According to the International Data Corporation (IDC) recently released 2025 V1 version of the IDC Worldwide AI and Generative AI Spending Guide, the total global investment in artificial intelligence (AI) IT is expected to reach $315.8 billion in 2024, and is projected to grow to $815.9 billion by 2028, with a five-year compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.9%. Focusing on generative AI, IDC predicts that the global generative AI market will have a five-year CAGR of 63.8%, reaching $284.2 billion by 2028, accounting for 35% of the total AI market investment.
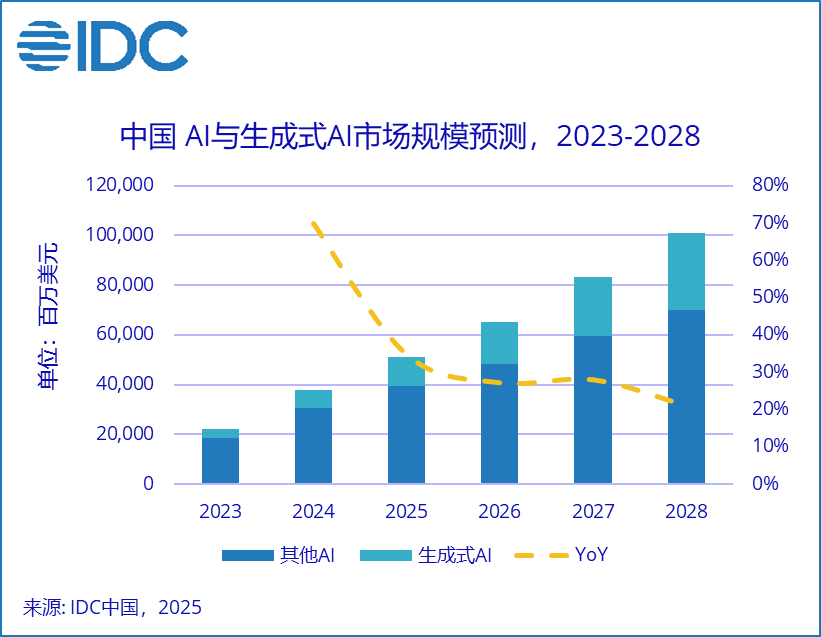
Focusing on AI spending in China, IDC data shows that China will continue to lead the development of the AI market in the Asia-Pacific region, accounting for over 50% of the total AI spending in the region. It is expected that by 2028, China’s total investment in AI will exceed $100 billion, with a five-year CAGR of 35.2%; the market size for AI large model (LLM) solutions in China is expected to reach 21.1 billion yuan, demonstrating strong growth momentum and significant market potential.
Based on this trend, the government work report at the 2025 National Two Sessions clearly listed the “AI +” initiative as a priority, requiring the promotion of the widespread application of large models and the vigorous development of new generation intelligent terminals such as smart connected new energy vehicles, AI smartphones and computers, intelligent robots, and the expansion of large-scale 5G applications.
Currently, the evolution of AI technology shows a dual trend. On one hand, the parameter scale of cloud-based large models continues to expand, with the Llama 3 70B model’s inference computing power demand increasing by over 300% compared to previous generations, driving the number of AI servers in data centers to grow by over 300% in the coming years. On the other hand, intelligent devices at the edge, such as smart cars and industrial IoT terminals, are experiencing a surge in demand for localized real-time processing, with the edge AI market expected to reach $176 billion by 2025.
This “cloud-edge” computing power differentiation poses stringent requirements for the energy efficiency and flexibility of computing platforms. The cloud needs to break through the power consumption wall, while the edge needs to achieve efficient inference at milliwatt-level power consumption, which traditional computing architectures struggle to accommodate.
Energy efficiency and scenario adaptation are the core challenges for the implementation of large models
Generative AI technology is reshaping the industrial landscape, with large language models becoming a core direction of technological development. As AI extends from the cloud to the edge, the demand for high performance, low latency, and local processing capabilities is becoming increasingly urgent, reflecting three major pain points currently faced by the computing power industry:

1. Significant energy efficiency bottlenecks in the cloud, with the power consumption of a single cluster in large data centers reaching the gigawatt level. “High energy efficiency” has become a basic requirement in the industry, as it directly relates to profitability.
2. Prominent computing power gap at the edge, as the parameter scale of large models continues to increase, with models exceeding 1 billion parameters becoming common. Devices such as smart cars require localized processing with latency below 100ms, posing dual challenges of performance and real-time capability for edge CPUs;
3. The deployment of large models is evolving towards broader, deeper, and more efficient directions, with the fragmentation of the ecosystem causing developers to repeatedly optimize for different architectures, increasing the complexity and difficulty of deployment, and extending the deployment cycle by 30%-50%.
Breaking through these challenges requires innovation at the architectural level.
A full-stack solution for cloud-edge collaboration reshaping the computing power landscape
1. Cloud: Redefining energy efficiency and performance benchmarks
Even before the full arrival of the AI era, the Arm Neoverse computing platform had already gained widespread recognition and demonstrated unique advantages in AI inference. The high energy efficiency characteristics of Neoverse make it the preferred computing power choice for leading cloud providers. According to Arm’s official data, by 2025, nearly 50% of the computing power shipped to leading hyperscale cloud service providers will be based on Arm architecture.
Hyperscale cloud service providers such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure are all using the Arm computing platform to create general-purpose custom chips. Some use cases show that chips based on Arm architecture have achieved up to 60% energy efficiency improvement compared to previous products. Typical cases include:
-
AWS Graviton4: The C8g instance based on the Neoverse V2 core runs the Llama 3 70B model, generating 10 tokens per second, reaching the human readability limit, with prompt encoding performance improved by 14%-26% compared to the previous Graviton3. When processing the int4 quantized Phi-3 model, throughput improved by 2.5 times, with single inference latency stable below 100ms.
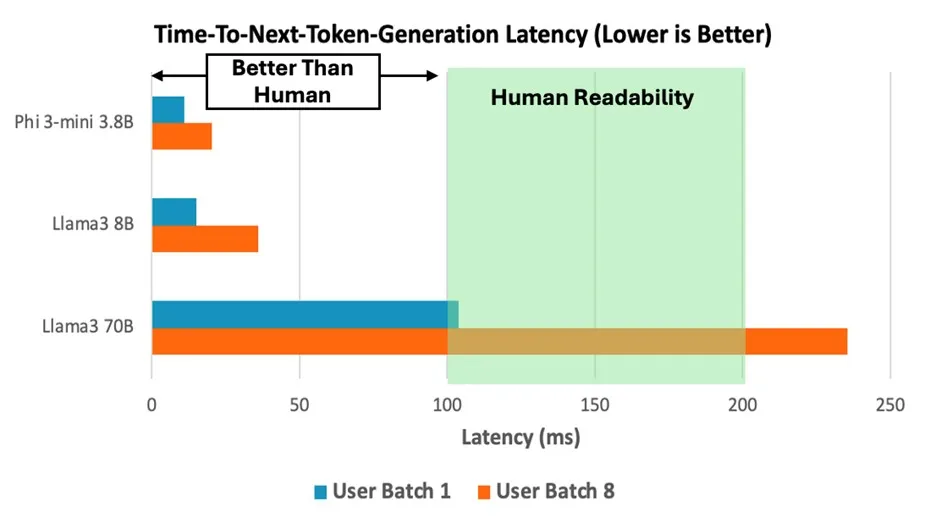
Performance of next token generation time when running Llama 3 70B, Phi-3-mini 3.8B, and Llama 3 8B models on the C8g.16xlarge instance, where the batch size simulates a scenario of one or more users calling the model simultaneously
-
Alibaba Cloud Yitian 710: The Yitian 710 server based on the Neoverse N2 architecture optimizes the int8 GEMM kernel through SMMLA instructions, improving the token processing speed of the Llama 3 model by 2.7 times, with overall ownership costs reduced by 60% compared to equivalent x86 platforms. In the FunASR speech recognition deployment, combined with BF16 Fast Math kernels, inference performance improved by 2.4 times compared to x86 instances, showing significant cost-performance advantages.
2. Edge: Armv9 Edge AI Computing Platform Accelerating IoT Intelligence
In February of this year, Paul Williamson, Senior Vice President and General Manager of Arm’s IoT Division, stated: “The innovation of AI is no longer limited to the cloud. With the increasing interconnectivity and intelligence of the world, processing AI workloads at the edge brings significant advantages and is becoming indispensable. The launch of the Armv9 Edge AI Computing Platform, designed specifically for IoT, marks an important milestone in this development trend.”
The AI computing platform mentioned here is the world’s first Armv9 Edge AI computing platform, centered around the ultra-high energy-efficient Cortex-A320 CPU and Ethos-U85 NPU based on the Armv9 architecture, optimized for IoT applications, with ML performance improved by 8 times compared to previous generations, supporting the operation of edge AI models with over 1 billion parameters.
It is reported that this platform has received support from several industry-leading companies, including AWS, Siemens, and Renesas Electronics, promoting advancements in industrial automation, smart cameras, and other fields.
3. Edge: Arm Terminal CSS Enhancing Terminal Performance
Arm Terminal CSS encompasses the latest Armv9.2 Cortex CPU clusters and Arm Immortalis and Arm Mali GPU, CoreLink interconnect system IP, as well as CPU and GPU physical implementations ready for production using 3nm technology, achieving leapfrog improvements in performance, efficiency, and scalability across a wide range of consumer electronics.
Data shows that the Arm Cortex-X925 achieves a 41% improvement in AI performance, significantly enhancing the responsiveness of edge generative AI such as LLMs. For example, in the deployment of the Meta Llama 3.2 3B model, the Cortex-X925 CPU optimizes the kernel, improving prompt processing speed by 5 times, with token generation speed reaching 19.92 tokens per second, and response latency reduced by 50% compared to the native implementation.
Hardware and software collaboration unleashing the potential of large model applications
Not only in hardware, but Arm’s investment in software is also helping to enhance the performance of large models and accelerate their implementation. In 2024, Arm will launch KleidiAI, enabling AI framework developers to easily achieve optimal performance on Arm CPUs across various devices, supporting key Arm architecture features such as Neon, SVE2, and SME2. As a set of computing kernels aimed at AI framework developers, KleidiAI can integrate with popular AI frameworks such as PyTorch, Tensorflow, MediaPipe, and Angel, aiming to accelerate the performance of key models such as Meta Llama 3, Phi-3, and mixed large models, bringing significant performance improvements to generative AI workloads.
For example, Alibaba’s Tongyi Qianwen model integrated with KleidiAI and the lightweight deep learning framework MNN achieved a 57% improvement in pre-fill performance and a 28% improvement in decoding performance. Additionally, Arm collaborated with Tencent to incorporate KleidiAI technology into Tencent’s self-developed Angel machine learning framework, bringing significant performance improvements to various Arm-based devices across different operating systems: the pre-fill part of the mixed large model accelerated by 100%, while the decoder’s speed increased by 10%.
Conclusion
As large models become the core productivity of the digital economy, the paradigm of computing power distribution determines the breadth and depth of industrial intelligence.
Arm builds the energy efficiency benchmark for the cloud with the Neoverse computing platform, opens up edge intelligence with the edge AI computing platform and terminal CSS, and through architectural innovation and ecosystem collaboration, creates a seamless computing power infrastructure for “cloud-edge” integration. This full-stack layout not only addresses the energy efficiency and scenario adaptation challenges of large model implementation but also builds an open and win-win technology ecosystem, making computing power a truly inclusive resource.
From cloud data centers to intelligent terminals at the edge, Arm’s role has far exceeded that of a chip supplier, becoming a driver of the computing power network in the AI era. As the implementation of AI accelerates, its technological layout will continue to unleash a multiplier effect, driving various industries to achieve “unbounded computing power, practical implementation” in the intelligent transformation—this is not only the practice of Arm’s vision but also the inevitable path for the industrialization of large models.
Hot Articles
Huawei Releases L3, Responsibility Definition Transitioning from “Driver Full Responsibility” to “Shared Responsibility between Manufacturers and Users”
2025-04-30

Analysis of Local MCU Companies’ 2024 Financial Reports: Consumer Electronics Recovery, Automotive Regulations Still Burning Money
2025-04-29

Intel CEO’s Internal Letter: Cut Processes, Cut Levels, Bet on Technology
2025-04-28
South Korea’s “National Treasure” Semiconductor Expert Takes Office in China
2025-04-27

Dissecting a 7kW Home Car Charging Pile: Engineering Design is Very Complex
2025-04-26

