
Abstract
This study explores the multi-UAV path planning problem and presents a comparative analysis of three different algorithms, including Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO), and Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA). MATLAB was used to implement multi-scenario simulation experiments to verify the performance of each algorithm in multi-UAV cooperative path planning. The experimental results indicate that GWO and WOA algorithms outperform the PSO algorithm in terms of convergence speed and path length, with WOA showing significant advantages in obstacle avoidance and path smoothness.
Theory
The goal of the multi-UAV path planning problem is to find the optimal flight paths for multiple UAVs while satisfying specific constraints. The optimization objectives for path planning typically include the shortest path, lowest energy consumption, and avoidance of obstacles. In this study, we selected three different intelligent optimization algorithms to address the multi-UAV path planning problem:
- Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO): PSO seeks the optimal solution by simulating the information sharing among individuals (particles) in a group, where each particle updates its position based on its own historical best position and the group’s best position.
- Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO): GWO simulates the social structure and hunting behavior of grey wolves, searching through leaders (α wolves), followers (β wolves, δ wolves), and scouts (ω wolves) to gradually approach the optimal solution.
- Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA): WOA finds the optimal solution by simulating the hunting behavior of whales, employing strategies such as the shrinking encircling mechanism and spiral updating positions, demonstrating good global search capabilities.
Experimental Results
In the experiments, we conducted multi-UAV path planning simulations for various terrain scenarios, specifically including:
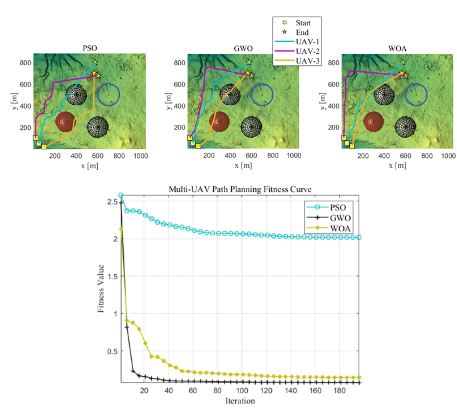
- 2D Plane Scenario: All algorithms successfully found the optimal paths for the UAVs, but GWO and WOA exhibited superior performance in path convergence speed, with WOA particularly demonstrating more efficient path planning capabilities in densely obstructed areas.
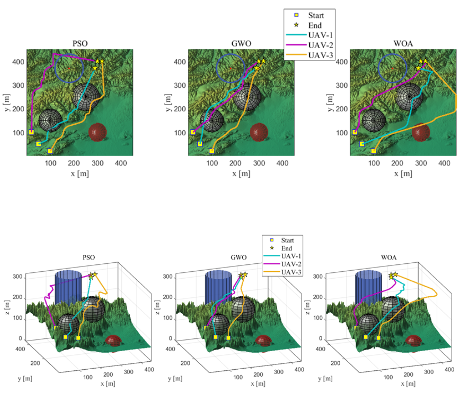
- 3D Complex Terrain Scenario: PSO’s performance in the 3D environment was somewhat inferior, resulting in longer and less smooth paths. GWO and WOA adapted better to complex terrains, with WOA excelling in path smoothness and obstacle avoidance.
Below are the path planning results of each algorithm and their fitness value convergence curves at different iteration counts:
- PSO: Slow convergence with excessive path curvature.
- GWO: Faster convergence with good path optimization, but still faces local convergence issues in complex environments.
- WOA: Fastest convergence with smooth paths and the best obstacle avoidance performance.
Sample Code
% Main program: MainMultiUAVMultiAlgo.m
% Initialize UAV positions, target positions, and obstacles
UAV_num = 3;
start_positions = [50, 50; 150, 150; 250, 250];
target_positions = [900, 900; 850, 850; 800, 800];
obstacles = [300, 300, 50; 600, 600, 80; 700, 400, 60];
% Select algorithm (PSO, GWO, WOA)
algorithm = 'WOA'; % Options: 'PSO', 'GWO', 'WOA'
% Run optimization algorithm
switch algorithm
case 'PSO'
result = PSO_path_planning(UAV_num, start_positions, target_positions, obstacles);
case 'GWO'
result = GWO_path_planning(UAV_num, start_positions, target_positions, obstacles);
case 'WOA'
result = WOA_path_planning(UAV_num, start_positions, target_positions, obstacles);
end
% Plot path
plot_path(result);
% PSO path planning algorithm
function result = PSO_path_planning(UAV_num, start_positions, target_positions, obstacles)
% Initialize particles
% PSO optimization path
% Specific algorithm logic omitted
end
% GWO path planning algorithm
function result = GWO_path_planning(UAV_num, start_positions, target_positions, obstacles)
% GWO optimization path
% Specific algorithm logic omitted
end
% WOA path planning algorithm
function result = WOA_path_planning(UAV_num, start_positions, target_positions, obstacles)
% WOA optimization path
% Specific algorithm logic omitted
end
% Path plotting function
function plot_path(result)
% Plot path based on planning results
figure;
plot(result.x, result.y, 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('x [m]');
ylabel('y [m]');
title('UAV Path Planning');
legend('UAV-1', 'UAV-2', 'UAV-3');
end
References
❝
- Kennedy, J., & Eberhart, R. (1995). Particle swarm optimization. Proceedings of ICNN’95 – International Conference on Neural Networks, 1942-1948.
- Mirjalili, S., Mirjalili, S. M., & Lewis, A. (2014). Grey Wolf Optimizer. Advances in Engineering Software, 69, 46-61.
- Mirjalili, S., & Lewis, A. (2016). The Whale Optimization Algorithm. Advances in Engineering Software, 95, 51-67.
