Internet of Things & Big Data
Cloud Computing & Artificial Intelligence
Is there a connection between the Internet of Things, Big Data, Cloud Computing, and Artificial Intelligence? How are they combined and applied in real-world scenarios?
To illustrate, consider the human body: our organs perceive everything in the world (Big Data), which is aggregated through the body’s meridians (Internet of Things) to the brain. The brain processes, analyzes, and summarizes this information (Cloud Computing), ultimately forming wisdom (Artificial Intelligence).
Big Data serves as the foundation, the Internet of Things is the architecture, Cloud Computing is the center, and Artificial Intelligence is the output. They coexist and rely on each other.
Big Data 👉 Our daily lives are filled with data. For example, the shopping apps we commonly use push products we might be interested in based on our purchase and browsing history; our frequently used map apps optimize more convenient routes based on our travel records. Behind these actions, Big Data is at work. Big Data acts like a large warehouse, collecting and storing various information, and then transforming this information into valuable insights through various algorithms, providing them to those who need it or to applications.


Cloud Computing 👉 Just like the water and electricity facilities in our daily lives. We don’t need to understand how these facilities work; we just need to enjoy the convenience they bring. Similarly, we don’t need to understand how Cloud Computing works; we just need to know it provides powerful computing capabilities and unlimited storage space. Whether for work, study, or entertainment, Cloud Computing offers us stable and efficient services.


Internet of Things 👉 The Internet of Things also plays an important role in our daily lives. For instance, home water and electricity meters no longer require a person to come and read the meter; the service company knows the readings automatically, and after recharging via a mobile phone, data updates occur automatically. Additionally, we can control smart home appliances such as smart lights and smart TVs through smart speakers; we can monitor and control smart locks and cameras at home via mobile apps. These are applications of IoT technology. The Internet of Things acts like a magical web, connecting various devices and items together, allowing us to remotely control and manage these devices anytime and anywhere.

Artificial Intelligence 👉 Artificial Intelligence also has many applications in our daily lives. For example, our smartphone voice assistants and smart home systems are applications of AI technology. Artificial Intelligence acts like a smart child, constantly improving its “IQ” by learning vast amounts of data and knowledge, providing us with more accurate and convenient services.

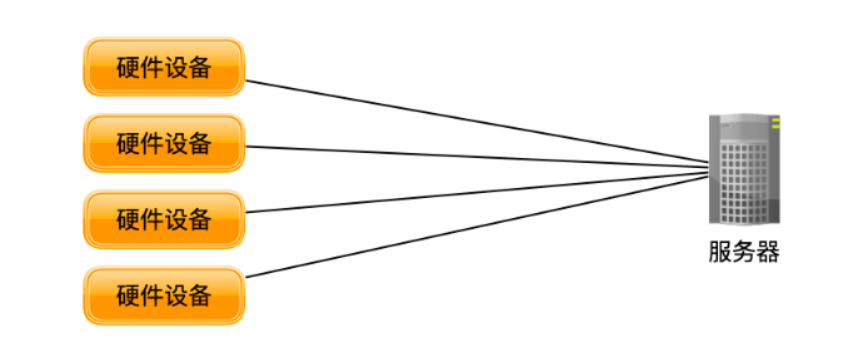
-
Device Identification: The unique identification code for network devices, just like everyone must have an ID number.
-
Device Discovery: When a device connects to the network, it must be able to detect when it goes online and offline.
-
Network Communication: There must be a data communication network, and communication security must be ensured so that devices and servers can communicate.
-
Data Transmission: Data must be transmitted securely over the network, with a data transmission mechanism in place.
-
Remote Control: The ability to control the actions of hardware devices, some of which can also be upgraded.
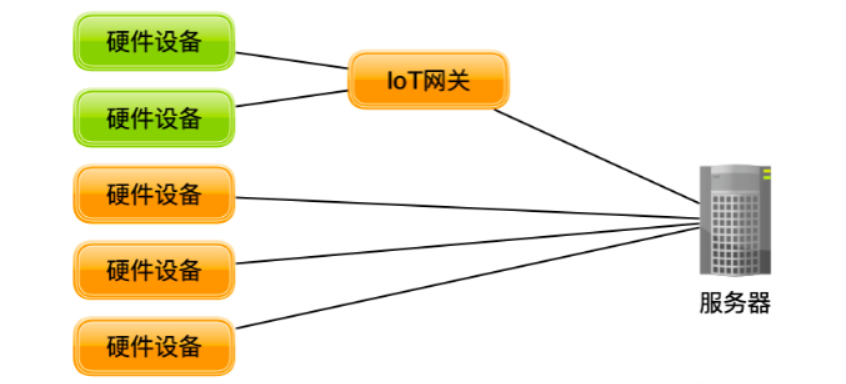

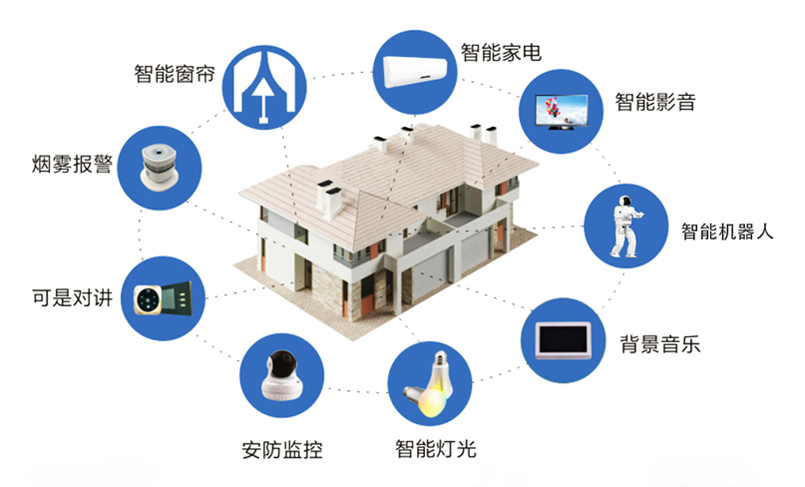
“AIoT” is the abbreviation for “Artificial Intelligence of Things,” referring to the concept of integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) with the Internet of Things (IoT). AIoT aims to achieve higher levels of automation, intelligence, and insights by applying AI technology to IoT devices and data.
AIoT Application Scenarios
Smart Home: AIoT enables home devices to learn your lifestyle and automatically adjust temperature, lighting, and security systems according to your preferences. You can remotely control various devices in your home through voice commands or smartphone apps.
Healthcare: Intelligent health monitoring devices can collect and analyze your health data, providing personalized recommendations and alerts. Medical institutions can also use AIoT to improve patient monitoring and treatment.
Traffic and Urban Management: AIoT can improve urban traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance the efficiency of public transport systems. Smart city management systems can monitor energy usage, waste management, etc., improving urban sustainability.
Industry and Manufacturing: In factories, AIoT can predict equipment failures, enhance production efficiency, and reduce maintenance costs. Robots and automation systems can also collaborate more flexibly.


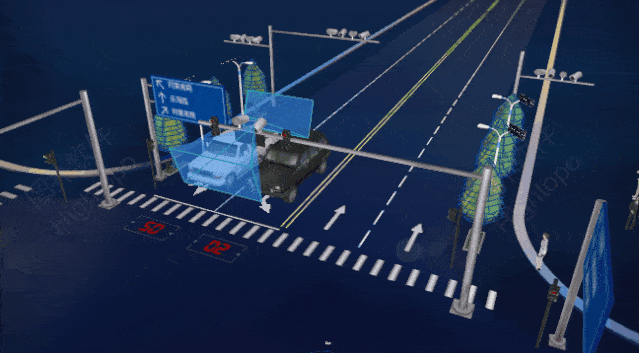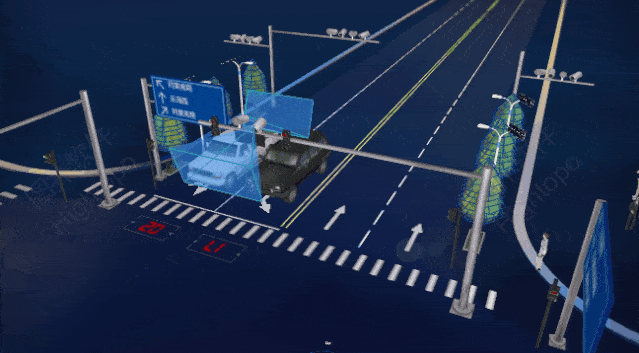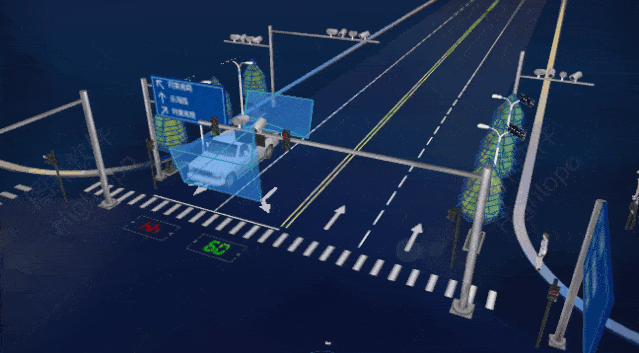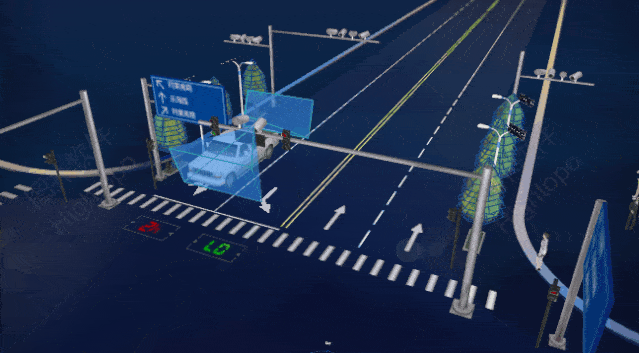


Source: Wenbin Consulting; China Smart City Guide