silly pid:113107781 by:paccha!!
DAC (Digital to Analog Converter, 数模转换器)
DAC 基础部分
The function of a DAC is to convert digital signals into analog signals. The working principle of a DAC is the opposite of that of an ADC. A DAC can convert digital signals into analog signals for output and control.
DACs have a wide range of applications in daily life, such as digital signal processing, mobile phones, MCU power supplies, audio amplifiers, etc.
A typical DAC module is shown in the figure below:
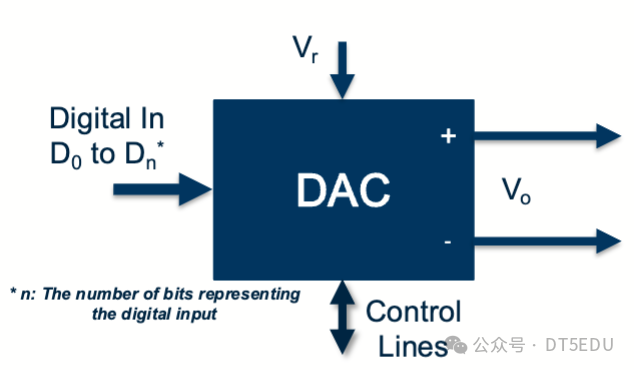
It includes pins for digital signal input, several control lines, an external reference voltage input, and the final voltage output.
For a typical DAC, the formula for its output voltage is as follows:
- Output voltage
- Digital input value
- DAC bit depth
- Reference voltage
From this, we can derive that the output range of the DAC is , and its resolution is
DAC in MBed OS
For the <span>NUCLEO-L432KC</span> development board we are using, it has 2 channels of DAC output, with the reference voltage and input voltage being the same at <span>3.3V</span>. In our experimental <span>MBed OS</span> environment, the DAC should be used as follows:
// Defines a DAC output object connected to pin A6
AnalogOut dac_out(A6);
// Sets the DAC output to 0.5 * Vref
dac_out = 0.5;
Similar to ADC, the value written to the DAC here is also a floating-point number, ranging from 0 to 1. Below are the specific methods of the <span>AnalogOut</span> class.
<span>AnalogOut(PinName pin)</span>- Constructor that initializes the DAC output object and connects it to the specified pin.
<span>void write(float val)</span>- Writes a floating-point value to the DAC output, ranging from 0 to 1.
<span>void write_u16(uint16_t val)</span>- Writes a 16-bit unsigned integer value to the DAC output, ranging from 0 to 65535.
<span>void operator=(float val)</span>- Equivalent to the
<span>write</span>method, ranging from 0 to 1.
