Click the business card to follow and add a “⭐” to learn anytime, anywhere.
When analyzing Tesla’s RF recruitment positions, we mentioned vehicle networking. So, what exactly is vehicle networking? The car space is one of the three most important spaces for human activities, alongside home and work spaces. Therefore, the importance of vehicle networking is also increasing.
What Is Vehicle Networking?
Vehicle networking includes V2V, V2I, V2P, V2N, and V2X. What do these letters mean? The letter V stands for Vehicle, representing the vehicle itself; 2 means ‘to’, which is commonly used in English abbreviations, such as B2B/B2C, etc.; the following letters represent the objects with which the vehicle needs to exchange information.
V2V stands for Vehicle to Vehicle, indicating wireless communication between vehicles. This allows cars to sense information from surrounding vehicles while driving, helping to prevent risks and notify drivers to take evasive actions. This function is already applied in many household cars today, primarily using millimeter-wave radar or cameras to detect safety risks.
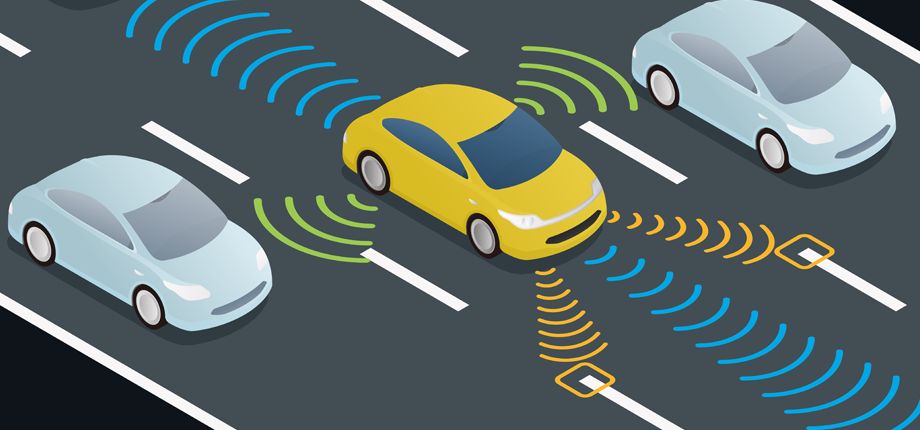
V2I, where I stands for Infrastructure, refers to communication between vehicles and road infrastructure, such as traffic lights, cameras, and other detection devices on the road, as well as lane markings and traffic signs. With this function, there is no need to worry about crossing lines or running red lights, while it can also reduce the likelihood of traffic accidents in poor visibility situations, thus improving driving safety. The countdown function for red lights displayed on Gaode Maps can also be considered a form of V2I.
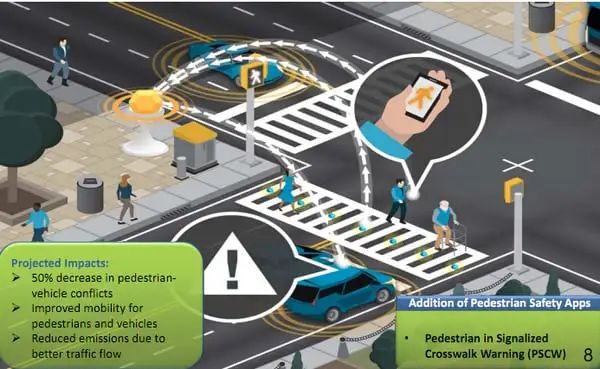
V2P, where P stands for Person, refers to communication between people and vehicles. When we are in the car, communication between humans and vehicles begins, involving speed displayed on the meter, fuel level, and door alarms, etc. This human-vehicle communication is also crucial, as a friend once said, once in the car, their legs become the accelerator and brake, their hands the steering wheel, and they must always be alert to their surroundings. In addition to communication between the vehicle and the driver, it also includes communication between the vehicle and pedestrians on the road. How the vehicle predicts the pedestrian’s movement direction and takes necessary safety measures is also an important topic for road traffic safety.

V2N, where N stands for Network, includes vehicles connecting to data centers or control centers, allowing control over the vehicle’s status through the control center.
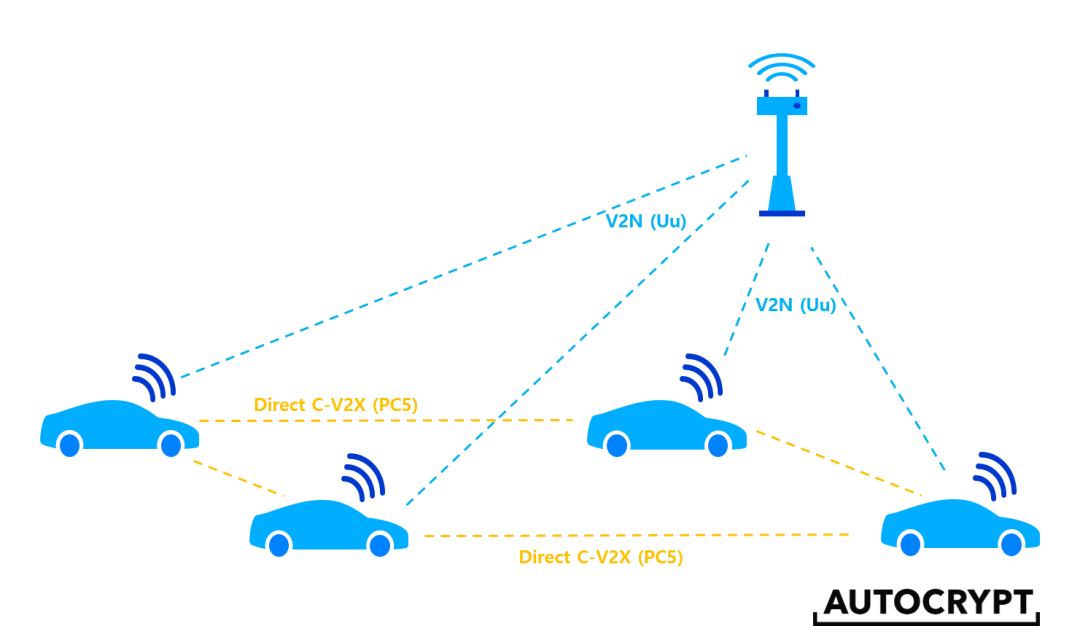
Clearly, these do not encompass all vehicle communications, hence we have V2X, where X represents Everything, the concept of connecting vehicles to all things, including V2V, V2I, V2P, and V2N, etc. Through V2X technology, the safety of both manual and autonomous driving can be achieved.
What Standards Exist for Vehicle Networking?
Currently, V2X mainly has two communication standards—DSRC and C-V2X. DSRC is a short-range wireless communication system based on the IEEE802.11 family, specifically the 802.11p standard; while C-V2X is a vehicle networking system established based on cellular communication networks, from the early LTE-V2X to the current 5G-V2X.
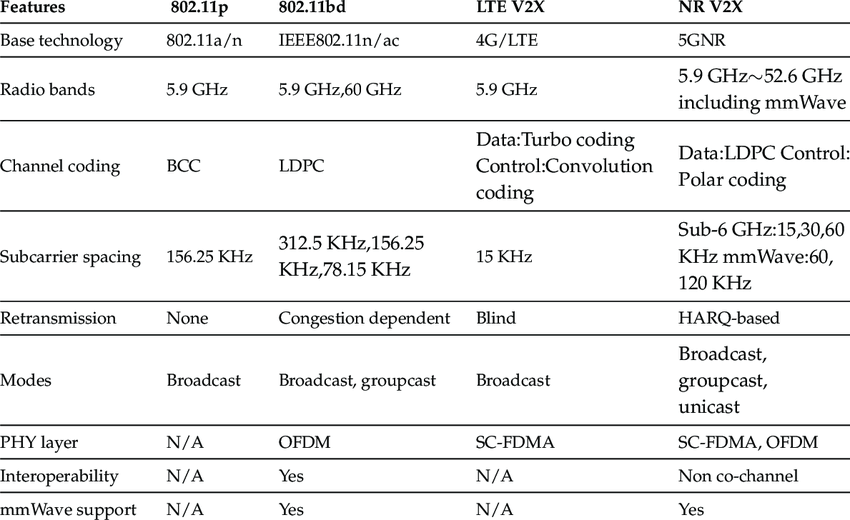
DSRC is a somewhat complex acronym, but its full name is actually simple. Dedicated Short-Range Communications, which means dedicated short-range communication. DSRC is a wireless communication technology based on 802.11p that enables highly secure, high-speed direct communication between vehicles and surrounding infrastructure without involving any cellular infrastructure. IEEE 802.11p is a revision of the IEEE 802.11 standard that defines enhancements to support intelligent transportation system (ITS) applications.
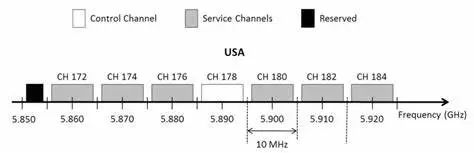
DSRC operates in the 5.9 GHz (5.85-5.925 GHz) frequency band, including 7 channels of 10MHz and reserving a 5MHz protection interval at the bottom, specifying whether each channel is a service channel (Service Channel, SCH) or a control channel (Control Channel, CCH).
NXP, a chip manufacturer, has high hopes for DSRC technology and is a strong advocate for it. In 2018, NXP released a white paper on DSRC technology—IEEE802.11p ahead of LTE-V2V for safety applications – White Paper. It compared the technologies of 802.11p and LTE-V2V in detail and launched a series of chips for DSRC short-range communication.


The V2X system platform launched by NXP operates at 5.9 GHz and 760 MHz, compatible with global software protocols from leading suppliers, achieving a true global V2X solution. This platform meets and exceeds the current guidelines of the proposed rulemaking notice from the U.S. Department of Transportation, as well as emerging standards in Europe, Japan, and South Korea. It is currently applied in vehicles from multiple manufacturers, including Volkswagen.
DSRC short-range wireless communication features low latency, high-speed communication, and does not require connection to cellular networks, but this Wi-Fi-based DSRC performance has limitations—Wi-Fi struggles to support high-speed moving scenarios. As speed increases, DSRC signals begin to drop sharply, leading to poor reliability and significant delay jitter, so for a long time, DSRC’s performance has been unstable and has remained in the testing phase.
Therefore, C-V2X was developed, where C stands for Cellular, meaning C-V2X is a vehicle networking based on cellular communication.
When 802.11p was positioned as the DSRC standard in 2010, 3GPP was also discussing the cellular communication vehicle networking standard C-V2X. However, during the 3G era, due to the speed and latency issues of cellular communication, it was difficult to apply in vehicle networking. It wasn’t until the 4G LTE era that the cellular communication standard based on LTE-V2X was incorporated into 3GPP’s Rel-4. Therefore, C-V2X mainly includes the earlier LTE-V2X and the current 5G/NR-V2X.
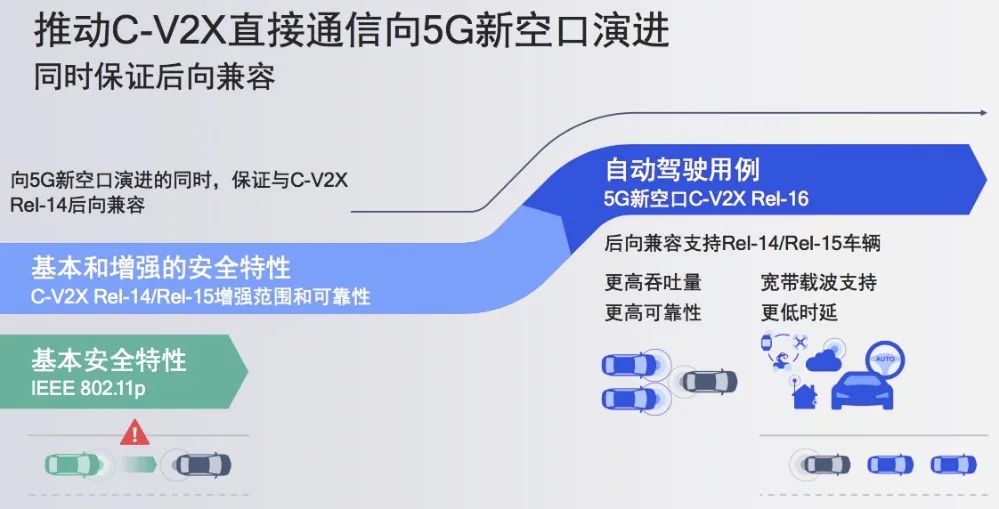
Qualcomm, a strong supporter of C-V2X, launched the 9150 C-V2X chipset as soon as the LTE-V2X standard was introduced. The 9150 chipset is optimized specifically for the Rel-14 version of C-V2X direct communication, supporting not only GPS positioning but also Beidou positioning and high-precision positioning.

-
https://www.nxp.com/products/wireless-connectivity/dsrc-safety-modem:DSRC-MODEM
-
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/541727482
-
https://www.auto-made.com/news/show-6479.html
-
http://www.shujubang.com/Htmls/NewsInfo/55/NewsInfo_16798.html
-
https://www.techwalker.com/2018/0912/3110972.shtml
-
https://carrier.huawei.com/cn/products/wireless-network-v3/Components/c-v2x
-
https://www.qualcomm.com/research/5g/cellular-v2x