The RS-485 bus is widely used in communication, industrial automation, and other fields. In practical applications, one often encounters the question of whether to add pull-up and pull-down resistors and what resistance values are appropriate. Below, we will analyze these issues in detail.
1. Why are Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors Needed?
1) When the differential voltage of the RS-485 bus is greater than +200mV, the RS-485 transceiver outputs a high level.
2) When the differential voltage of the RS-485 bus is less than -200mV, the RS-485 transceiver outputs a low level.
3) When the voltage on the RS-485 bus is between -200mV and +200mV, the RS-485 transceiver may output either a high or low level. However, it generally remains in one level state. If the RS-485 transceiver outputs a low level, this represents a start bit for UART communication, which can lead to communication issues.
When the RS-485 bus is open (the RS-485 transceiver is disconnected from the bus) or in an idle state (all RS-485 transceivers are in receive mode, and no transceiver is driving the bus), the differential voltage on the RS-485 bus is essentially 0, placing the bus in an uncertain state. Additionally, current RS-485 chips are designed with high input impedance to increase the number of nodes on the bus, such as an input impedance of 1/4 or 1/8 of the unit impedance (where the unit impedance is 12kΩ, making 1/4 unit impedance 48kΩ). This high impedance can make the bus susceptible to electromagnetic interference when the pins are floating.
Therefore, to prevent the RS-485 bus from experiencing the aforementioned issues, pull-up and pull-down resistors are typically added to the RS-485 bus (usually a pull-up resistor on A and a pull-down resistor on B). If using an isolated RS-485 transceiver module (e.g., RSM485PCHT), since the module has internal pull-up and pull-down resistors (for RSM485PCHT, the internal pull-up and pull-down resistors are 24kΩ), external pull-up and pull-down resistors are generally not needed.
2. When is it Necessary to Add Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors?
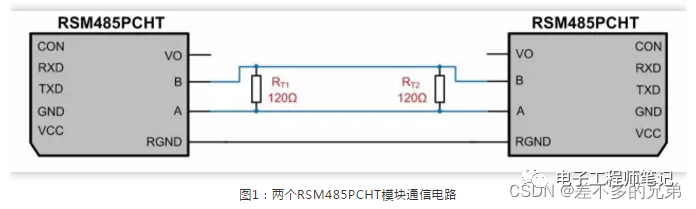
When encountering signal reflection issues, matching resistors are typically added to avoid signal reflection. For example, in a 1-to-1 communication scenario, as shown in Figure 1. Since the RS-485 bus usually uses twisted pair cable with a characteristic impedance of 120Ω, 120Ω termination resistors are added at both ends of the RS-485 bus to avoid signal reflection issues.
– END –
-
In-depth analysis by a Zhihu expert: What is the principle of the microcontroller crystal oscillator pin?
-
So cool! Using 200 LEDs to make a smart watch (open source)
-
The considerations for PCB panelization
-
33 microcontroller I/O interface circuits
If you like it, please give a thumbs up and share; this is the greatest encouragement for good articles.