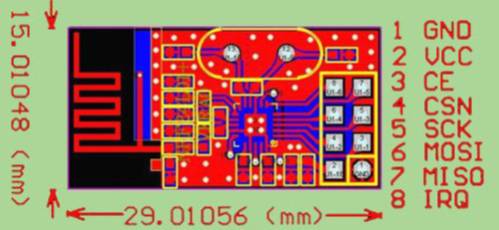
Implementing SPI Communication for Arduino
Hello everyone, Rabbit Brother is back! Today we are going to learn a super practical communication method – SPI communication. It’s like a “highway” between Arduino and peripherals, allowing data transfer to be fast and stable. Whether dealing with SD cards, displays, or various sensor modules, SPI is a great tool. Let Rabbit Brother guide … Read more