“Just a little click, please follow me~”👇
“You know—when a person is feeling down, they particularly enjoy watching the sunset.” — Antoine de Saint-Exupéry, “The Little Prince”
In Python programming, operations on directories are a fundamental and important skill. Whether for file management, data processing, or project deployment, operations such as creating, deleting, and traversing directories are frequently involved. The os module in Python provides a series of powerful functions to accomplish these tasks. This article will take you on a deep dive into the various operations on directories using the os module.1. Introduction to the os ModuleThe os module is an important module in the Python standard library for interacting with the operating system. It provides many functions for handling files and directories, and these functions can be used across different operating systems (such as Windows, Linux, macOS), ensuring good cross-platform compatibility. Before using the functions in the os module, you need to import it:

2. Getting the Current Working DirectoryObtaining the current working directory where the Python script is located is a common operation, which can be easily achieved using the os.getcwd() function:
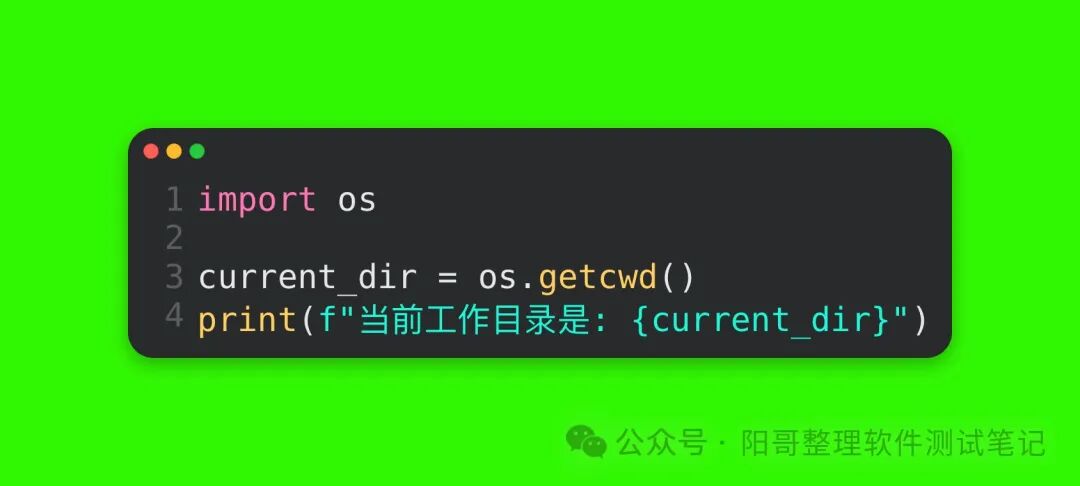
Run Result:
Assuming the script runs under the path C:\Users\YourUsername\Documents\PythonScripts, the result will be:

Code Explanation: The os.getcwd() function returns a string representing the current working directory. After assigning it to the current_dir variable, the print function outputs the result.3. Changing the Current Working DirectoryUsing the os.chdir(path) function allows you to change the current working directory, where the path parameter is the target directory path to switch to. For example, to switch to the root directory of the system (the root directory on Windows is the drive letter root, while on Linux and macOS it is /):
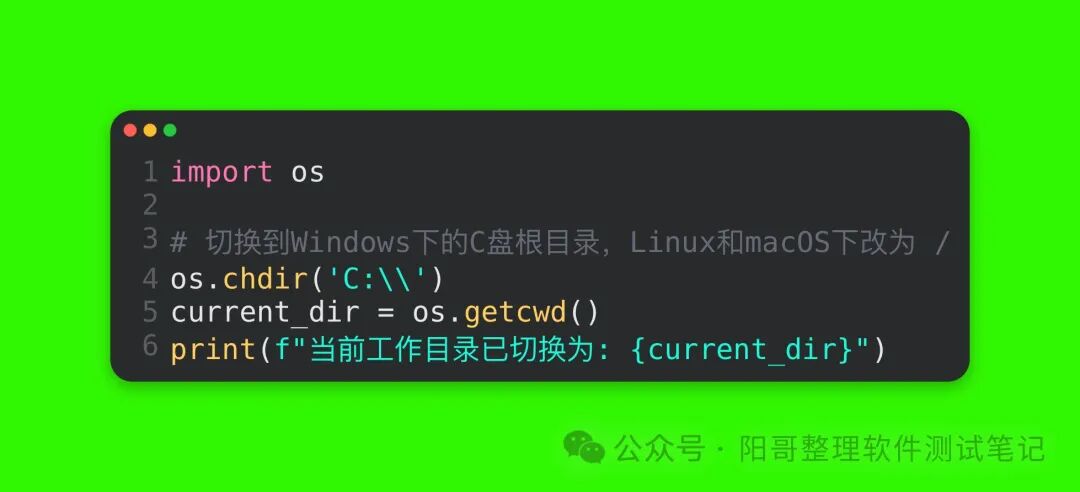
Run Result (Windows Environment):

Code Explanation: os.chdir(‘C:\’) switches the working directory to the root of the C drive. The double backslash is necessary because in Python strings, the backslash is an escape character, requiring two backslashes to represent a normal backslash. Then, the current working directory is retrieved again and outputted.4. Creating Directories(1) Creating a Single DirectoryUsing the os.mkdir(path) function allows you to create a new directory, where path is the path of the directory to be created. For example, to create a new directory named new_folder in the current working directory:

Run Result:

Code Explanation: os.path.join(os.getcwd(), ‘new_folder’) uses the os.path.join function to concatenate the current working directory and the new directory name new_folder into a complete path, ensuring that the path is correctly represented across different operating systems. os.mkdir creates the new directory based on the concatenated path, and finally outputs a success message.(2) Creating Multi-level DirectoriesIf the directory to be created includes multiple subdirectories, you can use the os.makedirs(path) function, which will recursively create all necessary intermediate directories. For example, to create a three-level directory structure like parent_folder/child_folder/grandchild_folder:
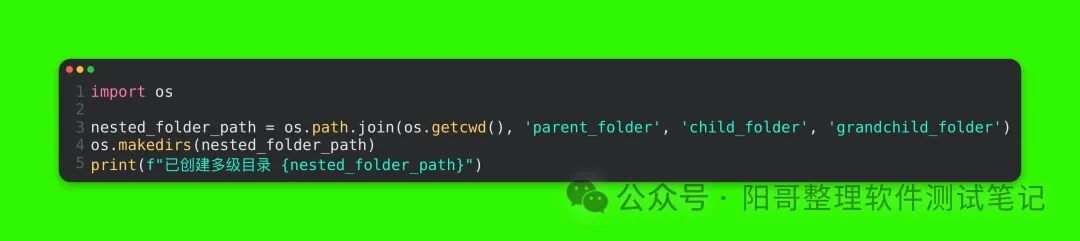
Run Result:

Code Explanation: Similarly, using os.path.join to concatenate the complete multi-level directory path, the os.makedirs function will create the entire directory structure based on this path, including the intermediate parent_folder and child_folder directories.5. Deleting Directories(1) Deleting an Empty DirectoryUsing the os.rmdir(path) function allows you to delete an empty directory, where path is the path of the directory to be deleted. For example, to delete the previously created new_folder directory:
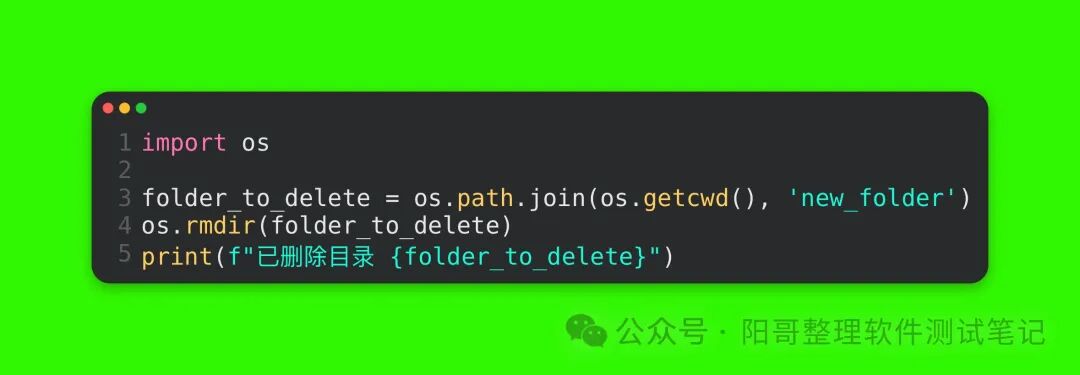
Run Result:

Code Explanation: First, concatenate the path of the directory to be deleted, then use the os.rmdir function to delete that directory. Note that this function can only delete empty directories; if the directory is not empty, it will raise an OSError exception.(2) Deleting a Non-empty DirectoryTo delete a non-empty directory, you need to use the shutil module’s rmtree function. shutil is a module in the Python standard library for advanced file operations. For example, to delete the previously created parent_folder that contains multiple subdirectories:
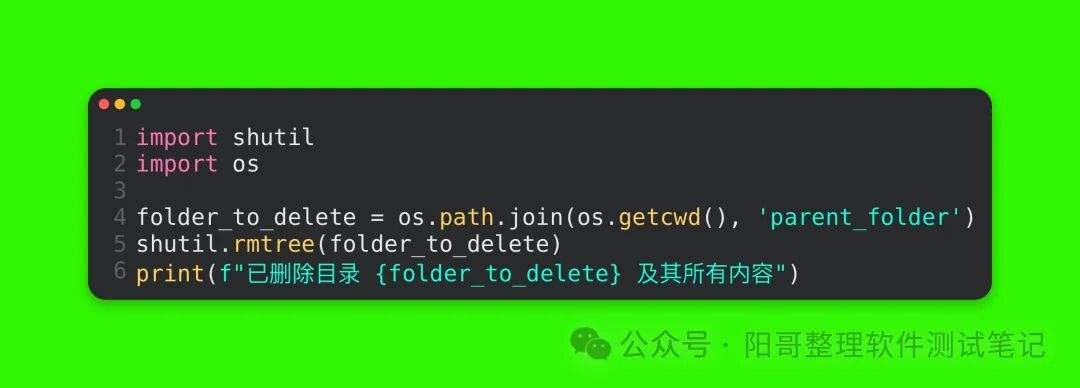
Run Result:

Code Explanation: The shutil.rmtree function will recursively delete the specified directory and all its contained files and subdirectories, effectively removing the entire directory structure from the file system.6. Traversing Directories(1) Simple Traversal of Files and Subdirectories in the Current DirectoryUsing the os.listdir(path) function allows you to list all files and subdirectories in a specified directory, returning a list containing their names. If no path parameter is provided, it defaults to listing the contents of the current working directory. For example:

Run Result (assuming the current directory contains file1.txt, file2.py, and the sub_folder subdirectory):

Code Explanation: os.listdir(current_dir) retrieves a list of all file and subdirectory names in the current working directory, which are then printed one by one using a for loop.(2) Deep Traversal of the Directory TreeUsing the os.walk(top) function allows for depth-first traversal of the directory tree, where top is the path of the directory to traverse. os.walk returns a tuple (dirpath, dirnames, filenames), where dirpath is the current directory path being traversed, dirnames is the list of subdirectory names in that directory, and filenames is the list of file names in that directory. For example, to traverse the entire C:\Users\YourUsername directory (note that this directory may contain many files during actual execution; this is just an example):
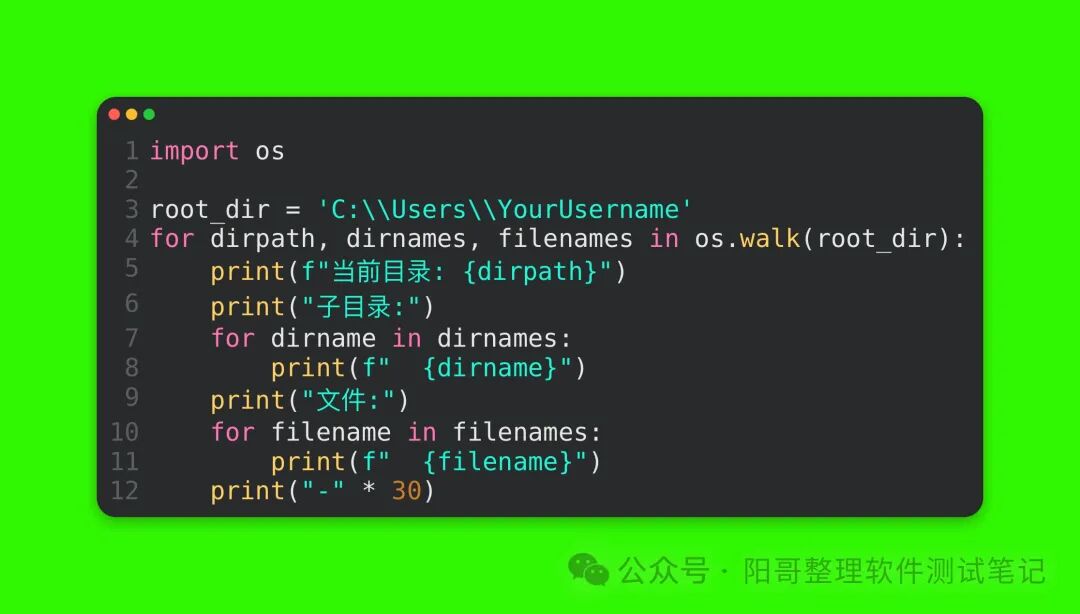
Code Explanation: By iterating over the results returned by os.walk(root_dir) in a for loop, each iteration prints the current directory path dirpath, then iterates through and prints the subdirectory names dirnames and file names filenames, finally printing 30 dashes as a separator to distinguish the output of different directory levels.7. ConclusionThrough the os module, we can easily perform various directory operations in Python. From obtaining and changing the working directory to creating, deleting directories, and traversing the directory tree, these operations are very practical in daily programming. Mastering these skills will enable you to handle file system-related tasks more efficiently, whether for small scripts or large project development. I hope the content introduced in this article will assist you in your Python programming learning and practice. Go ahead and try these directory operation functions of the os module!
“Just a little click, please follow me~”🫰