In the field of industrial communication, Modbus RTU and RS-485 are often mentioned together. Many people mistakenly believe they are the same thing, but in reality, these two concepts are entirely different; they are simply used in close conjunction in industrial control.
What is RS-485?
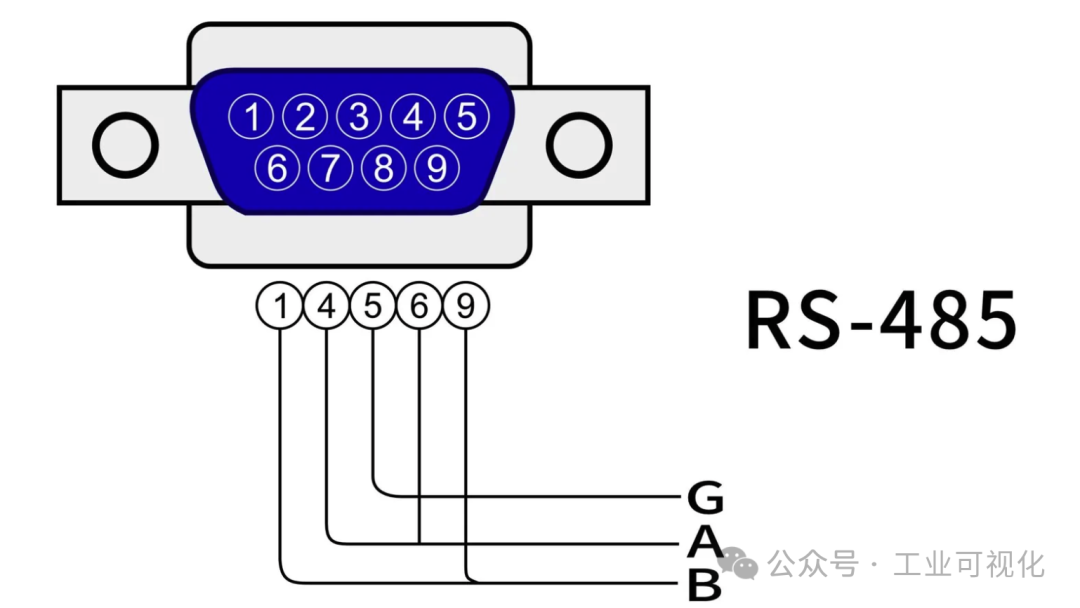
RS-485 is a physical layer communication standard that defines how devices transmit data through electrical signals. Similar to USB or Ethernet, RS-485 specifies the voltage, level changes, and communication protocols of the signals, but does not concern itself with the specific content or format of the data. Its main features include:
- Differential signal transmission: RS-485 uses two wires (A and B) for differential transmission, greatly enhancing its anti-interference capability, making it very reliable in industrial environments.
- Long-distance transmission: It can achieve stable signal transmission over approximately 1200 meters and supports high communication rates (typically from 1200bps to 115200bps).
- Multi-point communication: It supports up to 32 devices communicating on the same bus, making this point-to-multipoint structure very practical in industrial systems.
- Half-duplex communication: RS-485 is half-duplex, meaning it can either send or receive data at the same time, but not both simultaneously.
In short, RS-485 is a basic “data transmission channel” that specifies how electrical signals flow between devices and how they are connected.
What is Modbus RTU?
 RTU, due to its simple hardware architecture and low cost, plays an important role in small-scale automation systems. For example:
RTU, due to its simple hardware architecture and low cost, plays an important role in small-scale automation systems. For example:
Modbus RTU is an application layer protocol that focuses on defining and processing data content. The Modbus protocol was proposed by Modicon in 1979 to standardize communication between devices. RTU is one of its transmission modes, characterized by being compact, efficient, and suitable for scenarios with limited device resources.
The main features of Modbus RTU include:
- Data frame transmission: Communication data is organized into a frame structure, including device address, function code, data segment, and a checksum verified by cyclic redundancy check (CRC).
- Master-slave architecture: It adopts a master station controlling slave stations, where the master polls each slave to execute commands, and the slave responds with results after receiving instructions.
- Efficiency: The RTU mode improves communication efficiency by representing data in binary.
It is important to note that Modbus RTU does not concern itself with how data is transmitted at the lower level; it only defines the communication rules. To transmit Modbus protocol data frames, RS-485 is often used as the physical layer transmission medium.
The Relationship Between Modbus RTU and RS-485
From the definitions above, it is clear that RS-485 and Modbus RTU focus on entirely different layers. In simple terms:
- RS-485 is responsible for electrical transmission, acting as the “carrier” that transports data from device A to device B.
- Modbus RTU is responsible for data content, acting as the “commander” that defines how data is encoded, decoded, and parsed.
This is akin to a railway system, where RS-485 is the tracks that define the train’s route, while Modbus RTU is the cargo manifest on the train, detailing the goods and data content loaded in each car.
In industrial systems, Modbus RTU is typically used in conjunction with RS-485, as the point-to-multipoint capability and anti-interference performance of RS-485 are very suitable for the multi-device communication needs of Modbus. Through this combination, engineers can easily achieve data exchange between programmable logic controllers (PLCs), sensors, and actuators.
Case Study: RS-485 Data Communication Based on Modbus RTU

In the field of industrial automation, communication between variable frequency drives and PLCs is a typical example. Suppose we have a factory that needs to control the speed of a variable frequency drive through a PLC. The PLC and the variable frequency drive are connected via an RS-485 bus, and both communicate using the Modbus RTU protocol:
- The PLC issues a command: “Set the target speed of the variable frequency drive to 1500 RPM”; this command is packaged as a Modbus RTU data frame.
- RS-485 transmits this data frame in the form of electrical signals to the variable frequency drive.
- The variable frequency drive receives the command, parses the data frame, extracts the target speed, and then executes the speed adjustment task.
- If feedback is required, the variable frequency drive will return a Modbus RTU response frame via RS-485, informing the PLC that the current speed has been adjusted to 1500 RPM.
In this example, RS-485 is merely the “pipeline” for transmitting signals, while Modbus RTU ensures that the variable frequency drive and PLC communicate using the same “language”.
Although Modbus RTU and RS-485 are frequently used together, they are not the same thing. RS-485 addresses “how to transmit” and is a standard at the signal level; Modbus RTU addresses “what to transmit” and focuses on data format and protocol content. From a technical perspective, they resemble a “partnership between hardware and software”—one lays the road, while the other builds the bridge, together serving the communication needs of industrial devices.
Recent Articles:
| Unveiling the Correct Approach for MES to Utilize OPC UAModbus !!! RTU or TCP ???Why RS-485 to Ethernet is Indispensable in Industrial Sites?Apache Top Project !!! 50+ PLC Communication Fully CoveredIn-Depth Revelation !! Modbus from 0x01 to 0x10Insider Secrets !!! DTU and PLC Communication Techniques! |