 Join the exclusive group for electrical automation technology exchange
Join the exclusive group for electrical automation technology exchange Join the exclusive group for electrical automation procurement and sales
Join the exclusive group for electrical automation procurement and sales Join the exclusive group for electrical automation project docking
Join the exclusive group for electrical automation project docking Join the exclusive group for electrical automation personnel recruitment
Join the exclusive group for electrical automation personnel recruitmentOverview of Modbus Client Function Code 23
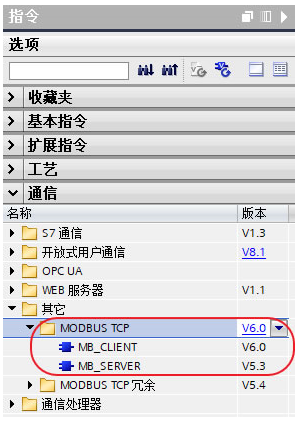
Testing Environment and Content for Modbus Client Function Code 23
Configuration and Programming of Modbus Client Function Code
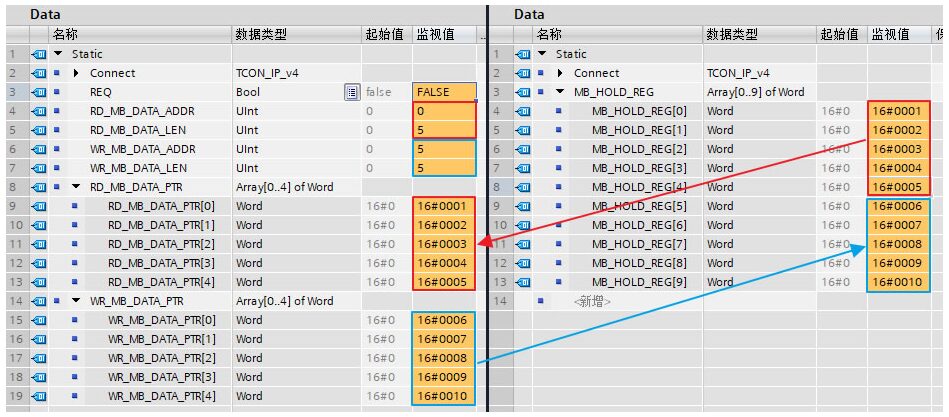
(1) Client Instruction Invocation and Parameter Allocation
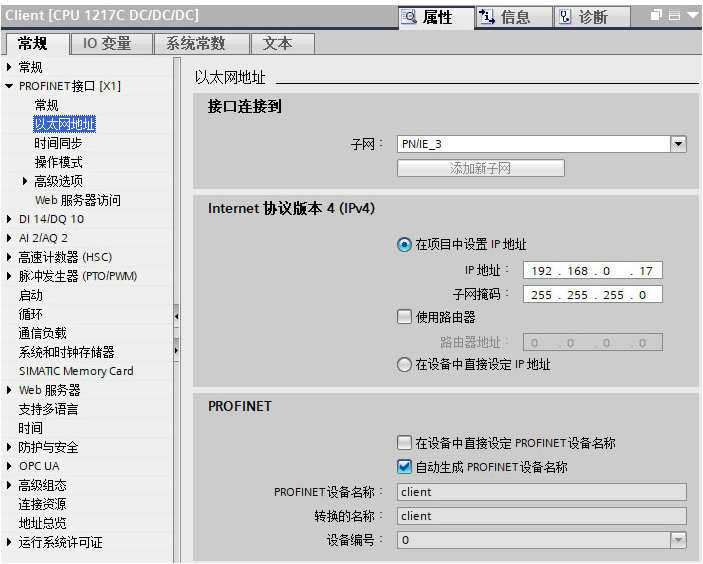
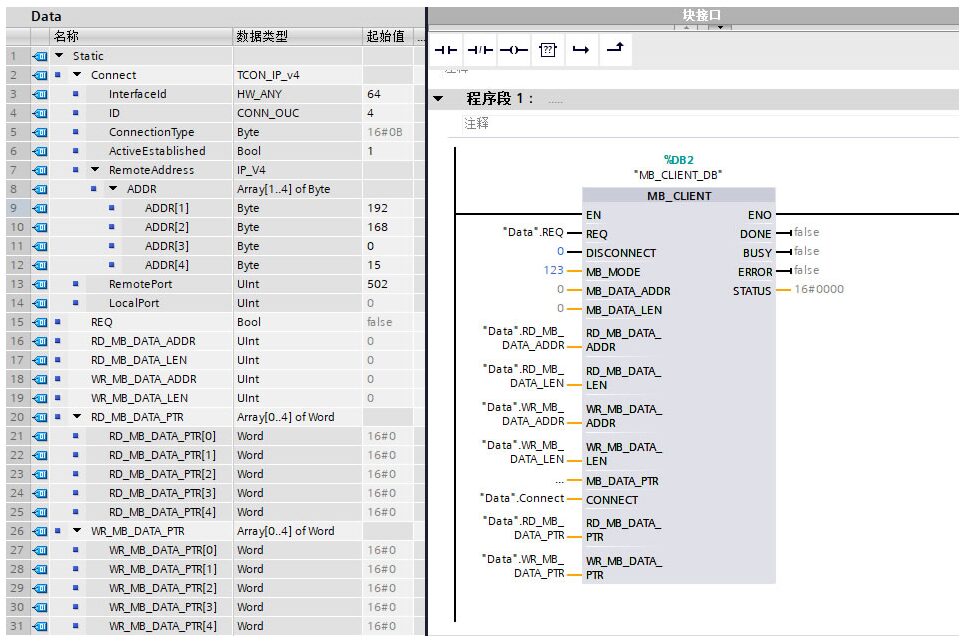
| Parameter | Declaration | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
RD_MB_DATA_ADDR |
Input |
UInt |
Starting address of the holding registers to be read from the server. Allowed values: 0 to 65535 |
|
RD_MB_DATA_LEN |
Input |
UInt |
Number of holding registers to be read from the server. Allowed values: 1 to 125 |
|
WR_MB_DATA_ADDR |
Input |
UInt |
Starting address of the holding registers to be written to the server. Allowed values: 0 to 65535 |
| WR_MB_DATA_LEN |
Input |
UInt |
Number of holding registers to be written to the server. Allowed values: 1 to 121 |
|
RD_MB_DATA_PTR |
InOut |
Variant |
Pointer to the buffer of register data to be read from the Modbus server. Allowed data types: same as MB_DATA_PTR. |
|
WR_MB_DATA_PTR |
InOut |
Variant |
Pointer to the buffer of register data to be written to the Modbus server. Allowed data types: same as MB_DATA_PTR. |
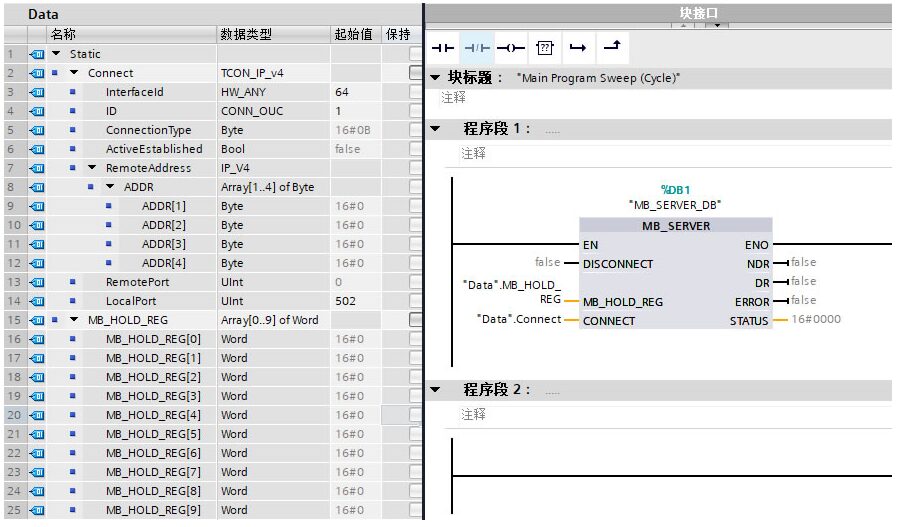
(2) Server Instruction Invocation and Parameter Allocation
(3) Test Results
What Everyone is Watching
 [Video] How German Engineers Make PLC Cabinets?
[Video] How German Engineers Make PLC Cabinets?
 [Video] How German WITRON Electrical Cabinets are Produced?
[Video] How German WITRON Electrical Cabinets are Produced?
 [Video] What is the Office Environment of German Engineers Like?
[Video] What is the Office Environment of German Engineers Like?
 [Video] Why is PROFINET Better than PROFIBUS?
[Video] Why is PROFINET Better than PROFIBUS?