The RS-485 bus is widely used in communication, industrial automation, and other fields. In practical applications, it is common to encounter questions about whether pull-up and pull-down resistors are needed and what resistance values are appropriate. Below, we will analyze these issues in detail.
1. Why are Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors Needed?
1) When the differential voltage on the RS-485 bus exceeds +200mV, the RS-485 transceiver outputs a high level.
2) When the differential voltage on the RS-485 bus is less than -200mV, the RS-485 transceiver outputs a low level.
3) When the voltage on the RS-485 bus is between -200mV and +200mV, the RS-485 transceiver may output either a high or low level. However, it generally remains in one level state. If the RS-485 transceiver outputs a low level, this represents a start bit for UART communication, which can lead to communication issues.
When the RS-485 bus is open (the RS-485 transceiver is disconnected from the bus) or in an idle state (all RS-485 transceivers are in receive mode, and no transceiver is driving the bus), the differential voltage on the RS-485 bus is essentially 0, placing the bus in an uncertain state. Additionally, due to the design of RS-485 chips to increase the number of nodes on the bus, the input impedance is relatively high, such as 1/4 unit impedance or 1/8 unit impedance (with a unit impedance of 12kΩ, 1/4 unit impedance is 48kΩ). When the pins are floating, they are susceptible to electromagnetic interference.
Therefore, to prevent the RS-485 bus from experiencing the above situations, pull-up and pull-down resistors are typically added to the RS-485 bus (usually a pull-up resistor is connected to A, and a pull-down resistor is connected to B). If using an isolated RS-485 transceiver module (e.g., RSM485PCHT), since the module has internal pull-up and pull-down resistors (for RSM485PCHT, the internal pull-up and pull-down resistors are 24kΩ), external pull-up and pull-down resistors are generally not needed.
2. When are Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors Required?
When encountering signal reflection issues, matching resistors are typically added to avoid signal reflection. For example, in a 1-to-1 communication scenario, as shown in Figure 1. Since the RS-485 bus usually uses twisted pair cable with a characteristic impedance of 120Ω, 120Ω termination resistors are added at both ends of the RS-485 bus to avoid signal reflection issues.
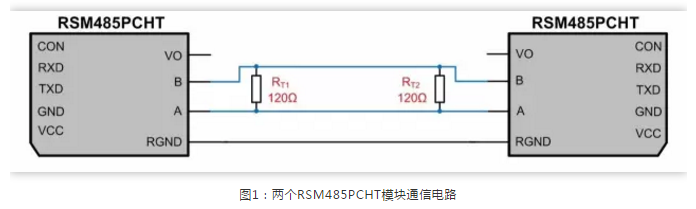
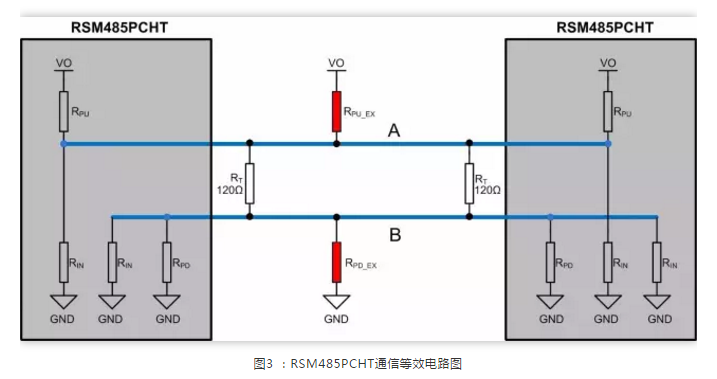
Based on the specific parameters of the RSM485PCHT (as shown in Table 1), the equivalent circuit can be derived as shown in Figure 2, where RPU and RPD are the internal pull-up and pull-down resistors added to the RS-485 bus, and RIN is the input impedance of the module.

When both modules are in receive mode, Kirchhoff’s current law can be applied to nodes A and B to derive the following equations:
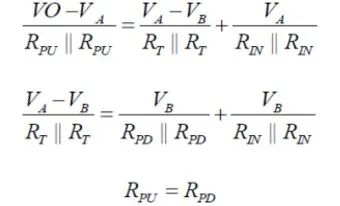
From the above equations, the differential voltage between A and B can be calculated as:
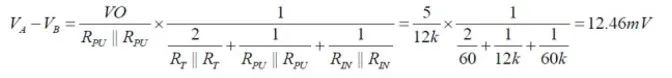
At this point, the module is in an uncertain state, and the module receiver may output either a high or low level. Therefore, it is necessary to add external pull-up and pull-down resistors to ensure that the module does not remain in an uncertain state when idle.
3. How to Choose Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors?
Assuming the output power supply voltage V_O of the module is the same, and since RGND is connected together, the internal pull-up resistors of the modules can be considered to be in parallel. For ease of explanation, the circuit in Figure 2 is organized as shown in Figure 3, where external pull-up and pull-down resistors can be added as a single set or added to each module. For simplicity, we will add a single set of pull-up and pull-down resistors to the RS-485 bus.

-
One article thoroughly explains TCP/IP!
-
Video explanation of operational amplifier principles, the animations are very easy to understand!
-
104 terms for PCB design and manufacturing, useful for both beginners and experts!
-
Are you still willing to be a new media editor in three years?
-
What did your unit distribute for the Mid-Autumn Festival?
-
BUCK circuit principles and PCB layout and wiring considerations
-
Why do microcontrollers need to use C language?
-
Microcontroller programming magic of the three powers separation
-
Detailed explanation of the selection of pull-up and pull-down resistors for RS-485
