Click the blue text to follow us
4.1Overview of Information Systems
[Fundamental Knowledge Points]
1. Definition of Information Systems
An information system is a human-machine integrated system composed of computer hardware and software, networks and communication devices, information resources, users, and regulations, aimed at processing information flows. The functions of an information system include: input, storage, processing, output, and control. Richard L. Nolan divides the development path of information systems into six stages: initiation, dissemination, control, integration, data management, and maturity.
2. Classification of Information Systems
 Information systems are classified into six categories: business (data) processing systems, management information systems, decision support systems, expert systems, office automation systems, and comprehensive information systems.
Information systems are classified into six categories: business (data) processing systems, management information systems, decision support systems, expert systems, office automation systems, and comprehensive information systems.
3. Lifecycle of Information Systems
The lifecycle of an information system consists of four stages: generation, development, operation, and extinction.
4. Principles of Information System Construction
The principles of information system construction can be divided into: the principle of involvement of senior management, the principle of user participation in development, the top-down planning principle, and the engineering principle.
5. Development Methods of Information Systems
The main development methods for information systems include: structured methods, prototyping methods, object-oriented methods, service-oriented methods, agile methods, and component-based development methods. The structured and object-oriented methods are detailed in Hour 7; here we introduce several other development methods.
(1) Prototyping Method. The prototyping method, also known as rapid prototyping, can quickly establish a system model based on users’ preliminary requirements using system tools for communication with users.
The prototyping method can be classified based on functional implementation into:
1) Horizontal Prototype: Behavioral prototype, used for interfaces. It refines requirements but does not implement functionality.
2) Vertical Prototype: Structured prototype, used for implementing complex algorithms, achieving partial functionality.
The prototyping method can also be classified based on the final result into:
1) Throwaway: Exploratory prototype, addressing uncertainty, ambiguity, incompleteness, and vagueness in requirements.
2) Evolutionary: Gradually evolves into the final system, suitable for scenarios that are easy to upgrade and optimize, applicable to web projects.
(2) Component-Based Development Method. Software development based on components is a means to address the scale and complexity of software in complex environments. A component does not necessarily contain classes; a class element can only belong to one component. Components can be obtained in the following ways:
1) Obtain suitable components from existing components, directly use or adapt them to create reusable components.
2) Through legacy engineering, extract components with potential reuse value to obtain reusable components.
3) Purchase off-the-shelf commercial components from the market.
4) Develop new components that meet requirements.
The obtained components can be stored in a component library and tailored for use based on demand. The classification of components is shown in Table 4.1.

Table 4.1 Classification of Components

|
Classification |
Specific Description |
|
Keyword Classification Method |
The keyword classification method decomposes the concepts of application domains into a tree or directed acyclic graph structure in a sequential order from abstract to concrete, with each concept represented by a descriptive keyword. |
|
Facet Classification Method |
The facet classification method defines several “facets” used to characterize component features, with each facet containing several concepts that describe the characteristics of the component on that facet. Facets can describe the functions executed by the component, the data being operated on, the context of component application, or other characteristics. |
|
Hypertext Method |
All components must be accompanied by detailed functional or behavioral documentation; important concepts or components mentioned in the documentation are interconnected in a networked manner; users can jump to documents containing related concepts or components according to human associative thinking while reading the documentation; a full-text retrieval system matches user-provided keywords with the text in the documentation to achieve browsing retrieval of components. |
 Component retrieval methods can also be divided into: keyword-based retrieval, facet retrieval method, and hypertext retrieval method.
Component retrieval methods can also be divided into: keyword-based retrieval, facet retrieval method, and hypertext retrieval method.
(3) Service-Oriented Method. The service-oriented method has developed from the object-oriented method, where cross-component function calls are exposed in the form of interfaces. Further decoupling the definition and implementation of interfaces has led to the emergence of service-oriented development methods. For the system architect examination, we focus on service-oriented architecture (SOA), which will be introduced in Hour 18.
(4) Agile Method. The agile method is a human-centered, iterative, and incremental development approach. Agile methods have two main characteristics that distinguish them from other methods, especially heavyweight methods.
1) Agile methods are “adaptive” rather than “prescriptive”. Heavyweight methods attempt to make detailed plans for a software development project over a long period and then develop according to the plan, refusing changes after the plan is completed. Agile methods welcome changes.
2) Agile methods are “people-oriented” rather than “process-oriented”. They aim to leverage human characteristics and fully utilize human creativity, emphasizing that software development should be an enjoyable activity.
The core ideas of agile methods include the following three points:
1) Agile methods are adaptive, not predictable.
2) Agile methods are people-centered, not process-centered.
3) They belong to an iterative and incremental development process.
4.2Typical Applications of Informatization
[Fundamental Knowledge Points]
1. TPS and EDPS
Transaction Processing Systems (TPS) or Electronic Data Processing Systems (EDPS) are typical applications of informatization. Transaction processing systems can achieve computer automation, reduce the burden of data processing, and improve processing efficiency. They are both the most basic form of information system development and serve as a foundation and bridge. Due to their simplicity and maturity, they are commonly developed using structured lifecycle methods. The data generated by transactions undergoes input, processing, and output (i.e., IPO). The data processing cycle of business systems is divided into five stages: data input, data processing, database maintenance, report generation, and query processing (for further elaboration on functionality). Data processing methods include batch processing and online transaction processing (OLTP).
2. Management Information Systems
Management Information Systems (MIS) are highly integrated human-machine information systems developed on the basis of TPS, used for certain management and business-level decision-making across the enterprise. The upper layer of an MIS consists of subsystems and functions, while the lower layer consists of various processes, with functions achieved through process combinations. An MIS can be represented by a function/hierarchy matrix. There are seven subsystems: sales and marketing subsystem, production subsystem, logistics subsystem, human resources subsystem, finance and accounting subsystem, information processing subsystem, and senior management subsystem.
 3. Decision Support Systems
3. Decision Support Systems
Decision Support Systems (DSS) have two definitions:
(1) Definition 1: DSS is a computer-based system composed of three interrelated parts: language system, knowledge system, and problem processing system. Its characteristics are as follows:
1) Data and models are the main resources of DSS.
2) It is used to support users in decision-making.
3) It is mainly used to solve semi-structured and unstructured problems.
4) Its role is to improve the effectiveness of decisions rather than the efficiency of decisions.
(2) Definition 2: DSS is an interactive, flexible, and adaptive computer-based information system. Its characteristics are as follows:
1) Targeted at upper management.
2) User-friendly interface.
3) Combines models and analytical techniques with traditional data access and retrieval techniques.
4) Flexibility and adaptability to changes in the environment and decision-making methods.
5) Supports but does not replace decision-making.
6) Utilizes advanced information technology for rapid information transmission and processing.
The manager of a DSS is at the core, making decisions with the support of DSS. DSS has two structural forms: two-database structure and knowledge-based structure.
DSS supports nine basic functions: ① multi-layer decision-making, organizing and providing data for decisions; ② collecting, storing, and providing external information; ③ collecting and providing feedback information on activities; ④ having storage and management capabilities for models; ⑤ storage and management of various commonly used methods; ⑥ management of various data, models, and methods; ⑦ data processing; ⑧ having human-machine interfaces and graphical processing; ⑨ supporting distributed usage. Its characteristics are decision-maker-oriented, supporting semi-structured problems, auxiliary support, dynamic processes, and interactivity. The assembly process includes: data reorganization, establishing data warehouses, creating data dictionaries, data mining, and model establishment.
4. Expert Systems
Knowledge-based Expert Systems (ES) are intelligent computer programs that use knowledge and reasoning processes to solve high-difficulty problems that require specialized knowledge from senior experts. ES belongs to artificial intelligence and is used to solve semi-structured or unstructured problems. Expert systems include branches such as robotics, vision systems, natural language processing, learning systems, and neural networks. A comparison between expert systems and general computer systems is shown in Table 4.2.
Table 4.2 Comparison of Expert Systems and General Computer Systems
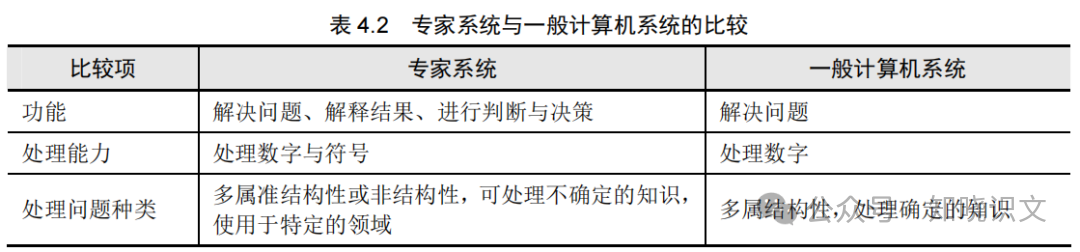
|
Comparison Item |
Expert System |
General Computer System |
|
Function |
Solving problems, explaining results, making judgments and decisions |
Solving problems |
|
Processing Capability |
Processing numbers and symbols |
Processing numbers |
|
Types of Problems Processed |
Mostly semi-structured or unstructured, capable of handling uncertain knowledge, used in specific fields |
Mostly structured, handling certain knowledge |

Specifically, ES has characteristics such as transcending time limitations, low operational costs, ease of transmission and replication, consistent processing methods, adeptness at overcoming challenges, and applicability in specific fields. ES consists of a knowledge base, integrated database, inference engine, knowledge acquisition, explanation program, and human-machine interface. Among these, the inference engine and knowledge base together form the core of the expert system. General expert systems solve domain problems through the interaction of the inference engine with the knowledge base and integrated database.
5. Office Automation Systems
Office Automation Systems (OAS) can solve the integrated processing problems of data, text, sound, images, etc. It is a comprehensive, interdisciplinary human-machine information processing system that integrates text, data, language, and images, capable of transaction processing, information management, and decision support. OAS consists of computer equipment, office equipment, data communication and network devices, and software systems.
6. Enterprise Resource Planning
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) encompasses all resources of an enterprise, including three major flows: logistics, capital flow, and information flow. ERP is a management information system that integrates all resource information of the enterprise based on information technology, providing a comprehensive and systematic management platform for decision-making, planning, control, and performance evaluation. The management scope of ERP covers all supply and demand processes of the enterprise, representing comprehensive management of the supply chain, and is also related to human resource systems and CRM. ERP includes 11 basic modules: production forecasting, sales management, operational planning, master production planning, material requirements planning, capacity requirements planning, workshop operation planning, procurement and inventory management, quality and equipment management, and financial management. The functions of ERP include: supporting decision-making, targeted IT solutions for different industries, and providing supply chains across industries.
4.3Typical Information System Architecture Models
[Fundamental Knowledge Points]
(1) Electronic Government (EG). Electronic government is a system engineering transformation of government forms that utilizes information technology and other related technologies to achieve integrated management and operation of public affairs, government affairs, business, and transactions. The main actors are: Government, Business entities, and Citizens. Specific classifications are shown in Table 4.3.
Table 4.3 Classification of Electronic Government
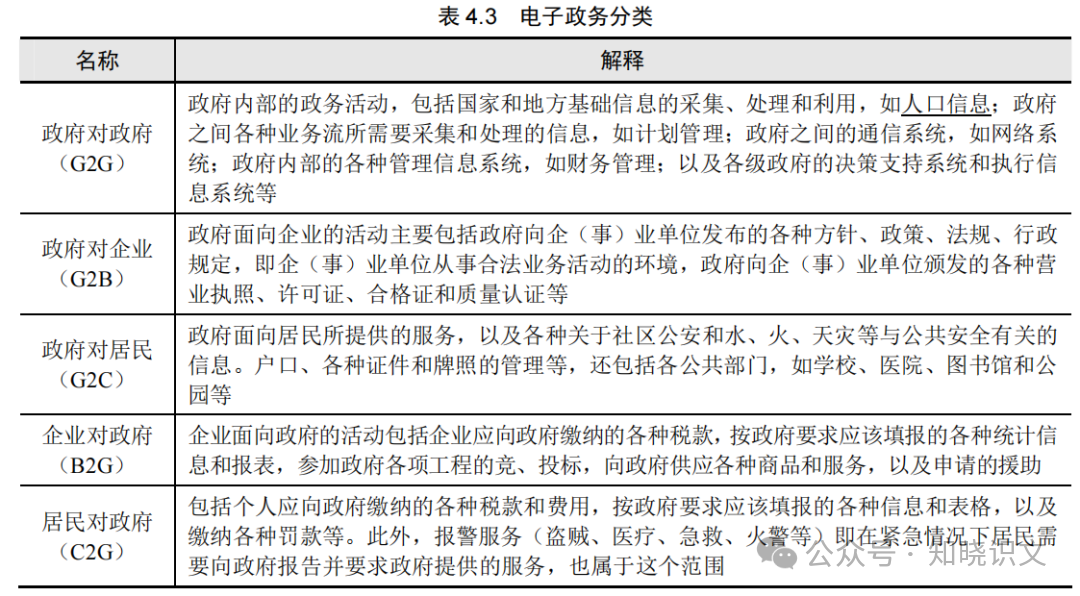
|
Name |
Explanation |
|
Government to Government (G2G) |
Government internal administrative activities, including the collection, processing, and utilization of national and local basic information, such as population information; various business flows between governments that require information collection and processing, such as planning management; communication systems between governments, such as network systems; various management information systems within governments, such as financial management; as well as decision support systems and execution information systems at all levels of government. |
|
Government to Business (G2B) |
Government activities directed at businesses mainly include various policies, regulations, and administrative provisions issued by the government to business entities, i.e., the environment for business entities to engage in legal business activities, and various business licenses, permits, qualifications, and quality certifications issued by the government to business entities. |
|
Government to Citizens (G2C) |
Services provided by the government to citizens, as well as various information related to community public security and disasters such as water, fire, and natural disasters. Management of household registration, various certificates and licenses, and includes various public sectors such as schools, hospitals, libraries, and parks. |
|
Business to Government (B2G) |
Business activities directed at the government include various taxes that businesses should pay to the government, various statistical information and reports that should be submitted to the government as required, participation in government projects for bidding, supplying various goods and services to the government, and applying for assistance. |
|
Citizens to Government (C2G) |
Includes various taxes and fees that individuals should pay to the government, various information and forms that should be submitted to the government as required, and payment of various fines, etc. Additionally, emergency services (theft, medical, emergency, fire, etc.) where residents need to report to the government and request services also fall within this scope. |
(2) Enterprise Informatization (EI). Enterprise informatization is the process by which enterprises utilize modern information technology to achieve automation, convenience, networking, and intelligence in business activities, thereby enhancing the core competitiveness of the enterprise. Enterprise informatization is the integration of technology and business, realized from three levels: enterprise strategy, business operations, and management operations. Methods of enterprise informatization include: business process reengineering methods, core business application methods, information system construction methods, thematic database methods, resource management methods, and human capital investment methods.
(3) Electronic Commerce (EC). Electronic commerce refers to buying and selling products or providing services online using communication means provided by the web, along with its derivative behaviors. The main models include: B2B, B2C, C2C, O2O (online purchase of offline services).
4.4Exercises
1. The resources of enterprises in ERP include ( ).
A. Logistics, capital flow, and information flow B. Logistics, workflow, and information flow
C. Logistics, capital flow, and workflow D. Capital flow, workflow, and information flow
Analysis: The resources of the enterprise include three major flows: logistics, capital flow, and information flow. ERP is a management information system that integrates these three resources comprehensively.
Answer: A
2. ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is a management information system established on the basis of information technology, utilizing advanced management concepts of modern enterprises to comprehensively integrate the management of logistics, capital flow, and (1) flow, providing a comprehensive and systematic management platform for decision-making, planning, control, and performance evaluation. In the ERP system, (2) management modules mainly manage the entry, exit, and storage of enterprise materials.
(1) A. Products B. Human resources C. Information D. Processing
(2) A. Inventory B. Materials C. Procurement D. Sales
Analysis: ERP is a management information system established on the basis of information technology, utilizing advanced management concepts of modern enterprises to comprehensively integrate the management of logistics, capital flow, and information flow, providing a comprehensive and systematic management platform for decision-making, planning, control, and performance evaluation. The module that mainly manages the entry, exit, and storage of enterprise materials is the inventory management module.
Answer: C A
3. Electronic government is a transformation of the existing government form, utilizing information technology and other related technologies to integrate its management and service functions, optimizing and reorganizing government organizational structures and workflows online. The three main actors related to electronic government are government, (1) and citizens. The collection, processing, and utilization of national and local population information belong to (2) electronic government activities.
(1) A. Departments B. Business entities C. Management institutions D. Administrative agencies
(2) A. Government to Government B. Government to Citizens C. Citizens to Citizens D. Citizens to Government
Analysis: Electronic government is a transformation of the existing government form, utilizing information technology and other related technologies to integrate its management and service functions, optimizing and reorganizing government organizational structures and workflows online. The three main actors related to electronic government are government, business entities, and citizens. The collection, processing, and utilization of national and local population information belong to government to government electronic government activities.
Answer: B A
BREAK AWAYPrevious Recommendations01Architect | Chapter 2 | Fundamentals of Computer Systems | Key Points Overview02Architect | Chapter 2 | Fundamentals of Embedded Systems | Key Points Overview03Architect | Chapter 2 | Fundamentals of Computer Networks | Key Points Overview
 Looking for Study PartnersHaving weathered storms, still full of enthusiasm for lifeOptimistic and open-minded, always maintaining confidence and progress
Looking for Study PartnersHaving weathered storms, still full of enthusiasm for lifeOptimistic and open-minded, always maintaining confidence and progress END
END