Through JTAG Debugging – Introduction to DAP, a DAP consists of a DP and an AP, where the AP serves as a window to access the resources behind it. In JTAG debugging, Halt and Step Execution actually control the resources of the CPU behind the AP.In STM32F4xx, the Cortex-M4 registers are controlled via AHB-AP, allowing for the suspension and single-step execution of the Core. The access to registers by AHB-AP is through the system bus, such as AHB or a private bus: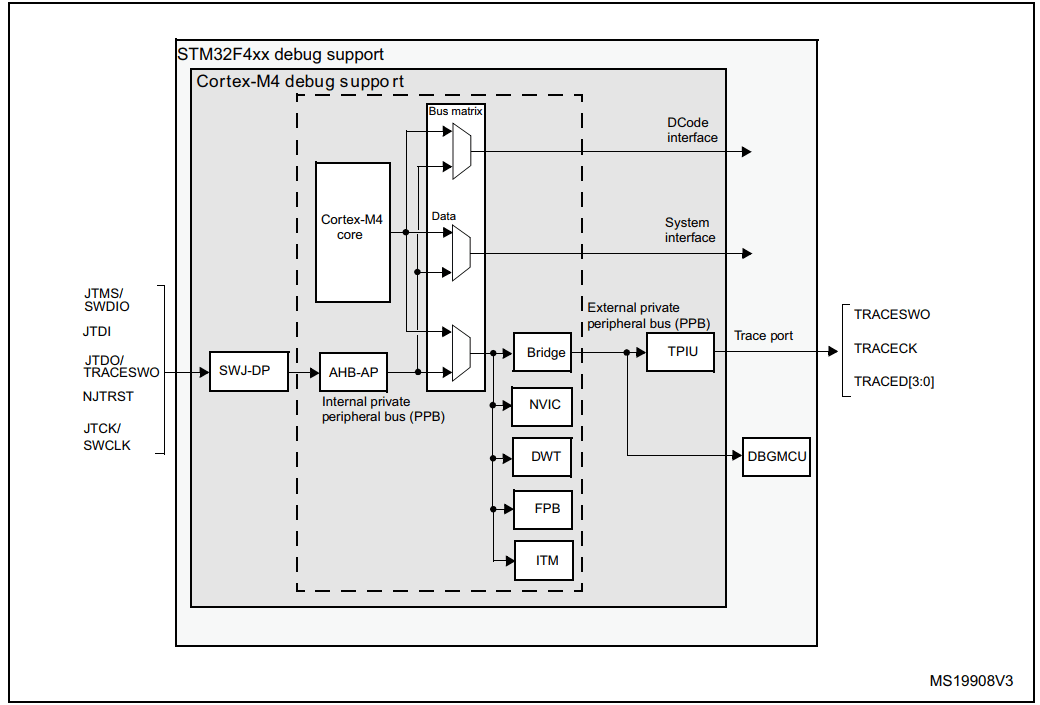 The debugging of the processor is specified by the processor vendor, such as the ARM-related documents below:
The debugging of the processor is specified by the processor vendor, such as the ARM-related documents below:
- Arm Cortex-M4 Processor Technical Reference Manual
- Arm®v7-M Architecture Reference Manual
Taking Context-M4 as an example, the Halt and Step Execution of the processor is accomplished by setting the relevant registers:
| Register | Function |
|---|---|
| DHCSR | Debug Halting Control and Status Register controls the start/stop of debugging, single-step execution, and enables debugging events.
C_DEBUGEN: Enables debug mode. C_HALT: Pauses/resumes processor execution. C_STEP: Single-step execution |
| DCRSR | Debug Core Register Selector Register selects the ARM processor register to accessREGSEL: Specifies access to Arm core register, special-purpose register, or Floating-point Extension register |
| DCRDR | Debug Core Register Data Register stores the data values read from and written to the processor register selected by DCRSR |
| DCMCR | Debug Exception and Monitor Control Register manages exceptions and DebugMonitor in debug mode. |
The above registers are only reset in the case of power-off. To pause the processor during reset:
-
Set DCMCR bit0 (VC_CORRESET)
-
Set DHCSR bit0 (C_DEBUGEN)
For single-step execution, Armv7-M supports two modes:
-
Halting debug stepping (intrusive complete stop single-step execution)
-
Debug monitor stepping (single-step execution controlled by DebugMonitor)
For the first mode, it is achieved by setting the C_STEP of the DHCSR register.