1. Phenomenon Description:
The user cannot connect to the network, and the local connection icon in the system tray shows an exclamation mark indicating that the IP is restricted.

2. Cause Analysis
1. Many users do not understand TCP/IP and do not know how to set parameters such as “IP address”, “subnet mask”, and “default gateway”. Sometimes users do not obtain this information from the administrator, or they may have inadvertently modified these settings. Many users are unaware of how to set parameters like “IP address”, “subnet mask”, and “default gateway”; they may not have received this information from the administrator, or they may have inadvertently changed it.
2. When administrators or users set parameters based on the information provided by the administrator, mistakes may lead to incorrect input of parameters.
3. During maintenance and debugging of client machines, temporary IP addresses may be used, causing conflicts.
3. Solutions
The following methods can resolve IP conflicts:
1. If Computer A has an IP address of 10.168.10.108 and receives an IP conflict warning at startup,
2. First, change Computer A’s IP address to an unused address within the local area network, such as: 10.168.10.253, to ensure it can communicate normally.
3. Identify the source of the conflict.
On Computer A, use the remote query command nbtstat –a 10.168.10.108 to find the computer information associated with that address, such as MAC address, computer name, etc. See the image below:
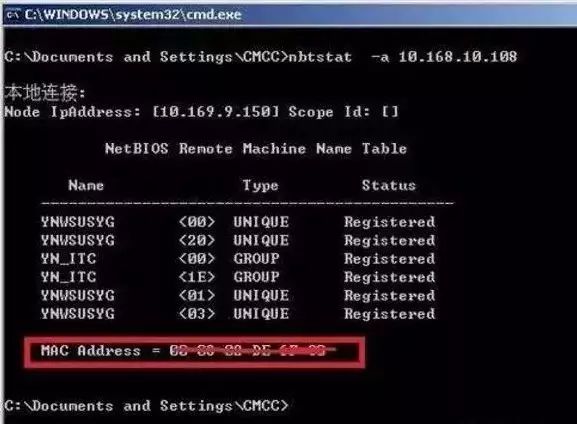
4. Based on the MAC address or computer name, you can trace the conflict source through previous records of IP, MAC, computer names, etc.
5. Then notify the person causing the conflict to change their IP address.
4. Prerequisites for This Method
For easier management, it is necessary to collect user computer IP, MAC, and computer names in advance, which serves as maintenance information resources and is also part of the basic work of network management.
1. Querying IP and MAC addresses
First, click on the computer “Start – Run”, enter CMD and press Enter to access the command prompt.
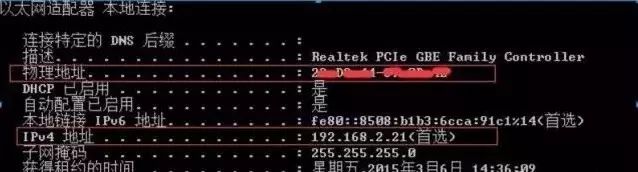
Then enter the command ipconfig /all

After pressing Enter, you will see the following result, with the MAC address and IP address highlighted in red.
2. Query the computer name and change it to the user’s name.
First, right-click on “Computer” on the desktop and select “Properties” to view the computer name on the pop-up page.
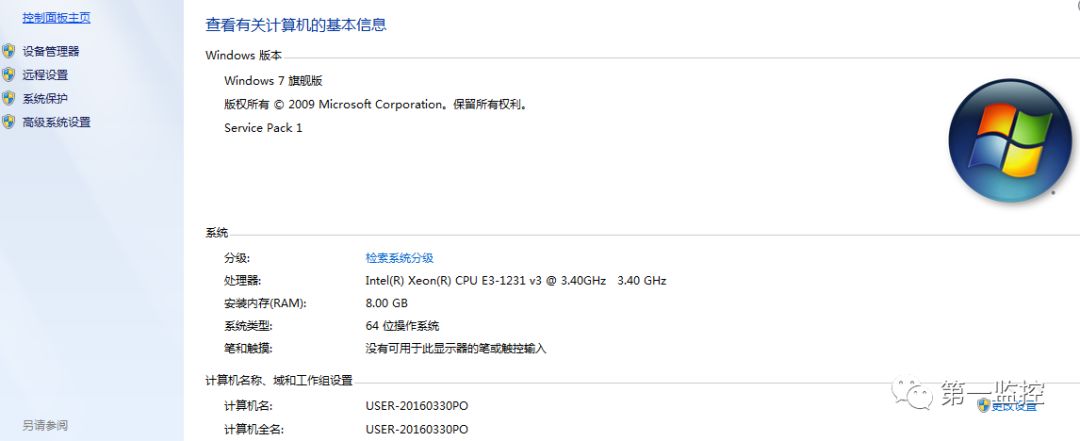
If the computer name appears random, you can click the “Change Settings” button to modify it to the appropriate user name.