SPI (Solder Paste Inspection) refers to the solder paste inspection system, whose main function is to detect the quality of solder paste printing, including volume, area, height, XY offset, shape, bridging, etc. To quickly and accurately detect extremely small solder paste, detection principles generally use PMP (Phase Modulation Profile Measurement Technology) and Laser (Laser Triangulation Measurement Technology).
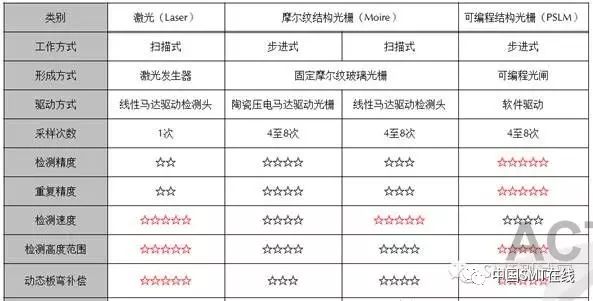
1. Laser Triangulation Measurement Technology
The detection light source used is laser. The distortion generated by the laser beam on different height planes causes the detection head to move continuously in a certain direction, and the camera takes pictures at set time intervals, thus obtaining a set of laser distortion data, which is then calculated to obtain the test results (as shown below).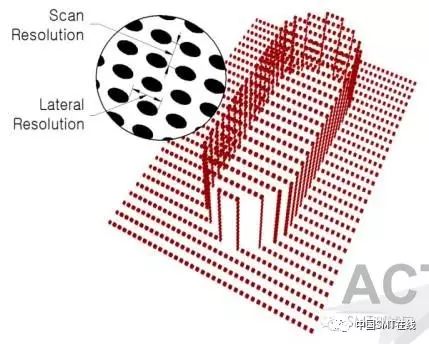
Advantages: Fast detection speed.
Disadvantages: 1) Low laser resolution, generally only 10 – 20um level.
2) Single sampling, low repeatability accuracy.
3) Sampling during motion, external vibrations and transmission vibrations have a significant impact on detection.
4) The monochromatic light of the laser has a weak adaptability to the color of PCB boards.
Market status: Laser technology has gradually withdrawn from the SPI industry. Currently, South Korea’s Parmi still uses laser technology (dual laser technology).
2. PMP Phase Modulation Profile Measurement Technology
1. Use white light sources to measure solder paste through the phase change of the structured light grating (see below)
2. Use the gray scale change of the structured light grating to measure and obtain high-precision height values (see below)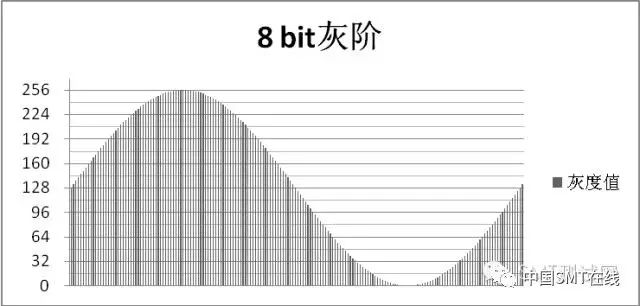
3. Using phase change, each solder paste is sampled 8 times, ensuring high repeatability accuracy of detection (see below)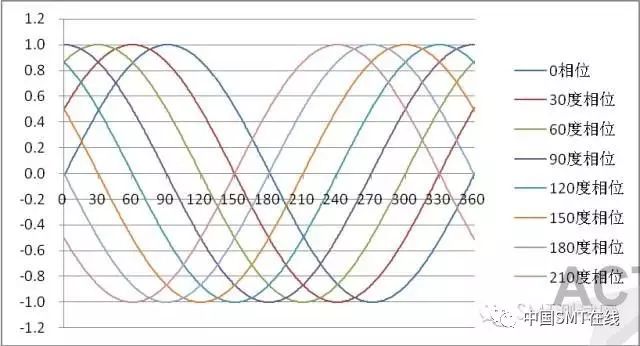
4. PMP technology is further divided into two detection methods: FOV stop-and-go and Scan scanning.
4.1 FOV Stop-and-Go
During detection, no sampling occurs while in motion, and no motion occurs during sampling. This minimizes the impact of vibrations on detection.
Advantages: 1) High detection resolution of PMP principle, 0.37um. 2) Stable multiple sampling, extremely high repeatability accuracy in detection. 3) Not picky about PCB colors.
Disadvantages: Relatively slow speed.
Market: Recognized as the best SPI solution in the industry for its stable detection results, represented by the foreign brand KohYoung from South Korea.
4.2 Scan Scanning
Uses the continuous movement of the detection head to form phase changes of the structured light grating. Sampling occurs while in motion.
Advantages: 1) High detection resolution of PMP principle, 0.37um. 2) Not picky about PCB colors. 3) Multiple sampling, detection repeatability is higher than laser-type devices. 4) Detection speed is faster than FOV stop-and-go.
Disadvantages: External vibrations have a significant impact, and detection repeatability is lower.
Market: Represented by the Taiwanese brand TRI and the foreign brand Cyber.
3. Programmable Structured Light Grating (PSLM)
Programmable Structured Light Grating (PSLM): Realizes software control of the movement of structured light grating, avoiding the mechanical devices necessary for traditional piezoelectric ceramic motors (PZT) driving glass moiré gratings, reducing mechanical wear and customer maintenance costs.
Utilizing advanced phase profile modulation measurement technology (PMP), 8-bit gray scale resolution achieves a detection resolution of 0.37 microns, improving measurement accuracy by two orders of magnitude compared to laser measurement, greatly enhancing the detection capability and applicability of the equipment.