Introduction: Recently, I have come into contact with the interfaces of small cameras, and I am reprinting this article. This article introduces the “camera” interfaces, while some industrial camera interfaces such as CameraLink and CoaXPress are not covered. I will organize them when I have time.
Original link:
https://www.liuwenhao.me/?p=5125
Table of Contents
1. Analog Cameras
-
1.1 First Generation: Standard Definition Camera: CVBS
-
1.2 Second Generation: High Definition, Full HD:AHD
-
1.3 Third Generation: Up to 4K: HDCVI / TVI
2. Digital Cameras
-
2.1 Compressed Interfaces: IPC/USB
-
2.2 Uncompressed Interfaces: SDI/HD-SDI/3G-SDI & HD-BaseT
-
2.3 Uncompressed Interfaces: Serdes
3. Internal Camera Interfaces
-
3.1 DVP (ITU BT601/656/1120)
-
3.2 MIPI (Mobile Industry Processor Interface)
1. Analog Cameras
1.1 First Generation: Standard Definition Camera
CVBS, composite video baseband signal, composite video signal, also referred to as: Color, Video, Blanking, Sync
It often uses three wires (RCA cables) to transmit audio and video:
-
White wire: Left channel
-
Red wire: Right channel
-
Yellow wire: CVBS video signal (only one wire is needed to transmit the video signal)
Composite video signal:
-
Includes a single analog signal for brightness and chrominance
-
Resolution generally reaches 350-450 lines
-
Brightness and chrominance are interleaved, making it difficult to restore perfectly consistent colors during signal playback
-
Image quality is greatly affected by the materials used for the cables

▲CVBS Video Interface

▲CVBS Video Waveform Signal
1.2 Second Generation: High Definition, Full HD
AHD: Analog High Definition
-
Proposed by South Korea’s Nextchip
-
More advanced pseudo-bright color separation, EQ, and noise reduction technologies achieve clearer image resolution
-
Image resolution supports up to 3840×2160, comparable to digital signal images transmitted via LVDS
-
Supports image transmission up to 500 meters
-
The receiving end can be compatible with CVBS signals
-
There are many automotive products with a large market share in automotive electronics
▲AHD Video Interface Chip Manufacturers
1.3 Third Generation: Up to 4K
HDCVI (High Definition Composite Video Interface):
-
Video interface with complete independent intellectual property rights released by Zhejiang Dahua in 2012
-
Uses coaxial cable for point-to-point transmission
-
Using 75-3 specification coaxial cable can achieve 1280×720 at 500 meters, 1920×1080 at 300 meters.
-
CVI3.0 provides support for 4K video.
-
Relatively low cost, technology is relatively closed.
TVI (High Definition Transport Video Interface):
-
Developed by Techpoint in the USA, mainly supported by Hikvision in China
-
Uses coaxial cable for point-to-point transmission
-
Using 75-3 specification coaxial cable can achieve 300-500 meters
-
Relatively open ecosystem
2. Digital Cameras
2.1 Compressed Interfaces: IPC/USB
IPC (IP Camera):
-
Composed of a network encoding module and a camera
-
The output image is encoded, so it has low bandwidth requirements for communication, but real-time performance is not strong
-
Generally consists of two main ICs: Sensor + backend SoC. The backend SoC completes many functions such as ISP, video encoding, audio encoding, infrared light control, and video signal transmission.
-
Can be directly connected to the Internet.
-
Mainstream manufacturers: Hisilicon, Fuhang Micro, TI, Ambarella
USB (USB Camera):
-
Composed of a USB interface module and a camera
-
The output image is encoded, so it has low bandwidth requirements for communication
-
Generally consists of a single chip that completes all functions such as image acquisition, ISP, video encoding, audio encoding, infrared light control, and USB signal transmission
-
Can be directly connected to a PC
-
Mainstream manufacturers: Sunplus, Lingtong, Jianrong

▲IPC

▲USB Camera
2.2 Uncompressed Interfaces: SDI / HD-SDI / 3G-SDI & HD-BaseT
SDI (Serial Digital Interface):
-
Proposed by SMPTE
-
3G-SDI can transmit 1080p@60Hz signals in real-time, previously only achievable using two coaxial cables via HD-SDI at 1.485Gbps (SMPTE 372M)
-
Long transmission distance, up to 100 meters
HD-BaseT:
-
Proposed by the HD-BaseT Alliance in 2010
-
Uses Ethernet cables for real-time HD video transmission, supporting up to 100 meters
-
Maximum data rate of 10.2Gbit/s (using Cat5/Cat6 cables)
-
Supports POE
2.3 Uncompressed Interfaces: Serdes
In the automotive industry, it is common to refer to the method of transmitting digital video signals over a single coaxial cable as LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling). However, this is a completely different concept from LVDS in the video transmission field.
The two biggest players:
-
TI & Maxim
Basic principle:
-
Serializes tens to hundreds of millions of pixels per second (each pixel is 16bit-32bit in length) into Gbps-level data packets
-
Transmits over a single coaxial cable or a pair of twisted pairs for distances up to 10-15m
Greatest advantage:
-
Combines video signal line, audio signal line, control line, and power line into one
Other players:
-
Rohm: ClocklessLink;
-
Thine: V-By-One;
-
Inova: APIX;
-
Sony: GVIF;
-
Amba: ??
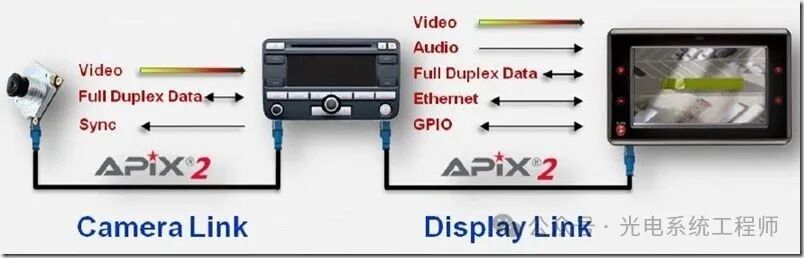
▲Inova’s APIX Interface
3. Internal Camera Interfaces
Internal camera interfaces are almost all digital interfaces, with DVP and MIPI being the most widely used.
3.1 DVP (ITU BT601/656/1120)
DVP: Digital Video Port or Digital Video Parallel, a parallel video interface.Includes the following pins:
-
PCLK: sensor output clock
-
VSYNC: frame synchronization
-
HSYNC: line synchronization
-
D[0:11]: parallel video data
-
ITU BT601/BT656/BT1120 are all types of DVP
-
“Class BT656 Interface”
PCLK in DVP should generally not exceed 100MHz
-
Considering EMC
-
Considering signal integrity
3.2 MIPI (Mobile Industry Processor Interface)
Designed by the MIPI Alliance in 2003,includes CSI and DSI, corresponding to camera interface applications and display interface applications, respectively.
Consists of a pair of differential clock lines and several pairs of differential data lines (generally 1/2/4 pairs).
Uses ECC and CRC encoding, providing some error correction capability
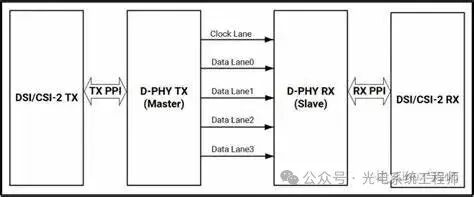
▲MIPI Interface Diagram