication areas and targets:
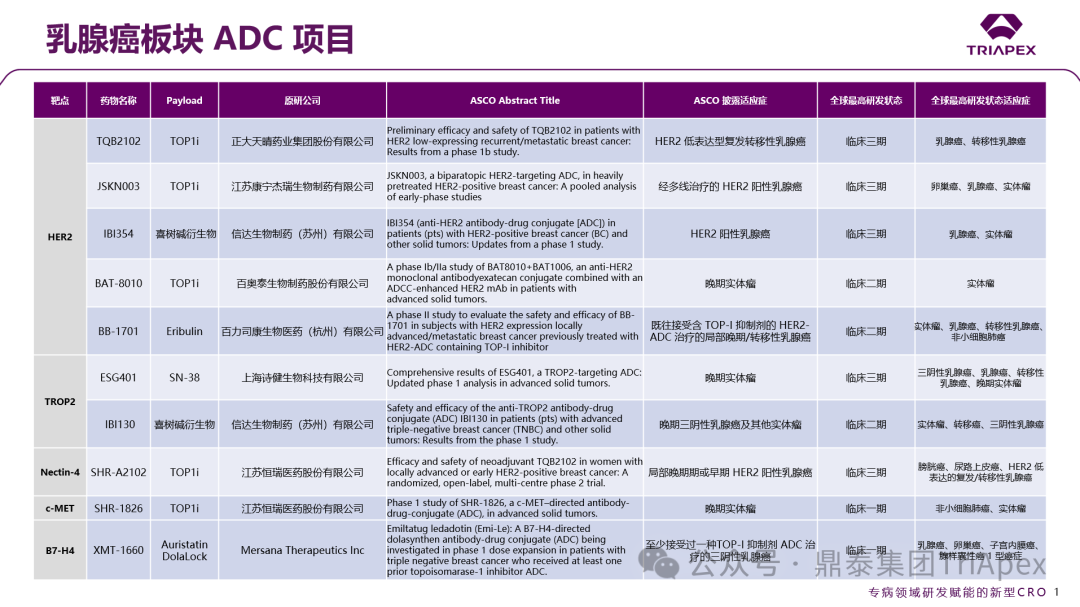
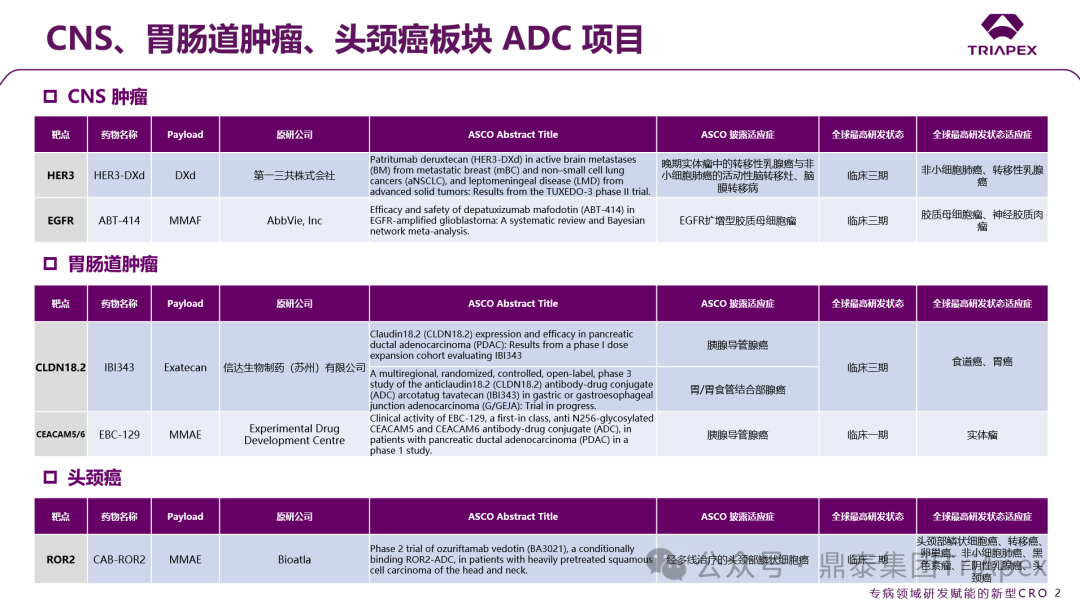
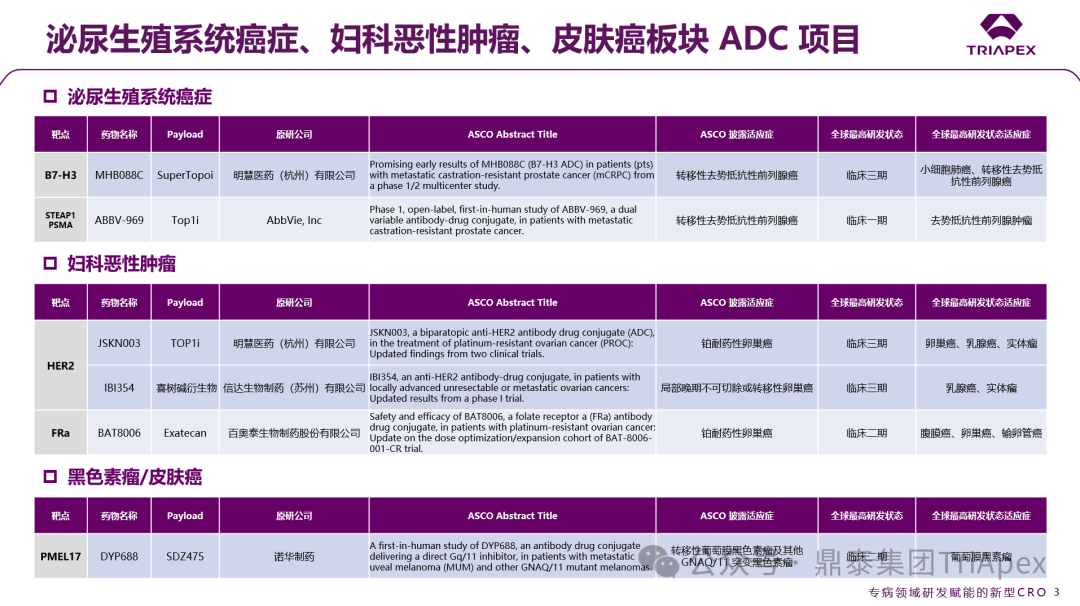
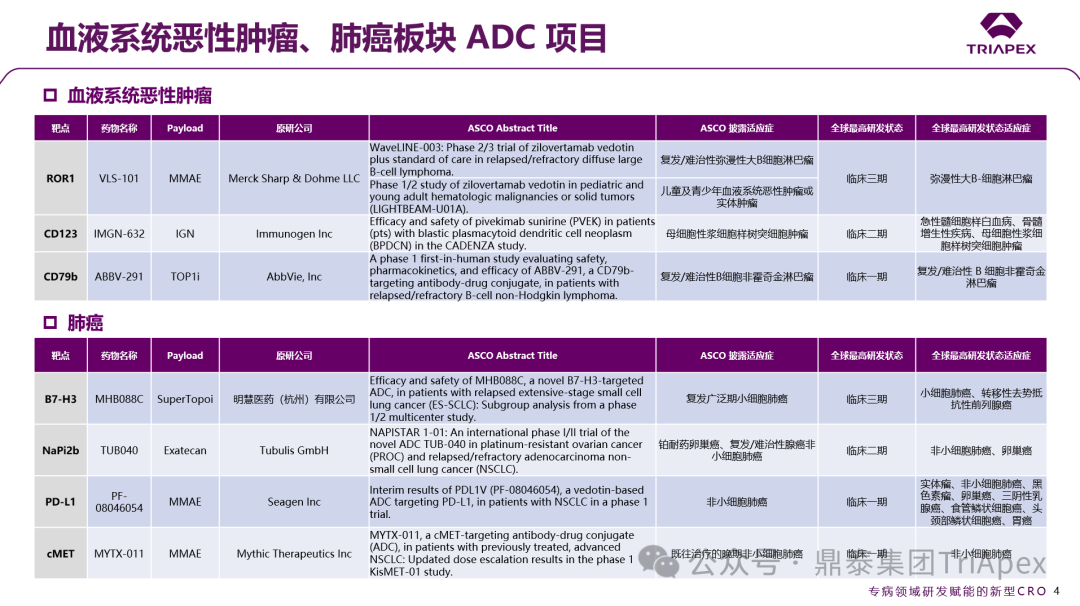
Figure 1. Classification of ADCs based on disease treatment areas
In addition, the conference also specifically established the Developmental Therapeutics category, breaking the traditional classification by organ system and focusing on the study of drug mechanisms of action, concentrating on early clinical exploration of new drugs. This category includes “Basket Trials” (which include patients with different tumor types carrying the same molecular target) and “Umbrella Trials” (which evaluate multiple drugs targeting different molecular targets within a single tumor type), integrating and strengthening the research content of basic tumor biology, providing a more universally applicable translational research communication platform for new targeted drug research. This section also summarizes the ADC projects selected for Developmental Therapeutics at the ASCO conference, aiming to provide a more comprehensive perspective to reflect the current dynamics at the forefront of oncology and new drug R&D trends.
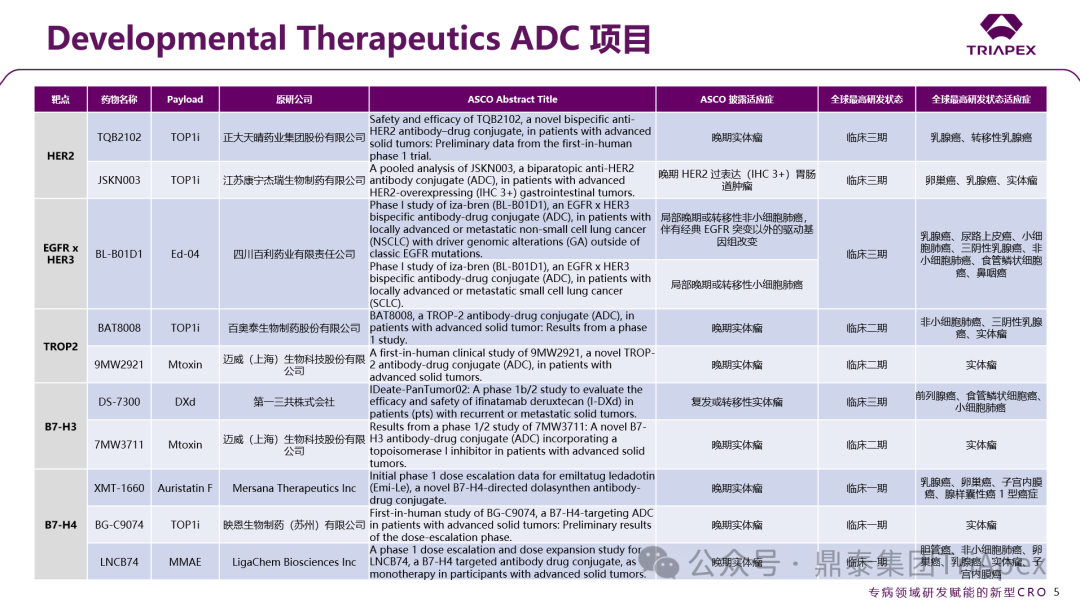
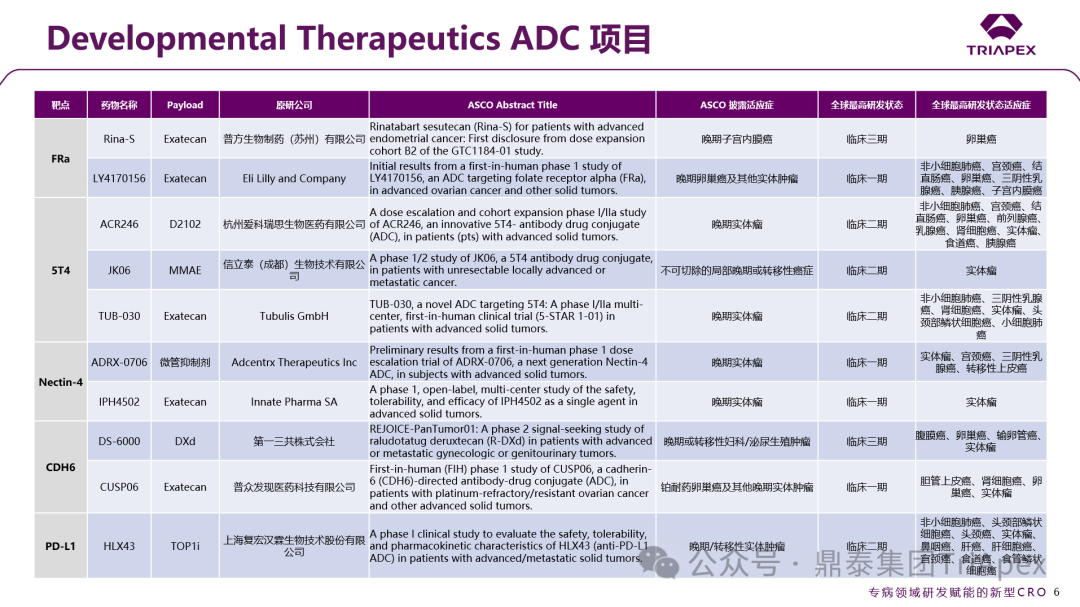
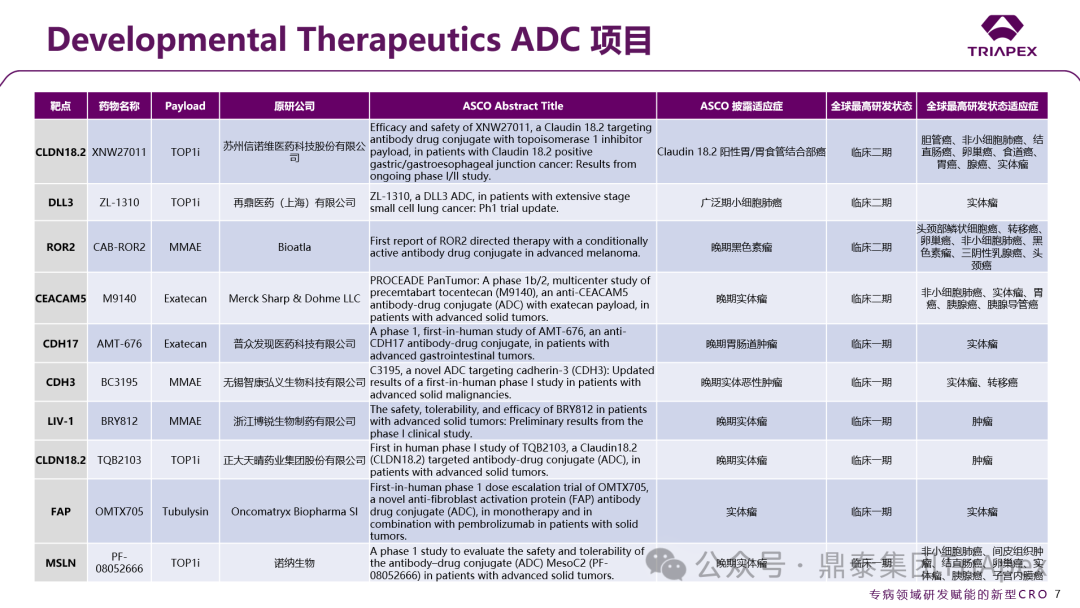
Figure 2. ADC projects under the Developmental Therapeutics category
As global ADC R&D enters deeper waters, Chinese pharmaceutical companies, through multiple breakthroughs in target innovation, technology iteration, and clinical strategy optimization, are gradually transforming from participants to leaders, occupying an important position in the global ADC drug R&D landscape.
Innovative Clinical Strategies Drive Clinical Breakthroughs for Old Target Drugs
According to ASCO, more than 15 ADC projects have entered critical clinical trial stages, covering classic targets such as EGFR/HER3 (Baili Pharmaceutical BL-B01D1), HER2 (Zhengda Tianqing TQB2102), and TROP2 (Innovent IBI130).
Combination Therapies Break Through Treatment Dilemmas for Difficult Subtypes
Based on predictions and solutions for resistance mechanisms, combination therapies (such as ADC+IO, ADC+targeted therapy) provide new options for patients who are ineffective with traditional therapies.
Technology Iteration Achieves Source Innovation
Chinese pharmaceutical companies’ ADC technology platforms are transitioning from “imported improvements” to “source innovation.” Taking the Yilian Biotech TMALIN™ platform as an example, its core breakthrough lies in the tumor microenvironment-responsive linker design, which releases toxins specifically through enzyme control, reducing systemic toxicity. At the 2025 ASCO, the technological achievements of this platform were prominently showcased: Zai Lab’s DLL3 ADC (ZL-1310), Fuhong Hanlin’s PD-L1 ADC (HLX43), and Sinovation’s CLDN18.2 ADC (XNW27011) are all developed based on this platform. Additionally, Yilian’s self-developed pipeline includes YL201 (B7-H3 ADC), YL202 (HER3 ADC), YL205 (Napi2b ADC), and YL242 (VEGF ADC), with the TMALIN™ platform driving 12 ADCs into clinical stages.
The above progress is just the tip of the iceberg of many domestic ADC R&D advancements, but it is enough to demonstrate that China’s ADC R&D has shifted from “catching up” to “running alongside” and has achieved “leading” in some areas. In the future, source innovation and precision treatment will further define the R&D direction of ADCs.
02
Analysis of ADC Projects in Critical Clinical Trial Stages
The number of ADC projects in critical clinical trial stages announced at this ASCO conference is numerous, with several projects showcasing impressive clinical data and potential. Given the limitations of this article’s length and to focus on the theme, we will consider the following two projects based on clinical value, innovation and treatment area focus to conduct in-depth analysis. It should be noted that although projects not discussed in this article also carry significant scientific meaning and provide potential breakthrough directions for unmet clinical needs, it is believed that more ADC projects with significant clinical value will enter the academic spotlight as clinical research progresses.
2.1
Becotatug Vedotin
(Global Highest R&D Status: Application for Market Approval)
Becotatug Vedotin (MRG003) is an ADC drug targeting EGFR independently developed by Lepu Biopharma, and it is the company’s core ADC product with the fastest clinical progress. Early clinical studies have shown that MRG003 is significantly effective in head and neck tumors (especially nasopharyngeal carcinoma). Its phase I/II trial data indicate that for R/M nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients who have failed platinum-based chemotherapy and PD-(L)1 inhibitors, the drug exhibits durable anti-tumor activity.
At this conference, MRG003 was selected for the highly anticipated breakthrough abstract (LBA) due to its phase II pivotal clinical trial (NCT05126719). This study has milestone significance in filling clinical gaps – it is the first to provide an effective treatment option for recurrent/metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients who have failed chemotherapy and PD-(L)1 inhibitors. The following will focus on the trial design, core endpoints, and data results of this study, revealing its scientific value in clinical practice.
Main Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:Histologically or cytologically confirmed nasopharyngeal carcinoma, EGFR expression status not limited; in the recurrent or metastatic stage; previously received at least two lines of chemotherapy and failed anti-PD-(L)1 inhibitor treatment.
Dosing Regimen and Grouping:Randomly assigned to the MRG003 group (2.3 mg/kg, Q3W) and chemotherapy control group – capecitabine (1000 mg/m2, Q3W), docetaxel (75 mg/m2, Q3W); patients in the chemotherapy control group were allowed to cross over to receive MRG003 treatment after disease progression.
Main Endpoints:Objective response rate (ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS), as well as overall survival (OS).
Number of Participants:238 (expected), 172 (completed)
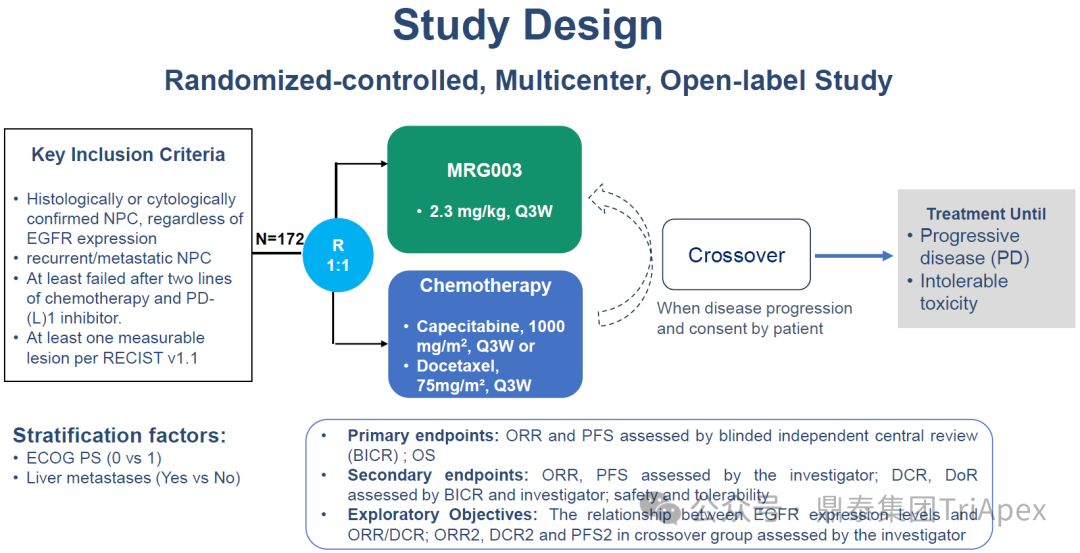
Figure 3. NCT05126719 Clinical Trial Design[1]
Clinical Trial Results
Data Analysis as of June 30, 2024:
-
ORR:Based on blinded independent central review (BICR), the ORR in the MRG003 group reached 30.2%, significantly higher than the chemotherapy group’s 11.5% (nearly a 3-fold increase)
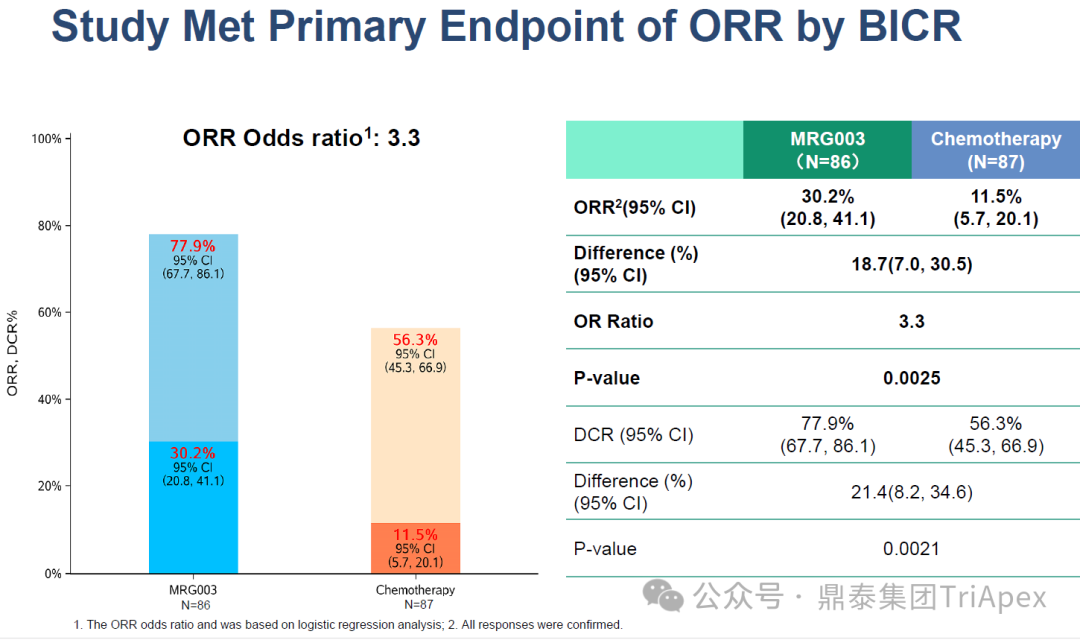
Figure 4. NCT05126719 Main Endpoint ORR Data
-
PFS:The median PFS in the MRG003 group was 5.82 months, extending 105% compared to the chemotherapy group (2.83 months), with a significantly reduced risk of disease progression or death by 37% (HR=0.63; 95% CI 0.44–0.91; P=0.0146)
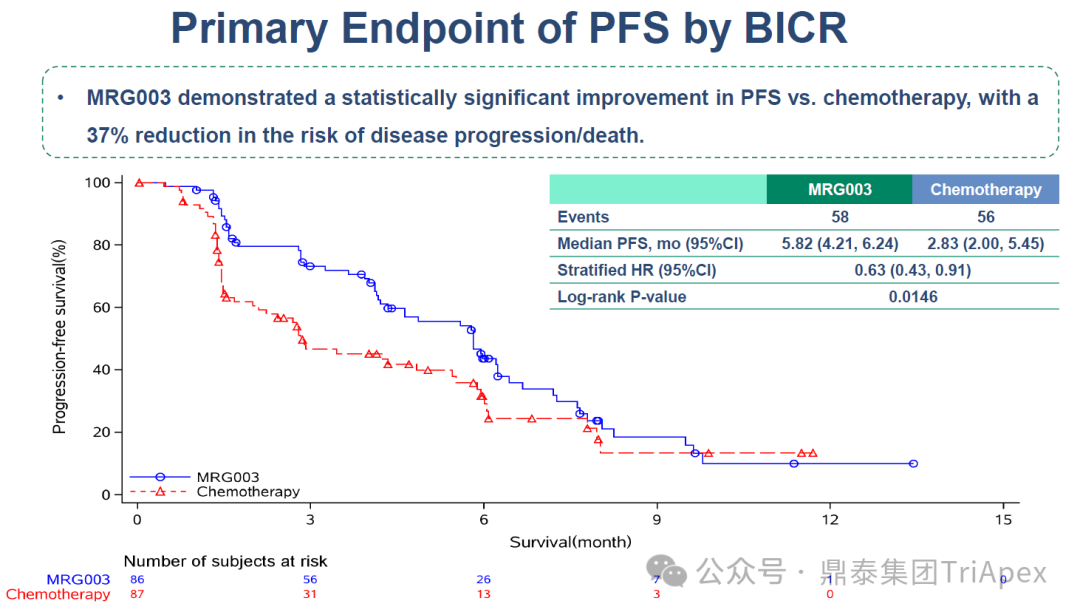
Figure 5. NCT05126719 Main Endpoint PFS Data
As of June 30, 2024
Interim Analysis as of December 30, 2024:
-
OS:The median OS in the MRG003 group was 17.08 months, while the chemotherapy control group was 11.99 months (HR=0.73; 95% CI 0.52–1.03). After adjusting for crossover treatment effects: the risk ratio for OS between the two groups was optimized to 0.59 (95% CI 0.37–0.93), further enhancing the survival benefit trend.
-
Safety Characteristics:The overall incidence of treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) in the MRG003 group was similar to that in the chemotherapy group, with ≥3 grade TRAE incidence: MRG003 group 45.3% vs chemotherapy group 50.6%; most adverse events were grade 1-2, with overall safety being manageable.
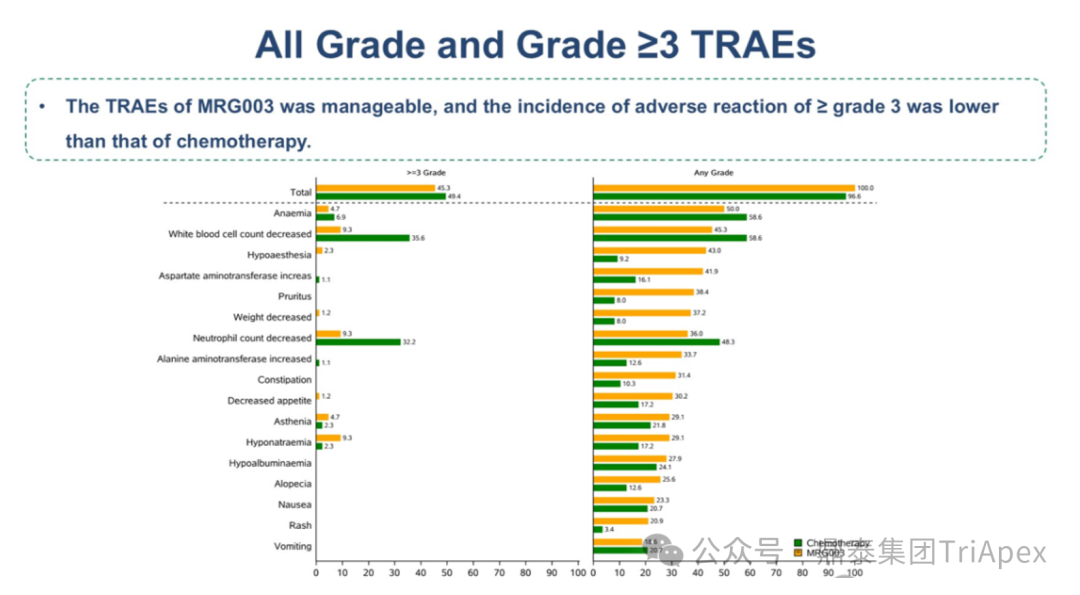
Figure 6. NCT05126719 Safety Characteristics
2.2
Izalontamab brengitecan
(Global Highest R&D Status: Phase III Clinical)
Izalontamab brengitecan (BL-B01D1) is a first-in-class bispecific ADC targeting EGFR/HER3 independently developed by Baili Pharmaceutical. Its innovation lies in its unique bispecific structure, which significantly enhances anti-tumor activity by synergistically blocking the aberrant pro-cancer downstream signaling pathways mediated by EGFR and HER3. The core advantages of BL-B01D1 are reflected in the following aspects: the dual-target design can overcome single-target resistance, significantly improving treatment response rates for EGFR/HER3 co-expressing tumors (such as urothelial carcinoma and triple-negative breast cancer).As the fastest progressing and the only bispecific ADC targeting EGFR/HER3 to enter Phase III clinical trials globally, BL-B01D1 holds an important position in the new generation of ADC R&D and has thus become a benchmark or target for many bispecific ADC drug developments.
As of March this year, BL-B01D1 has simultaneously advanced 9 Phase III pivotal registration clinical trials globally, covering six major high-incidence solid tumor areas: small cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, esophageal squamous carcinoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and urothelial carcinoma. With outstanding clinical value, it has received 3 breakthrough therapy designations (BTD) from the NMPA, covering advanced NSCLC (EGFR mutation/wild type), locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer, and advanced esophageal squamous carcinoma indications. These designations fully reflect its significant clinical value and are expected to accelerate the drug’s market entry in China.
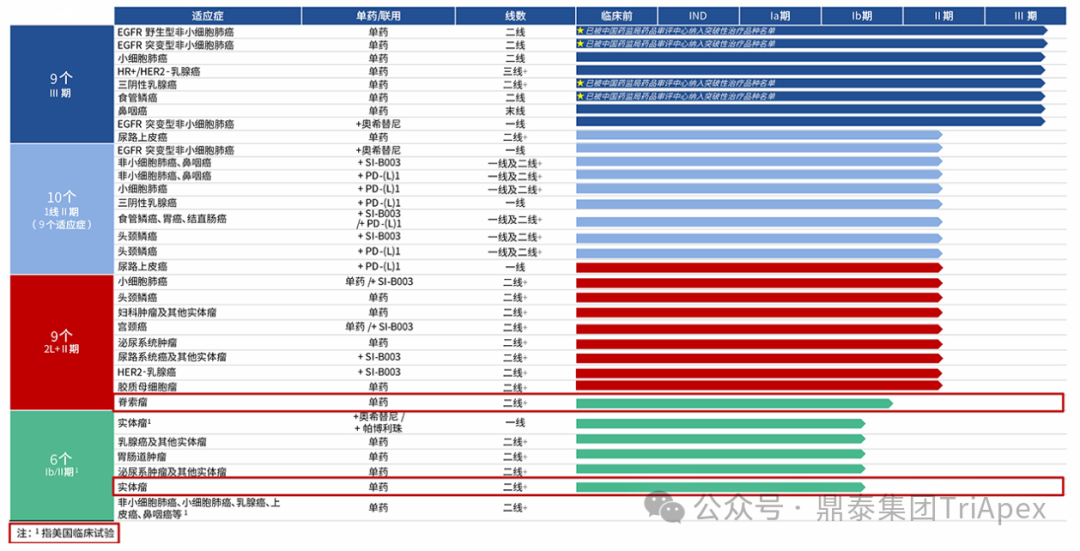
Figure 7. BL-B01D1 Clinical R&D Progress[2]
At this ASCO conference, although not selected for LBA, BL-B01D1 still attracted significant attention and discussion due to its breakthrough data from two Phase I clinical studies.
I. Iza-bren (BL-B01D1) Phase I Study in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with Driver Genomic Alterations (GA) Outside of Classic EGFR MutationsPhase I study of iza-bren (BL-B01D1), an EGFR x HER3 bispecific antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with driver genomic alterations (GA) outside of classic EGFR mutations.
Main Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:Patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations, non-classic EGFR mutations, HER2 mutations, ALK rearrangements, ROS1 rearrangements, BRAF mutations (V600E and others), KRAS mutations (G12C and others), SMARCA4 mutations, MET exon 14 skipping mutations, RET fusions, and NTRK fusions; disease progression after standard targeted therapy; ≤1 line of prior chemotherapy.
Dosing Regimen and Grouping:2.5 mg/kg; D1, D8, Q3W
Main Endpoints:Safety
Number of Participants:96 (expected), 83 (completed)
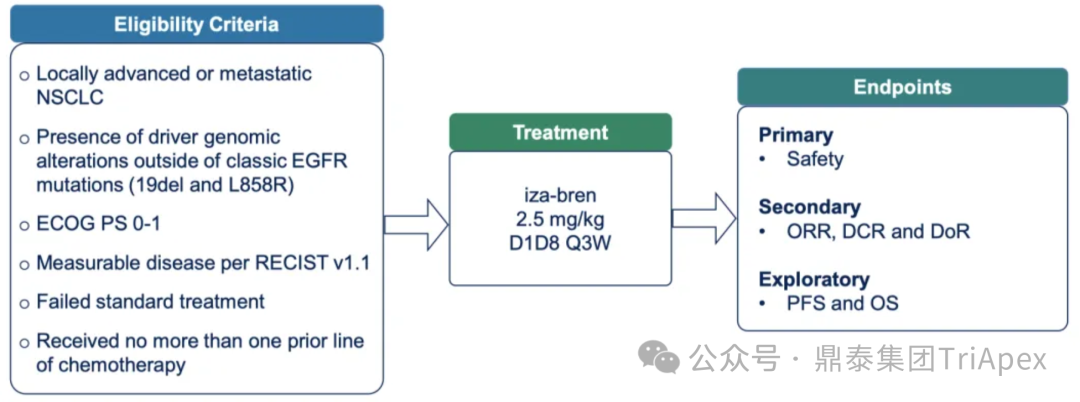
Figure 8. NCT05194982 Clinical Trial Design[3]
Clinical Trial Results
Efficacy Highlights:The drug exhibits deep and durable anti-tumor activity in advanced NSCLC patients with various driver gene alterations.
-
Overall Population:ORR 46.2% (confirmed ORR 39.7%), disease control rate (DCR) 85.9%; median duration of response (DoR) not reached, PFS was 7.0 months, OS data not reached.
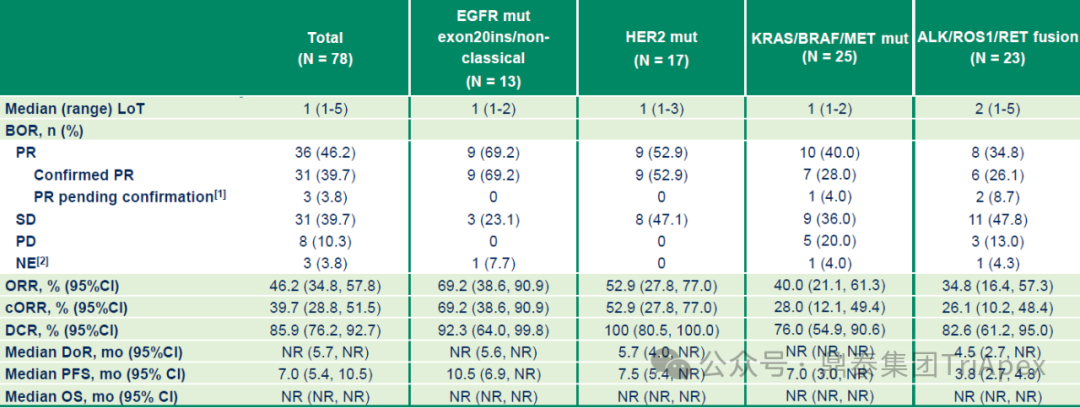
Figure 9. NCT05194982 Overall Subject Population Efficacy Data
-
Key Subgroup:
-
EGFR exon 20 insertion/non-classic EGFR mutations:confirmed ORR (cORR) 69.2%, DCR 92.3%; median DoR not reached, median PFS reached 10.5 months.
-
HER2 mutations:cORR 52.9%, DCR 100%; median DoR 5.7 months, median PFS 7.5 months.
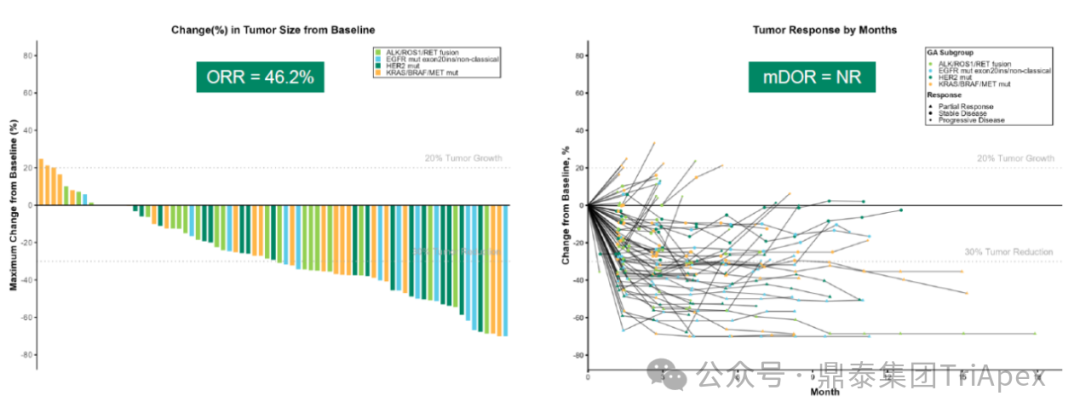
Figure 10. NCT05194982 Tumor Treatment Response Characteristics
-
Safety Characteristics:Good treatment tolerance, with a low incidence of ≥3 grade TRAEs (2.4% discontinuation rate), severe TRAEs primarily related to hematological toxicity, effectively controlled through dose adjustments and supportive treatment.
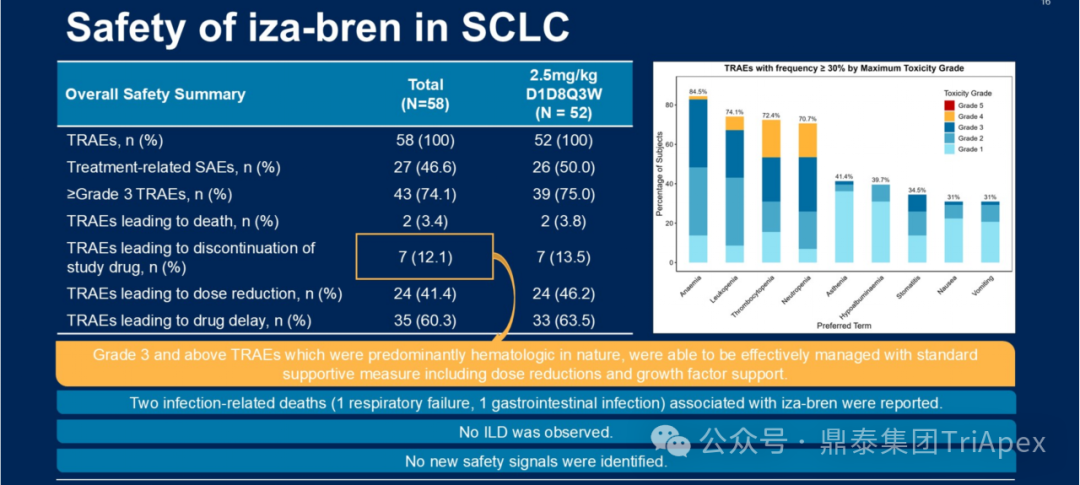
Figure 11. NCT05194982 Safety Characteristics
II. EGFR×HER3 Bispecific ADC Drug Iza-bren (BL-B01D1) Phase I Study in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)Phase I study of iza-bren (BL-B01D1), an EGFR x HER3 bispecific antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), in patients with locally advanced or metastatic small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Main Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:Locally advanced or metastatic small cell lung cancer (SCLC) or other solid tumors; ECOG performance status score 0-1; measurable lesions according to RECIST v1.1 standards; previous standard treatment failure or no feasible treatment options.
Dosing Regimen and Grouping:
Escalation phaseGroup A (D1, D8, Q3W): 2.0 mg/kg → 2.5 mg/kgGroup B (D1 Q3W): 4.5 mg/kg → 5.0 mg/kg
Expansion phase determined dose2.5 mg/kg (D1, D8, Q3W)
Main Endpoints:Dose-limiting toxicity (DLT), maximum tolerated dose (MTD), and recommended phase II dose (RP2D)
Number of Participants:96 (expected), 58 (completed)
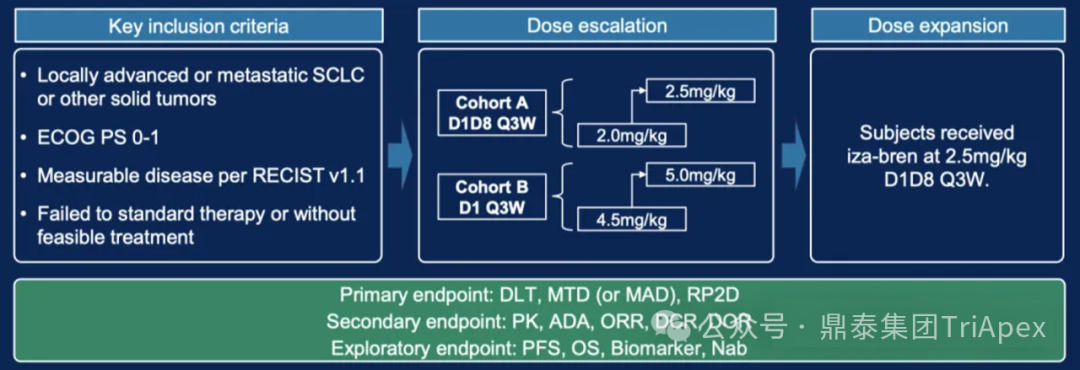
Figure 12. NCT05194982 Clinical Trial Design[4]
Clinical Trial Results
Efficacy Highlights:Despite the poor prognosis and limited treatment options for SCLC patients, and the lack of positive survival benefits in clinical research over the past 30 years, BL-B01D1 still demonstrates significant therapeutic value in patients who have previously received irinotecan treatment.
-
Efficacy Analysis (2.5 mg/kg D1D8 Q3W Regimen):
With a median follow-up of 16.4 months, the overall population (n=52) receiving this dose showed significant anti-tumor activity:
-
Objective response: ORR 55.2% (cORR 44.8%), DCR reached 81.0%
-
Survival benefit: median DoR 4.6 months, median PFS 4.0 months, median OS 12.0 months
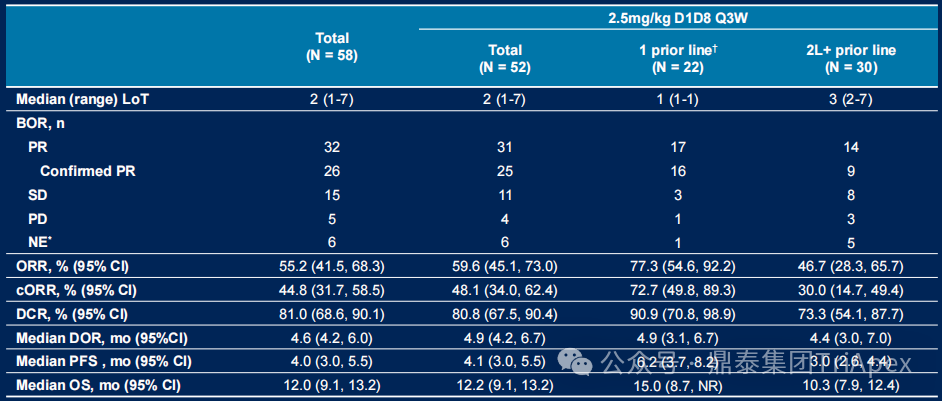
Figure 13. NCT05194982 Efficacy Analysis Data
-
Key Subgroup Efficacy Characteristics:
Patients who previously received only first-line PD-(L)1 inhibitor combined with platinum-based chemotherapy (n=20)
-
Showed a higher response rate: ORR 80.0% (cORR 75.0%), DCR 90.0%
-
Improved survival outcomes: median DoR 5.6 months, median OS extended to 15.0 months
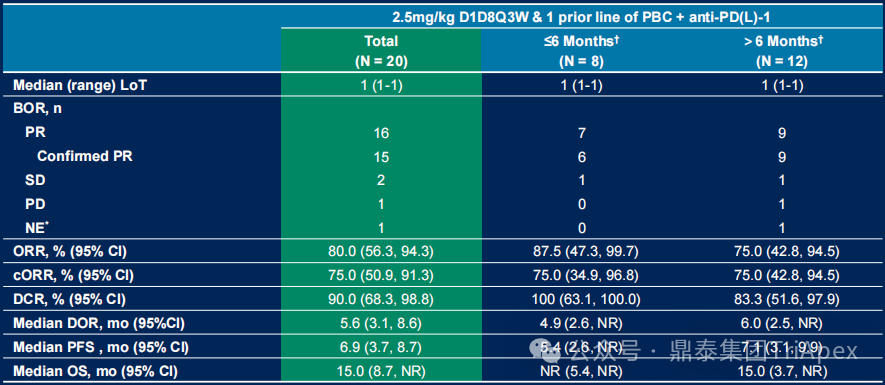
Figure 14. NCT05194982 Efficacy Data for Patients Previously Treated with First-Line PD-(L)1 Inhibitor Combined with Platinum-Based Chemotherapy
Analysis by Irinotecan Treatment History
-
Previously Treated Group (n=19):ORR 42.1%, DCR 68.4%, median DoR 5.7 months, median OS 10.3 months;
-
Untreated Group (n=33):ORR 69.7%, DCR 87.9%, median DoR 4.9 months, median PFS 5.4 months, median OS 12.9 months
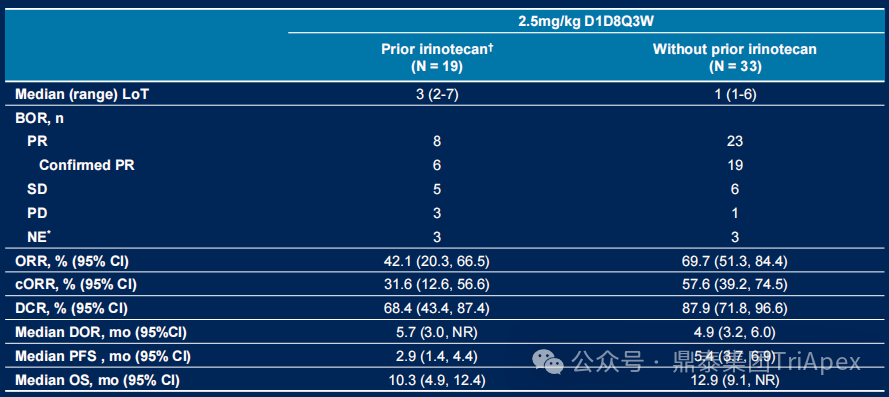
Figure 15. NCT05194982 Efficacy Data by Irinotecan Treatment History
-
Safety Characteristics:
≥3 grade TRAEs were primarily hematological toxicity (mainly neutropenia-related events), effectively controlled through symptomatic supportive treatment measures and dose adjustments, with a TRAE discontinuation rate of 12.1%.

Figure 16. NCT05194982 Safety Characteristics
03
Target Innovation and Concept Validation
This ASCO meeting also witnessed the expansion and transformation of the ADC target landscape.
In addition to traditional targets (such as HER2, TROP-2, EGFR), a number of emerging therapeutic targets such as FRα, CDH6, SEZ6, LIV-1, FAP, and PMEL17 are accelerating into clinical validation stages. Taking the FRα target as an example, there is currently only one ADC product, Elahere, approved globally, with 10 ongoing projects in clinical stages: Pufang Biotech’s Rina-S has entered Phase III clinical trials for platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer, Baiyoutai BAT8006 focuses on Phase II optimization, and Eli Lilly LY4170156 is exploring multiple cancer types in early stages.
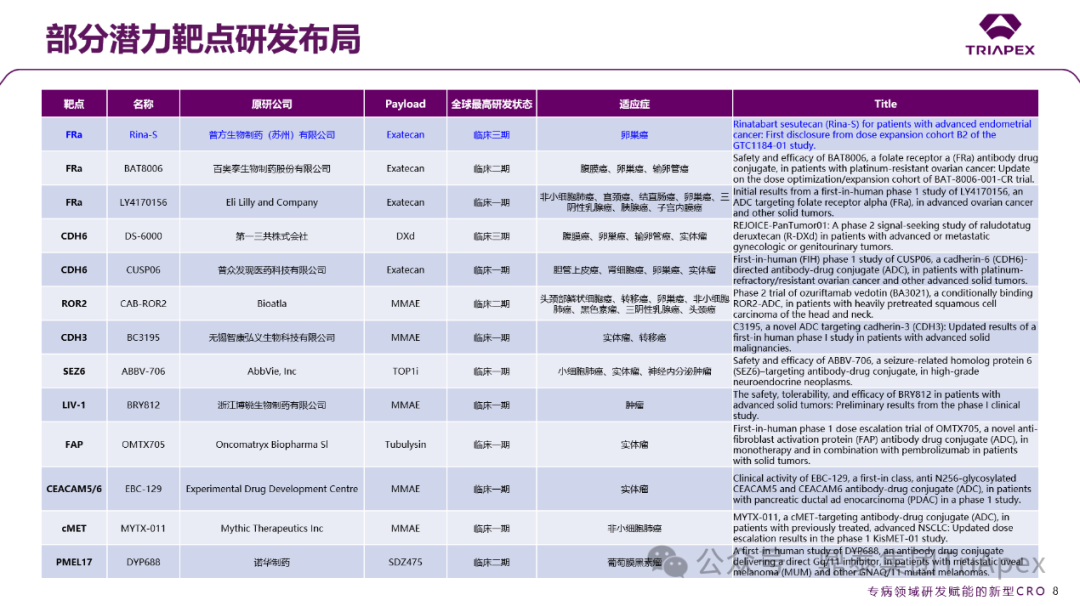
Figure 17. Summary of Potential Target R&D Layouts Announced at ASCO
The number of concept validation (Prove-of-Concept) projects announced at the conference is considerable. Considering that these early clinical projects have relatively few enrolled patients, with indications often being pan-tumor types and varying patient selection criteria, there is significant uncertainty in later clinical development. Therefore, I will focus on the Rina-S project, which has entered Phase III and announced its I/II phase data at this conference.
For patients with advanced endometrial cancer who have failed treatment with PD-(L)1 inhibitors combined with chemotherapy, existing single-agent chemotherapy regimens often have ORRs below 16%, with median PFS often less than 5 months, indicating poor prognosis and a lack of treatment options. In response to this dilemma, Rina-S has emerged, and its I/II clinical RAINFOL-01 (NCT05579366) efficacy data gradually confirms its “best-in-class” potential, and the following will analyze the trial design and results of RAINFOL-01:
Main Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:Histologically or cytologically confirmed metastatic or unresectable endometrial cancer patients; previously received platinum-based chemotherapy and PD-(L)1 inhibitor treatment
Dosing Regimen and Grouping:100 mg/m² (n=22) or 120 mg/m² (n=21)
Main Endpoints:Safety and tolerability
Number of Participants:529 (expected), 43 (completed)
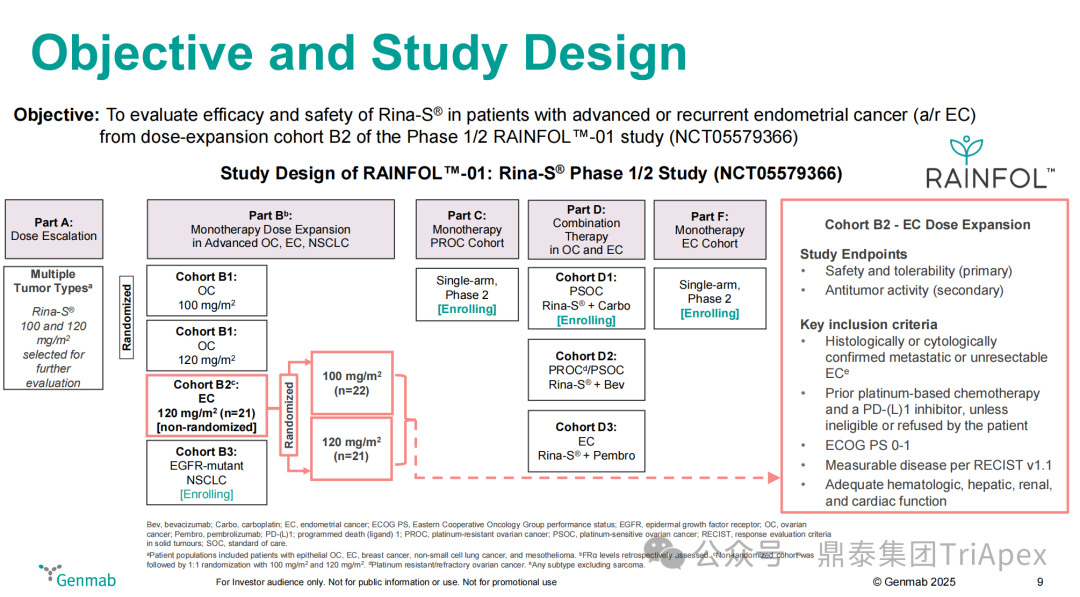
Figure 18. NCT05579366 Clinical Trial Design[5]
Clinical Trial Results
-
Efficacy Data:The 100 mg/m² dose group showed significant advantages, with a DCR of 100%, while the 120 mg/m² group was 81.8%; the DoR was similar between the two groups, with the 100 mg/m² group at 81.8% and the 120 mg/m² group at 80.0%, with no significant impact of dose on response durability.
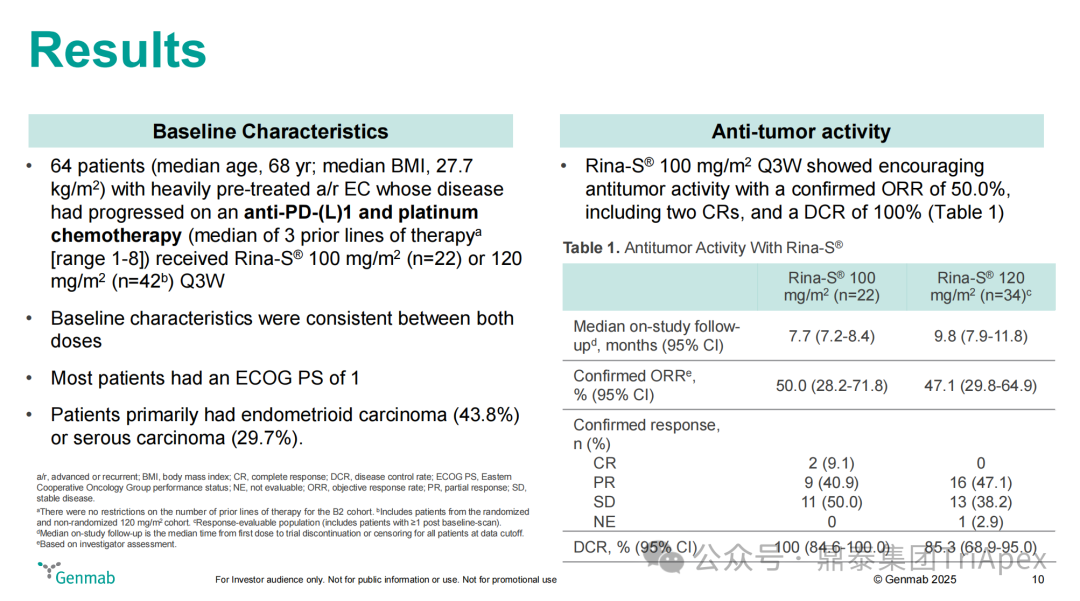
Figure 19. NCT05579366 Clinical Trial Results and Data
-
Safety Data:The common adverse event characteristics were consistent between the two dose groups; severe toxicities were concentrated in the high-dose group, with grade 3-4 TEAEs exceeding 75% – 100 mg/m² group 77.2%, 120 mg/m² group 76.1%, but the incidence of serious adverse events (SAEs) in the 120 mg/m² group was 50%, higher than the 100 mg/m² group’s 31.8%; no specific toxicity signals were observed – ocular toxicity, neuropathy, interstitial lung disease.
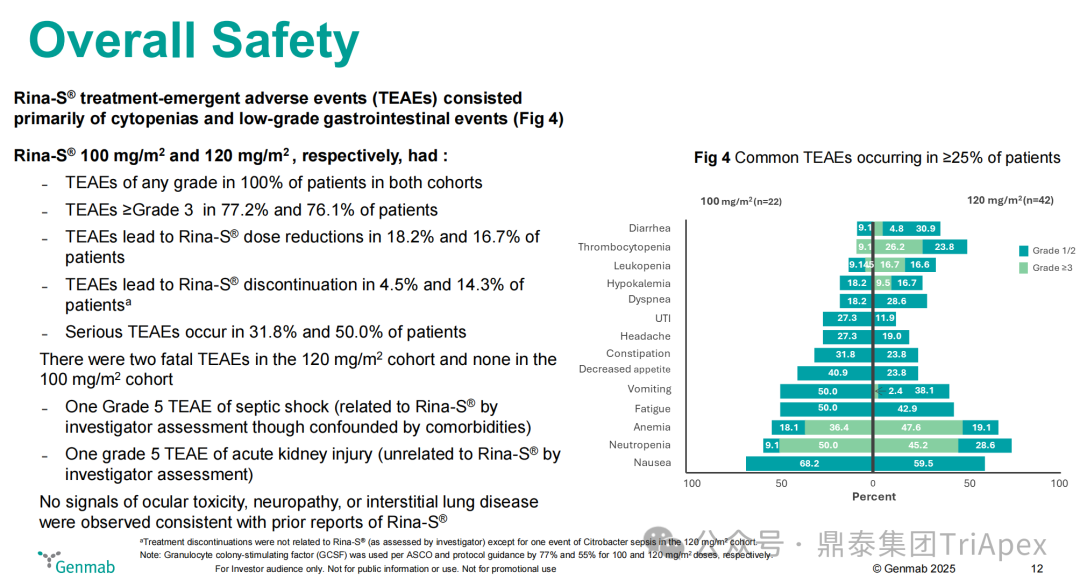
Figure 20. NCT05579366 Safety Characteristics
In summary, the development of new targets and target combinations has brought significant breakthroughs to the ADC treatment field, especially demonstrating great potential in addressing unmet clinical needs. Compared to the highly competitive landscape of mature targets, the exploration of new targets not only helps avoid excessive concentration of R&D resources but also hopes to provide patients with more diverse treatment options. However, like other treatment modalities, the development of emerging target ADC drugs also faces specific clinical challenges: although they can somewhat avoid “red ocean” competition, their biological characteristics are not yet fully elucidated, and the verification of clinical treatment benefits still requires more data support. For example, the CDH17 target has become one of the ideal ADC candidate targets due to its high expression in 90% of colorectal cancers, but its hidden expression in normal tissues also suggests potential off-target toxicity. Additionally, many seemingly ideal targets perform excellently in laboratory studies but often fail to translate successfully into clinical development due to differences between preclinical models and actual patient responses (Translational gap).
Clinical Trial Results
Data Analysis as of June 30, 2024:
-
ORR:Based on blinded independent central review (BICR), the ORR in the MRG003 group reached 30.2%, significantly higher than the chemotherapy group’s 11.5% (nearly a 3-fold increase)
Fortunately, the charm of new drug development lies precisely in the courage to try and explore when risks can be foreseen. As previously mentioned, Becotatug Vedotin and Izalontamab Brengitecan demonstrate that some seemingly difficult-to-develop ADC targets (such as EGFR) also have a very high potential for drug development. Five years ago, few believed that monoclonal or bispecific ADCs targeting EGFR could achieve clinical application.
04
New Trends in ADC Treatment
4.1
Potential of ADC+IO Combination Therapy and Advancement of Treatment Lines
Since the approval of two milestone PD-1 inhibitors – Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab – in 2014, dozens of indications have subsequently received regulatory approval. However, single-agent antibody therapies generally face limited efficacy and patients are prone to drug resistance and relapse.
To break through this bottleneck, combination therapies based on tumor immunotherapy (IO) have gradually become an important trend in industry development in recent years, showing significant potential in clinical research. At this year’s ASCO meeting, the ADC+IO combination therapy strategy received considerable attention. Several companies, including Daiichi Sankyo, Merck, AstraZeneca, Hengrui Medicine, Rongchang Biopharma, Kelun-Botai, and Maiwei Biopharma, announced Phase II-III clinical data of their self-developed ADC products combined with PD-1 monoclonal antibodies, many of which demonstrated excellent therapeutic effects. Here, we also summarize the ADC+IO combination therapy projects:
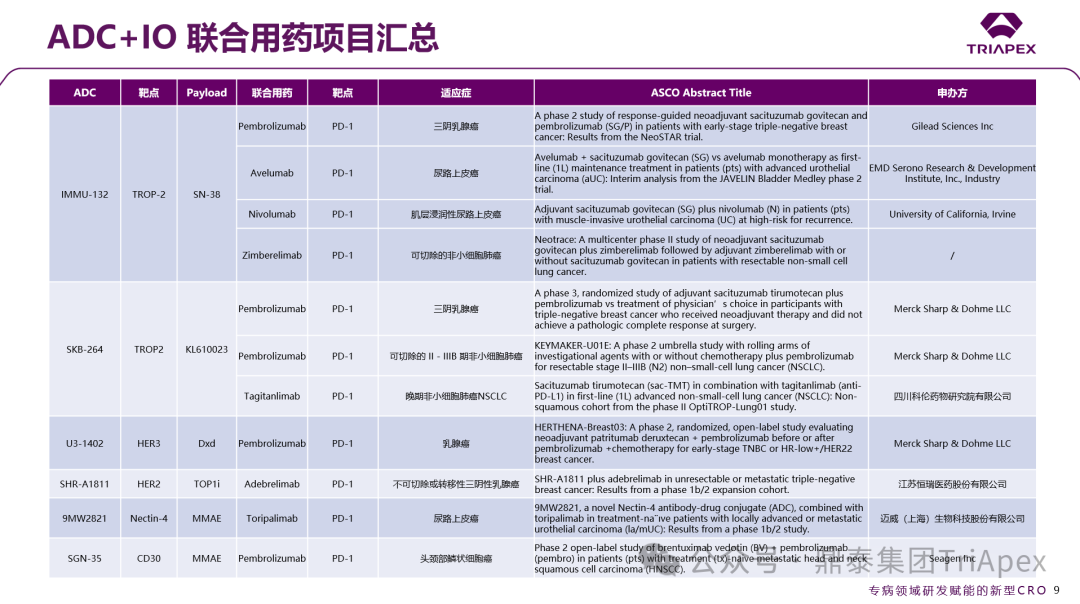
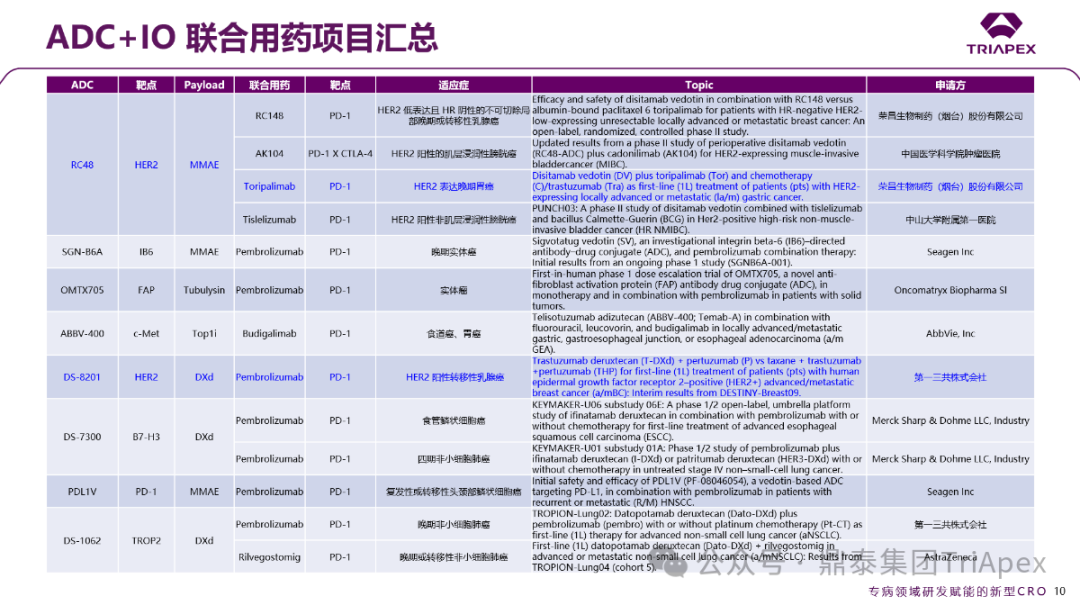
Figure 21. Summary of ADC+IO Combination Therapy Projects
Here, we focus on the study of the combination of DS-8201 (T-DXd) and Pembrolizumab in the DESTINY-Breast09 trial. This Phase III clinical study is the first to use T-DXd combined with Pembrolizumab as a first-line treatment for HER2-positive advanced breast cancer (HER2+mBC), successfully challenging the previous first-line standard treatment – taxane combined with trastuzumab and pertuzumab (THP regimen), and was selected for the conference LBA. Notably, T-DXd was previously only approved for second-line and above treatments, and this marks its first exploration into the first-line treatment field. This advancement in treatment lines requires clinical trial designs to validate efficacy while precisely managing the safety risks of de-chemotherapy regimens. To this end, the study adopted a three-arm random design (T-DXd+Pembrolizumab vs. THP vs. T-DXd monotherapy), and the following will systematically elaborate on the trial design and clinical data:
Main Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:Patients with HER2-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer; asymptomatic/non-active brain metastases allowed; previous first-line endocrine therapy during the metastatic stage allowed; no prior systemic treatment history for metastatic breast cancer
Dosing Regimen and Grouping:Randomly assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive T-DXd+placebo (T-DXd group), T-DXd+pertuzumab (T-DXd+P group), and THP (THP group) standard treatment regimens
Main Endpoints:PFS assessed by blinded independent central review (BICR)
Number of Participants:1157
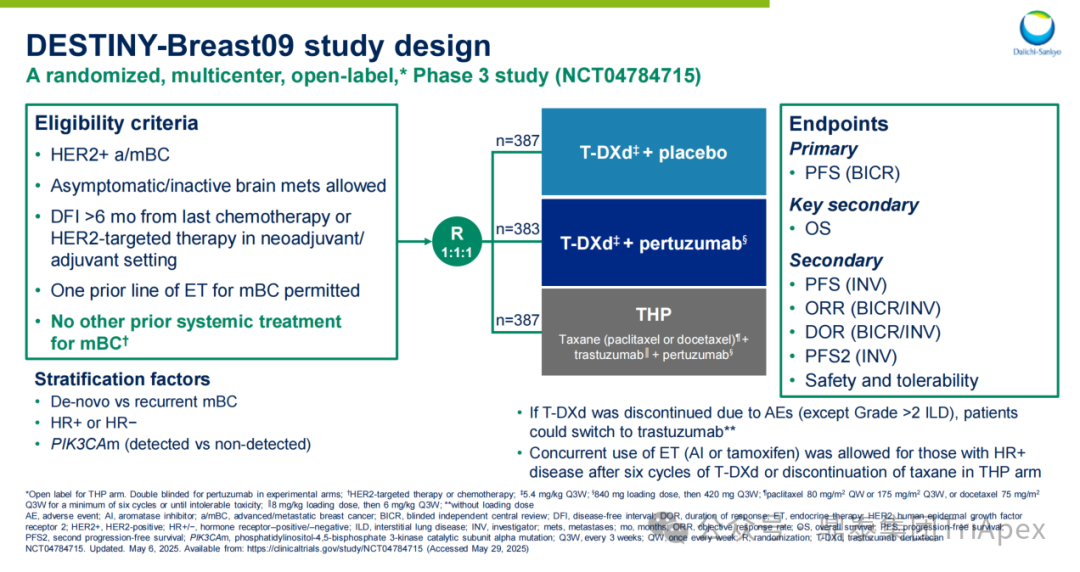
Figure 22. NCT04784715 Clinical Trial Design[7]
Clinical Trial Results
-
Median PFS Rate:T-DXd+P group: 40.7 months; THP group: 26.9 months; absolute benefit: 13.8 months (HR=0.56; 95% CI 0.44-0.71; P<0.00001), reducing the risk of disease progression or death by 44%
-
2-Year PFS Rate:T-DXd+P group 70.1%; THP group 52.1%
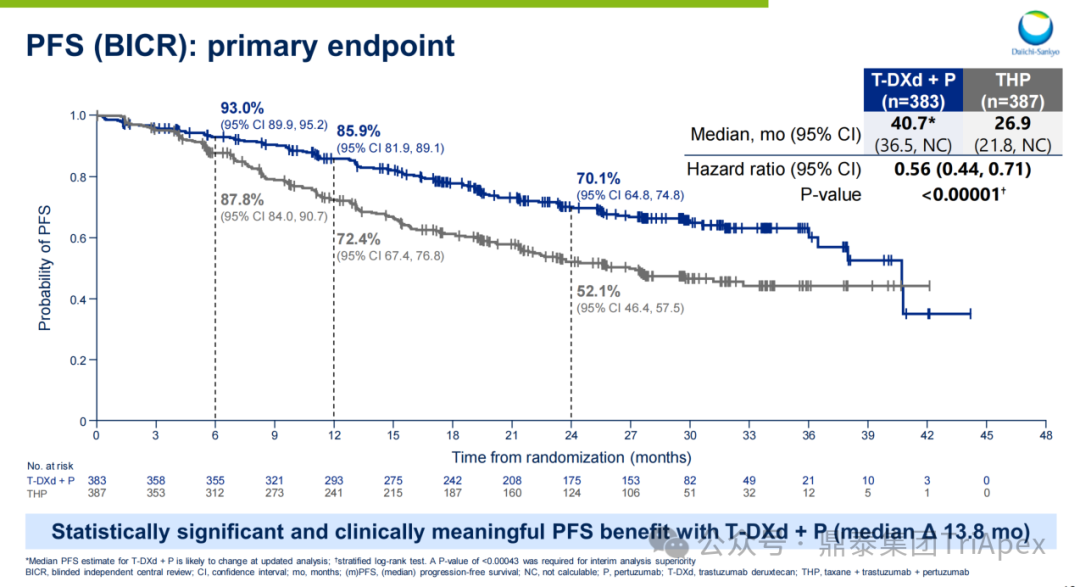
Figure 23. NCT04784715 Main Endpoint PFS
-
Subgroup Analysis:All pre-specified subgroups (including prior treatment history, HR status, PIK3CA mutation status) showed that the PFS of the T-DXd+P group was superior to that of the THP group
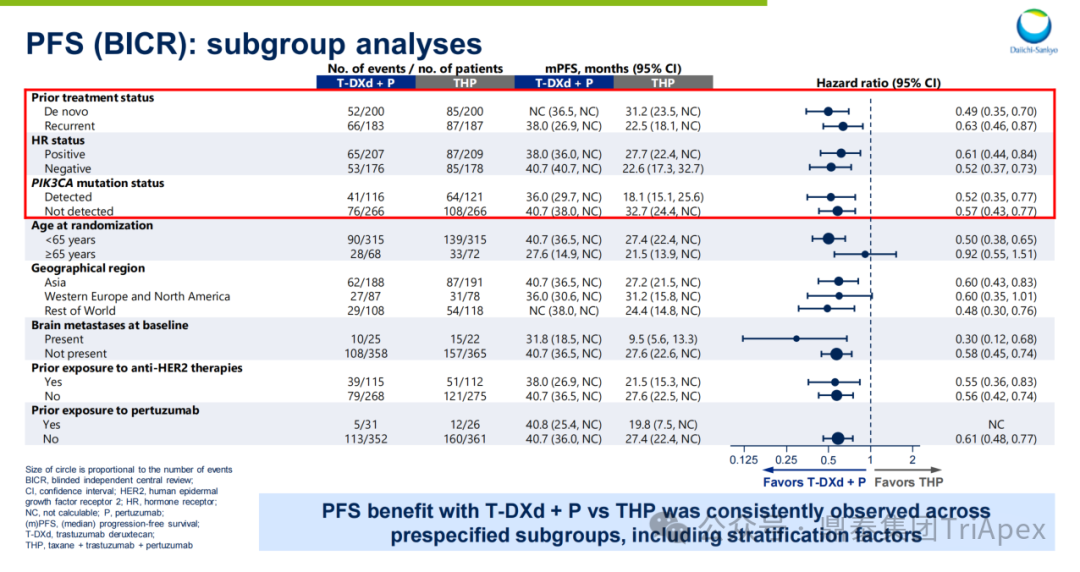
Figure 24. NCT04784715 PFS Subgroup Data Analysis
-
Treatment Duration:The median treatment time in the T-DXd+P group reached 21.7 months, significantly longer than the THP group’s 16.9 months (extended by 4.8 months)
-
Treatment Termination Rate:The proportion of treatment termination due to TEAEs in the T-DXd+P group was 20.7%, lower than the THP group’s 28.3%
-
Safety Consistency:The incidence of severe TEAEs was 27.0% in the T-DXd+P group, and 25.1% in the THP group, with no significant difference; the AEs in the T-DXd+P group were consistent with those in previous studies of both drugs, with no new safety signals identified.
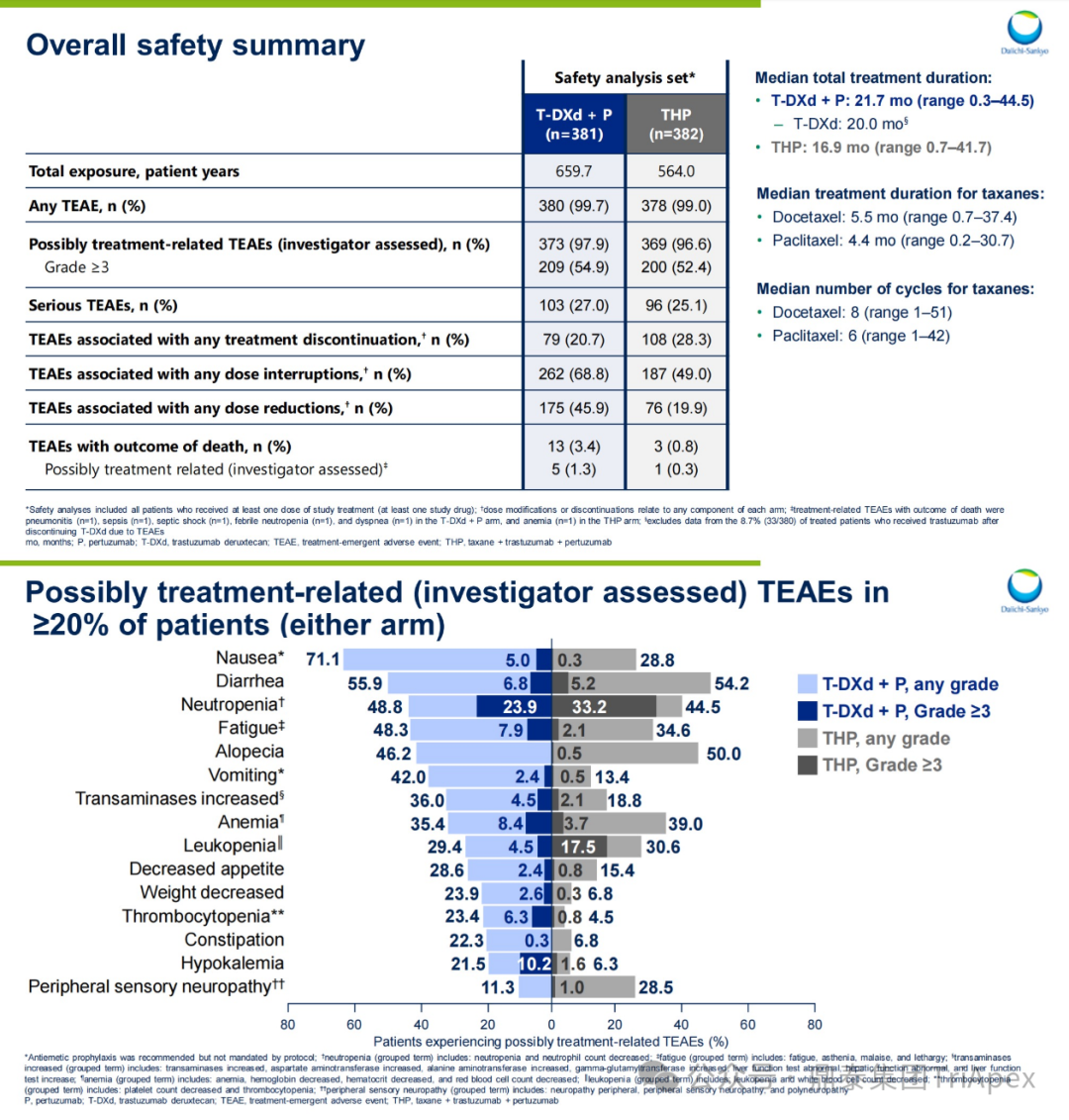
Figure 25. NCT04784715 Safety Characteristics
Another study selected for LBA was from Rongchang Biopharma, evaluating Disitamab vedotin (RC48) combined with toripalimab and chemotherapy or trastuzumab regimen for first-line treatment of HER2-expressing locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer (NCT05980481). Previously, RC48 was only approved for second-line and later treatments, and this study also marks the first time RC48 has moved its treatment line forward to first-line.
Main Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:Histologically or cytologically confirmed unresectable locally advanced/metastatic gastric/gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma; no prior systemic chemotherapy for this cancer; HER2 overexpression cohort: IHC 3+ or IHC 2+/FISH+; HER2 intermediate/low expression cohort: IHC 2+/FISH- (intermediate expression) or IHC 1+ (low expression)
Dosing Regimen and Grouping:
HER2 high expression patients are randomly divided into 3 groups:
-
Experimental Group 1:RC48 (2.5 mg/kg) + toripalimab + CAPOX chemotherapy (oxaliplatin 130 mg/m2 + capecitabine 1000 mg/m2)
-
Experimental Group 2:RC48 (2.5 mg/kg) + toripalimab + trastuzumab (no chemotherapy regimen)
-
Control Group:toripalimab + trastuzumab + CAPOX chemotherapy
HER2 intermediate/low expression patients:
Phase 1 –Patients are randomly divided into two groups:
-
Experimental Group 1:RC48 (2.5 mg/kg) + toripalimab + CAPOX chemotherapy
-
Control Group 1:toripalimab + CAPOX chemotherapy
Phase 2 (Dose Optimization) –Based on Phase 1 safety data, patients are randomly divided into three groups:
-
Experimental Group 2:RC48 (2.5 mg/kg) + toripalimab + CAPOX chemotherapy (oxaliplatin 100 mg/m2 + capecitabine 750 mg/m2)
-
Experimental Group 3:RC48 (2.0 mg/kg) + toripalimab + CAPOX chemotherapy (oxaliplatin 100 mg/m2 + capecitabine 750 mg/m2)
-
Control Group 2:toripalimab + CAPOX chemotherapy
Main Endpoints:ORR
Number of Participants:144
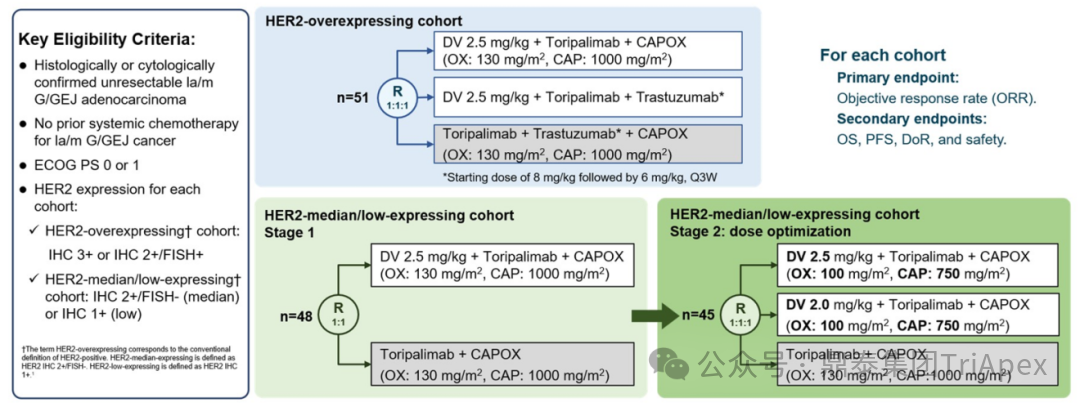
Figure 26. NCT05980481 Clinical Trial Design[8]
Clinical Trial Results
-
Efficacy Data:
HER2 high expression patients:In Experimental Group 2, the ORR reached 82.4%, the best among previous single-agent combined immunotherapy and targeted therapy for first-line treatment of gastric cancer; median follow-up time 13.2 months
HER2 low expression patients:
-
Phase 1: Experimental Group 1 ORR was 70.8%; compared to Control Group 1, median PFS was 9.9 months vs 7.2 months (HR=0.69), indicating significant benefits for the experimental group
-
Phase 2: Experimental Group 2 ORR reached 76.9%
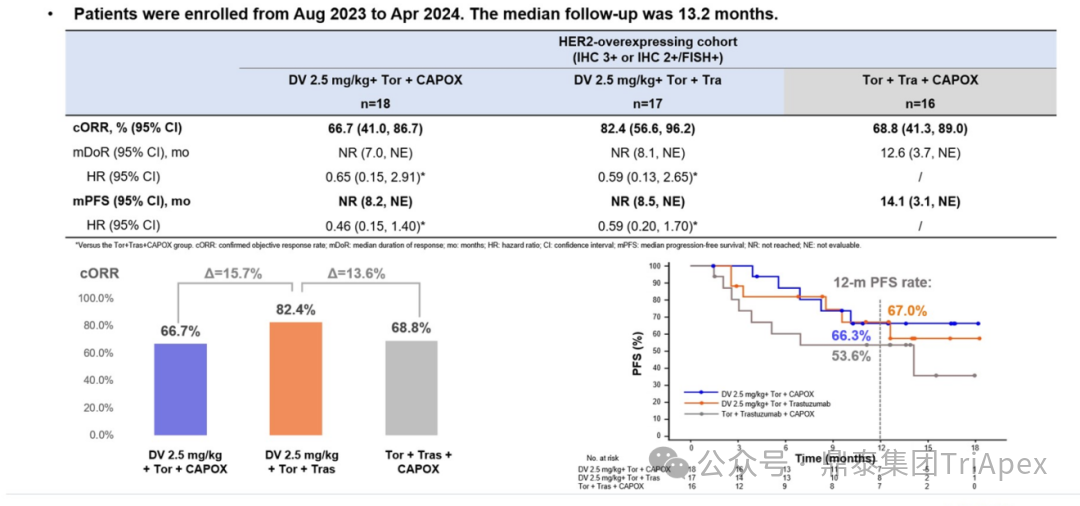
Figure 27. NCT05980481 Efficacy Data for HER2 High Expression Patients
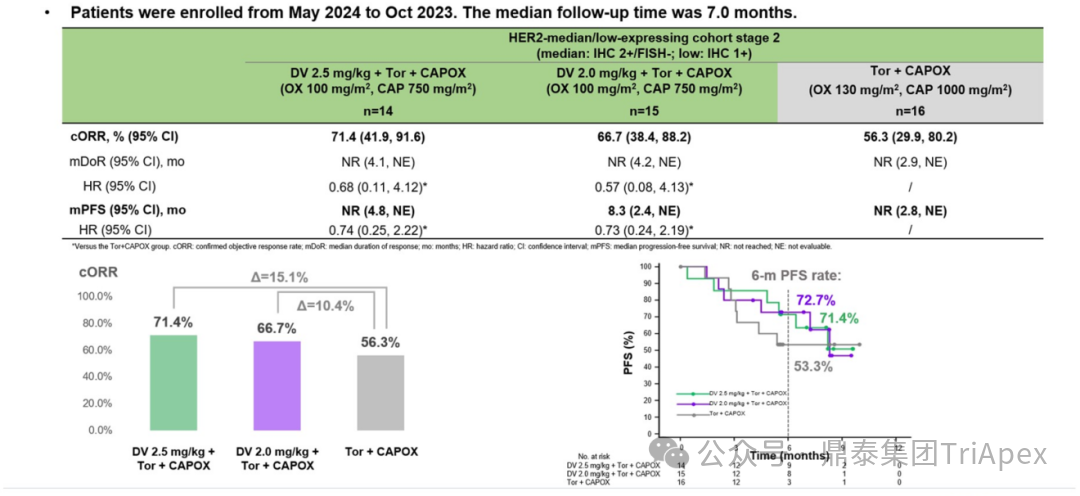
Figure 28. NCT05980481 Efficacy Data for HER2 Intermediate/Low Expression Patients in Phase 1

Figure 29. NCT05980481 Efficacy Data for HER2 Intermediate/Low Expression Patients in Phase 2
4.2
Attempts at Neoadjuvant Therapy
In the field of solid tumor treatment, neoadjuvant therapy serves as a preoperative systemic treatment plan, playing a key role in improving surgical resection rates and patient survival outcomes. In recent years, with the rapid development of ADC drugs and gradual breakthroughs in later-line treatments, there is a trend towards optimizing and innovating the application model of traditional chemotherapy regimens, promoting neoadjuvant therapy towards a more “de-escalated and less toxic” precision and individualized direction.
The 2025 ASCO meeting further witnessed groundbreaking attempts of ADCs in neoadjuvant therapy, represented by Zhengda Tianqing’s HER2 bispecific ADC TQB2102, which showed promising potential in a Phase II trial (NCT06198751) targeting HER2-positive breast cancer. This article will interpret this clinical study, hoping to provide references for further research progress in this field.
Main Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria:HER2-positive II-III stage breast cancer patients
Dosing Regimen and Grouping:
-
Phase 1: 6 mg/kg group, with two treatment cycle subgroups (6 cycles; 8 cycles)
-
Phase 2: 7.5 mg/kg group, with two subgroups (6 cycles; 8 cycles)
-
Each subgroup has 26 patients
Main Endpoints:Pathological complete response (pCR)
Number of Participants:104
Clinical Trial Results
-
Efficacy Data:
8-cycle treatment group –overall tpCR rate: 73.1%
-
6.0 mg/kg cohort: 76.9%
-
7.5 mg/kg cohort: 69.2%
-
6-cycle treatment group –overall tpCR rate: 59.6%
-
6.0 mg/kg cohort: 57.7%
-
7.5 mg/kg cohort: 61.5%
-
Safety Data:≥3 grade TRAE incidence was 27.9%, with an incidence of interstitial pneumonia at 0.96%
4.3
Biomarker-Driven Efficacy Prediction Studies
In addition to the clinical progress of specific ADC drugs, the 2025 ASCO meeting also presented several results of biomarker-driven efficacy prediction studies, systematically integrating key factors such as genomic variations related to resistance, indicator target expression characteristics, and multi-omics data. Notably, some of these studies focused on the value of liquid biopsy technology in assessing clinical efficacy. Based on this, we summarized such studies from this conference, selecting two multi-drug comparative studies focusing on metastatic breast cancer for analysis.
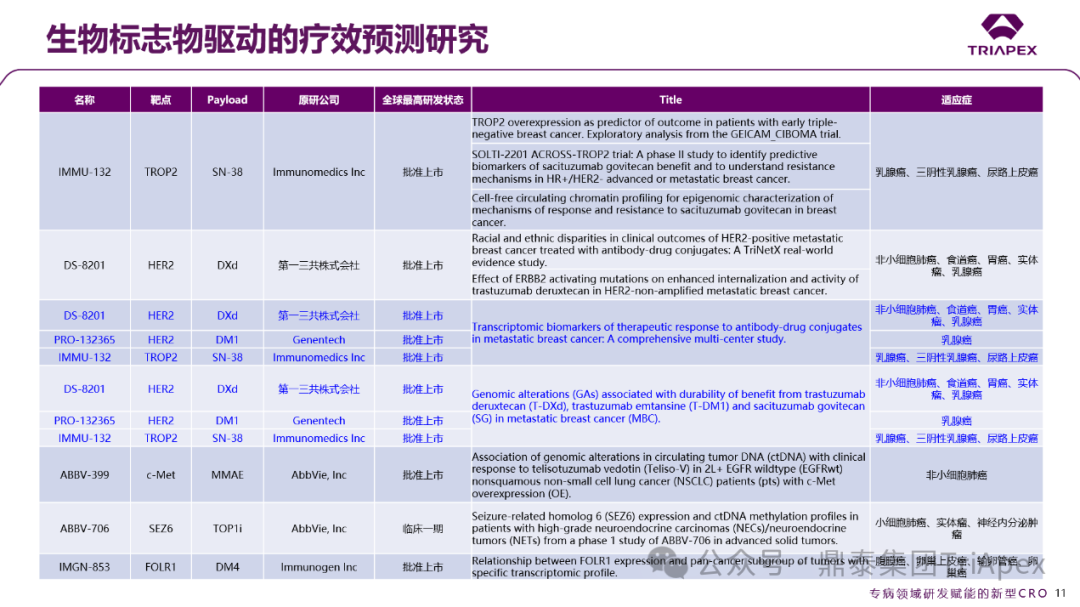
Figure 31. Biomarker-Driven Efficacy Prediction Studies
I. Transcriptomic Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response to Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Comprehensive Multi-Center Study[10]Transcriptomic biomarkers of therapeutic response to antibody-drug conjugates in metastatic breast cancer: A comprehensive multi-center study.
This study analyzed the transcriptomic data before treatment of metastatic breast cancer patients (n=453) receiving DS-8201 (T-DXd), PRO-132365 (T-DM1), and IMMU-132 (SG), finding potential correlations of drug efflux transporters ABCB1 and ABCC1 with ADC drug treatment responses.
T-DXd Group:High expression of ABCB1 and ABCC1 was associated with shorter treatment duration (r=-0.290, p=0.017; r=-0.274, p=0.025), and high expression of ABCB1 increased the risk of death by 30% (HR=1.30, p=0.002)
SG Group:Patients with high expression of ABCC1 and ABCC4 had poorer OS (HR=1.34, p=0.034; HR=1.19, p=0.042)
T-DM1 Group:No significant associations were found
The above studies suggest that drug efflux transporters, such as ABCB1, can serve as predictive biomarkers for T-DXd resistance and targets for combination therapy.
II. Genomic Alterations Associated with Durability of Benefit from Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (T-DXd), Trastuzumab Emtansine (T-DM1), and Sacituzumab Govitecan (SG) in Metastatic Breast Cancer (MBC)[11]Genomic alterations (GAs) associated with durability of benefit from trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd), trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) and sacituzumab govitecan (SG) in metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
By analyzing genomic alterations (GAs) before and after treatment in 1177 metastatic breast cancer patients treated with T-DXd, T-DM1, and SG from real-world genomic databases, it was found that ERBB2 amplification (ERBB2amp) has universal predictive value for ADC efficacy:
In HER2-positive patients:ERBB2amp significantly extended the median time to next treatment (TTNT) for T-DXd and T-DM1, with the median TTNT for ERBB2amp patients receiving T-DXd reaching 22.5 months (non-amplified group 6.4 months); the median TTNT for T-DM1 was 8.3 months (non-amplified group 2.6 months);
In HER2 low expression patients:ERBB2amp also indicated better efficacy for T-DXd, with TTNT not reached (non-amplified group median TTNT 7.4 months).
This suggests that ERBB2amp detection based on comprehensive genomic sequencing (CGP) can surpass traditional IHC/FISH typing, becoming an important basis for optimizing individualized treatment decisions for T-DXd or T-DM1. This precise stratification strategy helps improve the clinical benefit rate of ADC drugs.
05
Conclusion
Continued deepening of mainstream targets and the gradual rise of emerging targets have become the development direction of global ADC R&D. Mature targets represented by HER2 and Trop2 have gathered nearly half of the global ADC pipeline layout, and with the approval of heavyweight ADCs such as Enhertu and Datropan, the competitive landscape in this field has become relatively saturated, raising the regulatory standards for “best standard treatment.” In this context, latecomers can only win survival space by establishing breakthrough advantages in efficacy or safety. However, even if efficacy surpasses, latecomers often find it difficult to shake the established commercial ecology of pioneers. When “me-better” cannot be transformed into “market-better,” latecomers are prone to fall into the dilemma of “burning money to catch up but failing to break barriers,” posing profound strategic questions for innovation decisions in the industry: “Go or No Go?”
In this context, the global ADC pipeline layout is undergoing structural adjustments: on the one hand, companies are seeking differentiated breakthroughs among mainstream targets, such as improving existing products’ clinical benefits through optimized linker-toxin modifications and antibody engineering; on the other hand, the exploration and validation of emerging targets have become new breakthrough points. From the latest trends at the 2025 ASCO meeting, some brand-new targets have obtained preliminary positive data, demonstrating unique therapeutic potential. Due to the high uncertainty in the emerging target field, the tolerance for clinical development of emerging target ADC drugs is extremely low. This means that R&D teams need to have higher technical thresholds and precise R&D strategies, especially in target selection, molecular design, clinical trial planning, and external collaboration (BD). Therefore, companies innovating in this field not only need deep technical accumulation but also need to have stronger comprehensive strength in interdisciplinary collaboration, non-clinical research, translational medicine, and clinical development, with resource integration and R&D strategy upgrades through BD being a key path that cannot be ignored.
It is worth noting that in ADC R&D, the “combination strategy” is gradually becoming another important breakthrough direction. ASCO 2025 meeting data shows that the “strong alliance” model of ADC and IO has achieved preliminary significant results, which not only expands the boundaries of traditional treatment methods but also provides important references for future exploration of more efficient anti-tumor strategies. In addition, biomarker-driven personalized treatment is expected to provide scientific basis for personalized precision treatment strategies. The success of these innovative combination treatment models will further enhance the clinical application value of ADC drugs and bring new treatment hope to cancer patients.
Contributed by: Translational Science and Drug Policy Strategy Department
References
[1]Becotatug vedotin vs. chemotherapy in pre-heavily treated advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A randomized, controlled, multicenter, open-label study. 2025. ASCO.
[2]http://www.baili-pharm.com/about.aspx?mid=110&sid=
[3]Phase I study of iza-bren (BL-B01D1), an EGFR x HER3 bispecific antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), in patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with driver genomic alterations (GA) outside of classic EGFR mutations. 2025. ASCO
[4]Phase I study of iza-bren (BL-B01D1), an EGFR x HER3 bispecific antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), in patients with locally advanced or metastatic small cell lung cancer (SCLC). 2025. ASCO
[5]Rinatabart sesutecan (Rina-S) for patients with advanced endometrial cancer: First disclosure from dose expansion cohort B2 of the GTC1184-01 study. 2025. ASCO
[6]Su MC, Yuan RH, Lin CY, Jeng YM. Cadherin-17 is a useful diagnostic marker for adenocarcinomas of the digestive system. Mod Pathol. 2008;21(11):1379-1386.
[7]Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) + pertuzumab (P) vs taxane + trastuzumab +pertuzumab (THP) for first-line (1L) treatment of patients (pts) with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive (HER2+) advanced/metastatic breast cancer (a/mBC): Interim results from DESTINY-Breast09. 2025. ASCO
[8]Disitamab vedotin (DV) plus toripalimab (Tor) and chemotherapy (C)/trastuzumab (Tra) as first-line (1L) treatment of patients (pts) with HER2-expressing locally advanced or metastatic (la/m) gastric cancer. 2025. ASCO
[9]Efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant TQB2102 in women with locally advanced or early HER2-positive breast cancer: A randomized, open-label, multi-centre phase 2 trial. 2025. ASCO
[10]Transcriptomic biomarkers of therapeutic response to antibody-drug conjugates in metastatic breast cancer: A comprehensive multi-center study. 2025. ASCO
[11]Genomic alterations (GAs) associated with durability of benefit from trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd), trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1) and sacituzumab govitecan (SG) in metastatic breast cancer (MBC). 2025. ASCO





Disclaimer: This article is from the content team of Ding Tai Group. Personal forwarding to WeChat Moments is welcome, but media or organizations are prohibited from reprinting to other platforms in any form without authorization. For reprints, please add WeChat LXL–7. This article is for information exchange and not for commercial profit purposes, and the content is for sharing and learning only.