Noticing that the domestic RISC-V ecosystem and industry have made good progress in 2024, recently, after the U.S. technology blockade, several ARM server CPU companies have begun to downsize. There are mixed voices in the industry regarding the RISC-V CPU route, with some people also starting to sing the blues for ARM server CPU companies. In this context, this article presents the core viewpoint: “Under pressure, RISC-V CPU +1, ARM CPU -1”, and summarizes three mind maps for reference.Core Viewpoint 1 – Under Pressure, RISC-V CPU +1:The significance of pursuing the RISC-V server CPU route is not merely aboutdomestic substitutionandlow cost, but also about the potentially more prosperous future brought by the open instruction set (ecological moat + market competition). However, RISC-V is currently not very mature, and pursuing the RISC-V server CPU route is a relatively long-term game and nurturing process.Core Viewpoint 2 – Under Pressure, ARM CPU -1:Although facing a technology blockade, the ARM server CPU route in the domestic market will not come to a complete end. After all, a thin dead camel is still bigger than a horse; the existing ARM embedded and ARM server CPU versions can still operate based on current software, while the next-generation versions, especially the server CPU versions, face certain uncertainties and temporary performance and ecological advantages. It may be a matter of waiting and seeing, using what is available or what has the strength to use (for example, customizing the CMN-XX next-generation bus or obtaining ARM core RTL authorization and evolving independently).Startups in the ARM CPU sector could have sailed smoothly, but due to the technology blockade, their development will be somewhat delayed. The best outcome for startup ARM CPU companies is to eventually achieve a self-sufficient ecosystem similar to Huawei’s Kunpeng CPU, and if they cannot use it, they will switch to the RISC-V ecosystem or other possible options.At this point, some may ask, since there are already Kunpeng, Feiteng, Haiguang X86, and Loongson ecosystems in the country, why are there still so many RISC-V CPU startups and ARM CPU startups? This question is akin to asking why there are so many MCU chip startups; the answer is self-evident: free competition + capital/profit-driven.Developing any ecosystem and standard ultimately needs to map to market interests’ rebalancing; otherwise, developing new ecosystems and standards will lose significance. In the current state of continuous blockade, big players today may cut off five cities, and tomorrow ten cities, which inevitably reminds one of the description by Song Su Xun in “The Six States”: “Today, cut off five cities, tomorrow cut off ten cities, and then have a peaceful night. Looking at the surroundings, the Qin army is coming again.” If the technology blockade is lifted in the future (Will big players allow such fantasies to exist for the people?), then each CPU ecosystem will shift to a logic of commercial free competition. Regardless of whether there is a technology blockade, the ecosystem that can continuously meet customer needs will ultimately gain an advantageous position, and we hope to eventuallymasterthe entire server CPU industry chain and surpass it.Below are three mind maps: Advantages of RISC-V, Challenges Facing ARM Server CPUs, Concerns and Countermeasures for the RISC-V Route to further elaborate on the above viewpoints.Advantages of RISC-V
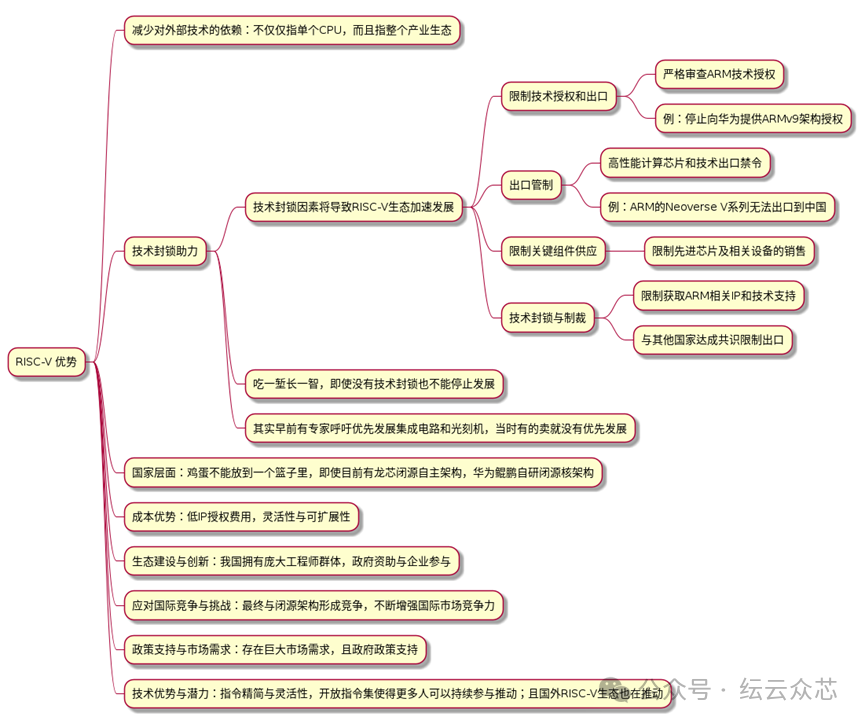
As an open instruction set architecture, RISC-V has multiple advantages, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Reducing dependence on external technologies
– This refers not only to individual CPUs but also to the entire industrial ecosystem
– Helps to break free from dependence on certain key technologies
2. Technology blockade as a catalyst
– Factors of technology blockade will accelerate the development of the RISC-V ecosystem
– Including restrictions on technology licensing and exports, export controls, and limitations on key component supplies
– Even without a technology blockade, a continuous development attitude must be maintained
3. National strategic layout
– Not putting all eggs in one basket
– Need to layout and invest in multiple architectures
4. Cost advantages
– Low IP licensing fees
– Flexibility and scalability
5. Ecological construction and innovation
– Our country has a large pool of engineers
– Government funding and corporate participation are key
6. Responding to international competition and challenges
– Competing with closed-source architectures
– Continuously enhancing international market competitiveness
7. Policy support and market demand
– There is a huge market demand
– Government policies provide strong support
8. Technical advantages and potential
– Simplified instructions and flexibility
– Open instruction sets facilitate broader participation
– The foreign RISC-V ecosystem is also thriving
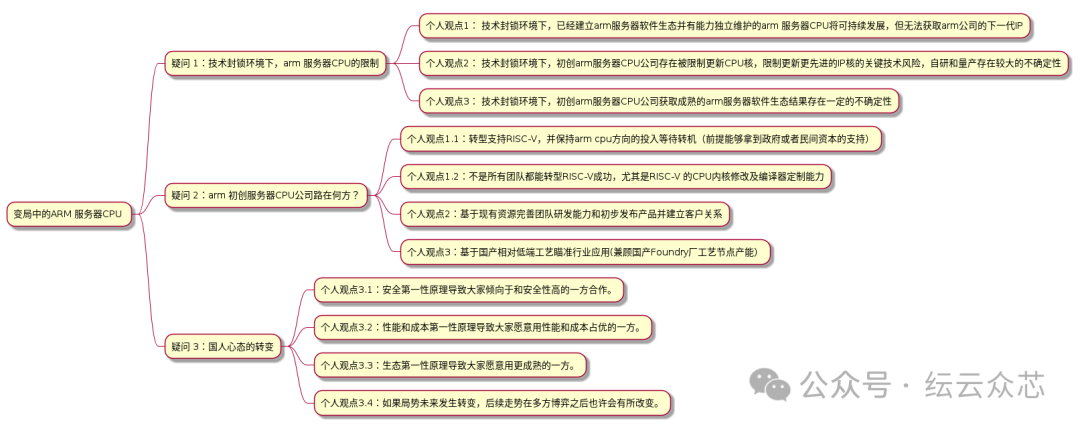
Challenges Facing ARM Server CPUs
ARM server CPUs face a series of challenges, mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1. Restrictions in a technology blockade environment
– 1.1: For companies that have established an ARM server software ecosystem and have independent maintenance capabilities, they can continue to develop in a technology blockade environment, but may not be able to access the next-generation IP from ARM.
– 1.2: For startup ARM server CPU companies, there are key technology risks in updating CPU cores and more advanced IP cores in a technology blockade environment, with significant uncertainty in self-research and mass production. Originally, ARM server CPUs could have sailed smoothly, but due to the technology blockade, the emerging RISC-V server CPUs can take advantage of the situation.
– 1.3: Startups in the ARM server CPU sector may also face uncertainty in acquiring a mature ARM server software ecosystem.
2. Development paths for startup ARM server CPU companies
– 2.1: Transition to support RISC-V while maintaining investment in ARM CPU direction, waiting for opportunities (provided they can obtain support from government or private capital).
– 2.2: Not all teams can successfully transition to RISC-V, especially in terms of CPU core modification and compiler customization capabilities.
– 2.3: Improve team R&D capabilities based on existing resources, quickly release products and establish customer relationships, establish core R&D capabilities for the blocked parts, such as customizing the CMN-XX next-generation bus or obtaining ARM core RTL authorization and evolving independently,not all CPU startup teams can ultimately successfully self-develop these core components.
– 2.4: Target specific industry applications based on relatively low-end domestic processes (while considering the production capacity of domestic foundry factories).
3. Changes in the mindset of the Chinese people
– 3.1: The principle of safety first leads everyone to prefer to cooperate with the safer side.
– 3.2: The principle of performance and cost first leads everyone to be willing to use solutions that excel in performance and cost.
– 3.3: The principle of ecosystem first leads everyone to prefer more mature solutions.
– 3.4: If the situation changes in the future, subsequent trends may change, requiring multi-party games.
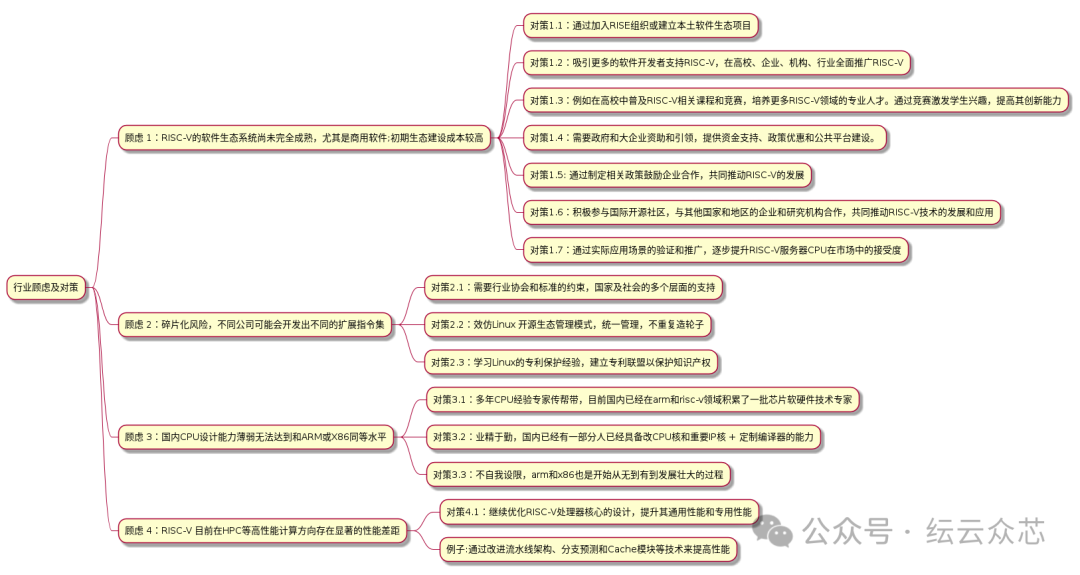
 Concerns and Countermeasures for the RISC-V Route
Concerns and Countermeasures for the RISC-V Route
In the development process of RISC-V, there are some concerns in the industry, but there are also corresponding countermeasures:
1. The software ecosystem is not yet fully mature
– Countermeasure 1.1: Join the RISE organization or establish local software ecosystem projects
– Countermeasure 1.2: Attract more software developers to support RISC-V, promoting it comprehensively in universities, enterprises, institutions, and industries
– Countermeasure 1.3: Popularize RISC-V related courses and competitions in universities to cultivate professionals
– Countermeasure 1.4: Government and large enterprises need to provide funding support, policy incentives, and public platform construction
– Countermeasure 1.5: Formulate policies to encourage enterprise cooperation to jointly promote RISC-V development
– Countermeasure 1.6: Actively participate in international open-source communities and collaborate with other countries and regions
– Countermeasure 1.7: Improve market acceptance through verification and promotion in practical application scenarios
2. Fragmentation risks
– Countermeasure 2.1: Industry associations and standards need to impose constraints, with multi-party support
– Countermeasure 2.2: Imitate the Linux open-source ecosystem management model for unified management
– Countermeasure 2.3: Learn from Linux’s patent protection experience to establish a patent alliance
3. Weak domestic CPU design capabilities
– Countermeasure 3.1: Experts with years of CPU experience can mentor and guide, accumulating a group of experts
– Countermeasure 3.2: There are already individuals in the country capable of modifying CPU cores and important IP cores + customizing compilers
– Countermeasure 3.3: Do not self-limit; ARM and X86 also developed from nothing
4. Performance gaps of RISC-V in HPC and other high-performance computing directions
– 4.1 Countermeasure: Continue to optimize RISC-V processor core design to enhance general and specialized performance
– 4.2 For example: Improve pipeline architecture, branch prediction, and cache module technologies
Overall, the industry needs to adopt multi-faceted measures to address various concerns facing RISC-V development.