
Abstract: The RISC-V instruction set has formed a significant advantage over ARM and Intel due to its open-source sharing, and its application is gradually expanding globally, resulting in a large amount of research literature. This study uses important literature on RISC-V themes worldwide as a dataset and analyzes the research trends, main research institutions, and research categories in the RISC-V research field through bibliometric analysis. By using Vosviewer co-occurrence analysis and LDA topic modeling, the main research topics in the RISC-V research field are analyzed, providing insights into research topic judgments and future research trends.
Keywords: RISC-V; research trends; bibliometrics; co-occurrence; topic modeling; LDA
In 2010, a research team from the University of California, Berkeley, designed a new instruction set from scratch – “RISC-V”. RISC-V is an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA) based on the principles of Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC). Compared to the completely closed X86 instruction set and the high licensing fees of ARM instruction sets, RISC-V is a fully open-source instruction set based on the BSD license, characterized by superior performance and complete free access. The design goal of RISC-V is to meet the processor demands of various complexities from microcontrollers to supercomputers, supporting multiple implementation methods from FPGA, ASIC, and future devices, while efficiently realizing various microarchitectures, supporting extensive customization and acceleration features, and adapting well to existing software and programming languages. RISC-V not only breaks the monopoly of ARM and Intel in the current ISA environment but also establishes an open framework to promote global cooperation and innovation[1]. Given the importance of RISC-V, understanding the global research trends of RISC-V is of great significance for research and application in the field. This study uses important journal and conference papers on RISC-V as a dataset, applying bibliometric analysis, co-occurrence, and LDA topic modeling to conduct an in-depth analysis of the research trends from the perspectives of publication trends, major research institutions, and research themes.
This study retrieves journal and conference literature from the SCI and CPCI source databases, using the search term TS=”RISC-V”, with the retrieval date being November 10, 2020, resulting in a total of 298 articles.
2.1 Overall Research Trends
As shown in Figure 1, the overall time trend of RISC-V publications indicates that the earliest research publication was in 2014, which is the fourth year after the birth of RISC-V. From 2014 to 2019, the publication volume grew rapidly, indicating a period of rapid development, but there was a noticeable decline in publication volume in 2020. However, due to policy restrictions on the use of related technologies in the United States, restricted countries are attempting to break through by applying RISC-V. Therefore, it is predicted that RISC-V research will continue to rise rapidly in the coming years, possibly entering an explosive phase.
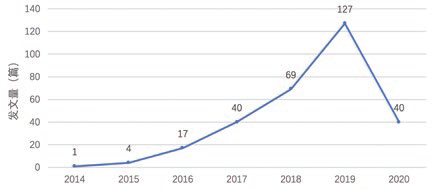
Figure 1 Overall Time Trend of RISC-V Publications
Regarding the countries involved, the top 20 countries in terms of literature output in the RISC-V field are shown in Figure 2, with the top five being the United States, India, France, Switzerland, and China. The United States has an absolute advantage in research on this topic, with a publication volume far exceeding that of India, making it the main battlefield for RISC-V research in the world today. Although China ranks fifth, its publication volume is relatively low compared to that of the United States. In 2020, to ensure that universities, governments, and companies outside the United States could use the open-source RISC-V without political influence, the headquarters of the RISC-V Foundation moved to Switzerland. It is predicted that Swiss research institutions will increasingly join the field of research in the future, making Switzerland a more important research country.
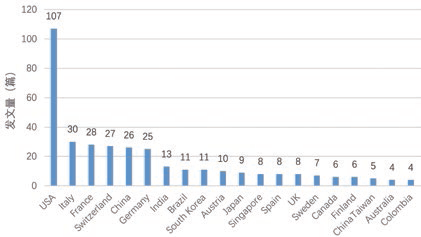
Figure 2 Top 20 Countries/Regions in RISC-V Publications
2.2 Major Research Institutions
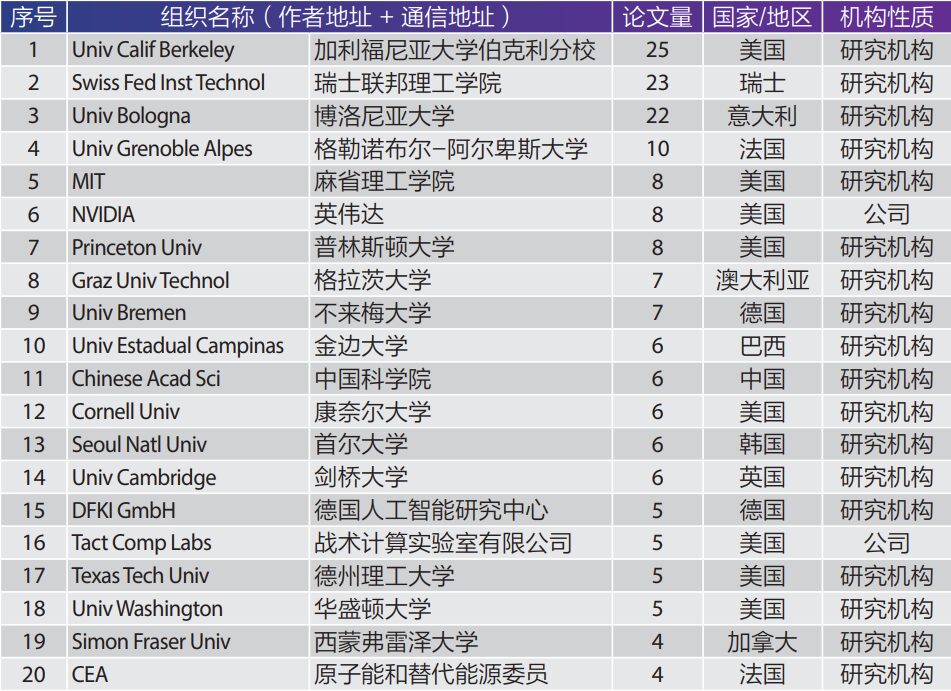
In terms of research institutions, Table 1 lists the top twenty institutions in the RISC-V research field, with eight from the United States, two each from Germany and France, and one each from China, Australia, Brazil, South Korea, Canada, Switzerland, Italy, and the United Kingdom. The University of California, Berkeley, as the birthplace of RISC-V, has the highest publication volume (25 articles), while the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, as the headquarters of the RISC-V Foundation, ranks second (23 articles). Among the top 20 institutions, only NVIDIA and the U.S. Tactical Computing Laboratory are companies, while the other 18 are research institutions. The only institution from China to enter the top 20 is the Chinese Academy of Sciences (6 articles), with 3 from the Institute of Information Engineering, 1 from the Institute of Automation, 1 from the Institute of Computing Technology, and 1 from the Institute of Microelectronics.
Table 1 Top 20 Institutions in RISC-V Research Field
2.3 Major Research Categories
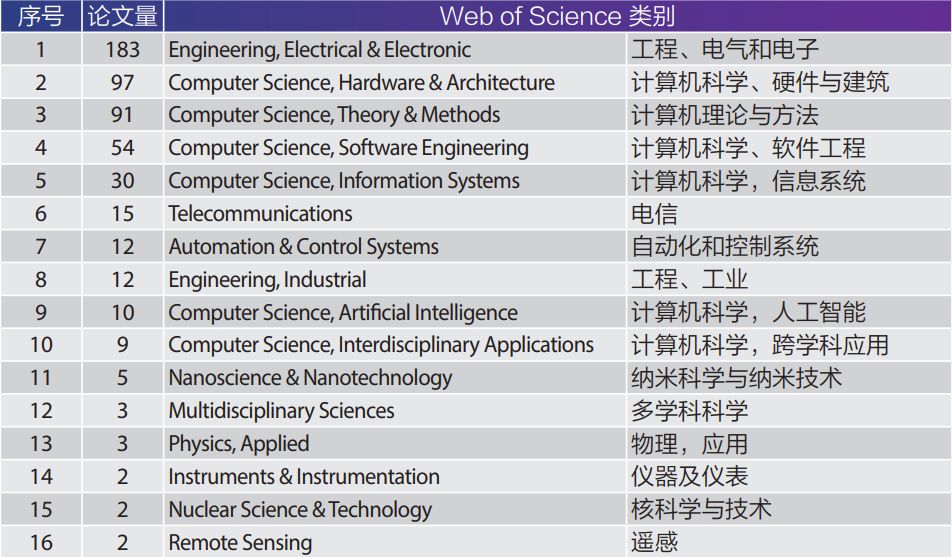
Based on the WOS categories of the 298 papers, the main research application areas of RISC-V can be analyzed. As shown in Table 2, the primary research distribution of RISC-V is in Engineering, Electrical and Electronics, followed by Computer Science, Hardware, and Architecture. Interdisciplinary applications mainly include Telecommunications, Automation and Control Systems, Industry, Nanoscience, Instrumentation, Nuclear Science and Technology, and Remote Sensing.
Table 2 Major Research Distribution of RISC-V
Identifying research topics in the field is crucial for judging research trends. Currently, research topic identification techniques are mainly divided into three categories: topic identification based on word frequency statistics, topic identification based on network community, and topic identification based on topic models. This study employs Vosviewer co-occurrence network analysis and LDA topic modeling to jointly identify research topics.
3.1 Research Topic Analysis Based on VOSviewer Co-occurrence Network
VOSviewer is one of many scientific knowledge mapping software, which constructs and visualizes analyses through the relationships of literature knowledge units to create scientific knowledge maps that showcase the structure, evolution, cooperation, and other relationships in knowledge domains[2]. This section of the study uses co-occurrence network analysis of extracted words from titles and abstracts of 298 papers as a dataset, utilizing VOSviewer software to cluster the high-frequency topic words that represent this theme. Certain co-occurrence frequencies and strengths are set based on the size of the paper dataset to cluster keywords. Each cluster is named and interpreted, and the publication themes of journals are identified and analyzed. The average citation frequency of core topic words in the analysis results represents the average citation frequency of papers containing this topic word since their publication; the average association strength represents the degree of closeness of the core topic words contained in this concept; the greater the topic association strength, the greater the co-occurrence strength among core topic words, indicating more concentrated research; conversely, lower association strength indicates more dispersed research.
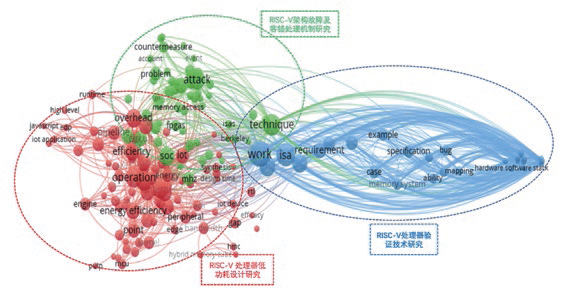
Figure 3 VOSviewer Clustering Results of RISC-V Title and Abstract Keywords
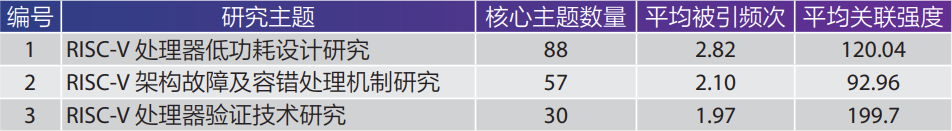
Using titles and abstracts as analysis fields, the core topic words with the highest co-occurrence strength were clustered after extracting and cleaning 6433 keywords, selecting 60% of the topic words that appeared more than 5 times (175 words) for analysis. Through clustering of these core topic words, three clusters were obtained. As shown in Table 3, the research content focuses on three aspects. Among them, the core topic concept of “Research on Low-Power Design of RISC-V Processors” has the most occurrences and relatively high relevance, making it the most concentrated research theme in this field.
Table 3 Three Research Themes Based on VOSviewer Co-occurrence of RISC-V Keywords
3.2 Research Topics Based on LDA Topic Model
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) is an unsupervised machine learning text mining method based on a bag-of-words model, essentially a three-level Bayesian probability graphical model. When LDA is applied to literature content analysis, it can better retain the internal relationships of disciplines, facilitating the revelation of the internal structure of the research field[3].
This article uses the perplexity evaluation metric to determine the optimal number of topics for the documents. Perplexity is commonly used to measure the quality of a probability distribution or model in predicting samples, which can be used to adjust the number of topics. Its calculation formula is as follows:
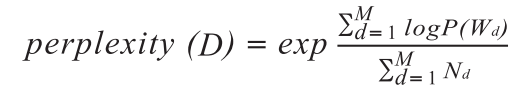
Where D represents the set of all words in the document, M represents the number of documents, Wd represents the words in document d, Nd represents the number of words in each document d, and p(wd) represents the probability of word occurrence in the document. Perplexity generally decreases as the number of latent topics increases; the smaller the perplexity value, the stronger the generation ability of the topic model.
After preprocessing the title and abstract fields of the 298 papers, this article uses the LDA topic model instantiated in gensim to classify and train the processed texts. Integers in the range of 2 to 32 are proposed as candidate topic numbers, with iterations set to 20000, and the perplexity values are calculated as shown in Figure 4. Perplexity shows local minima at points 6 and 16, and the visualizations for Topic=6 and Topic=16 are shown in Figure 5. To ensure that the model covers diverse topics as much as possible, Topic=6 is chosen as the parameter value for the LDA topic model.
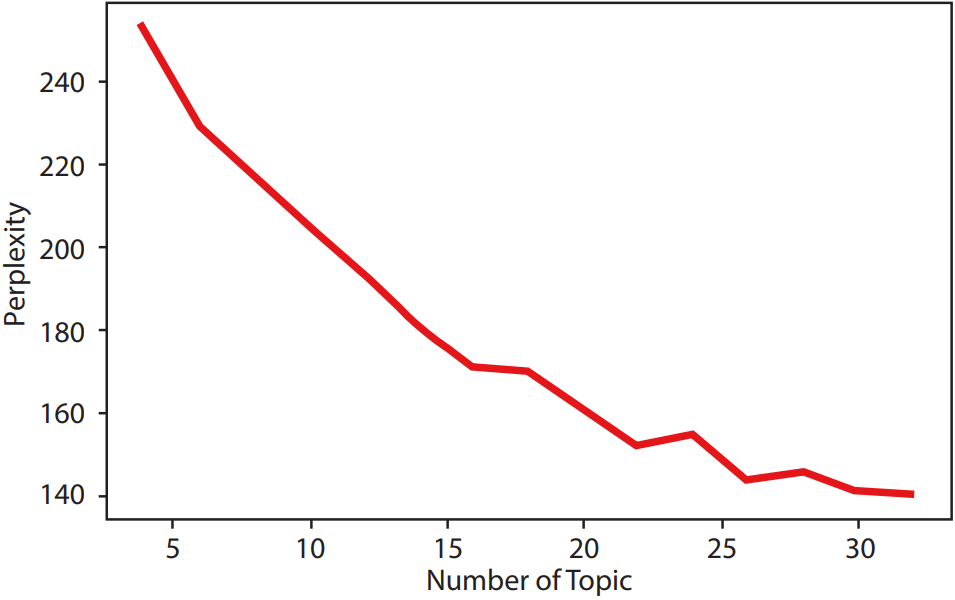
Figure 4 Perplexity-Topic Line Chart
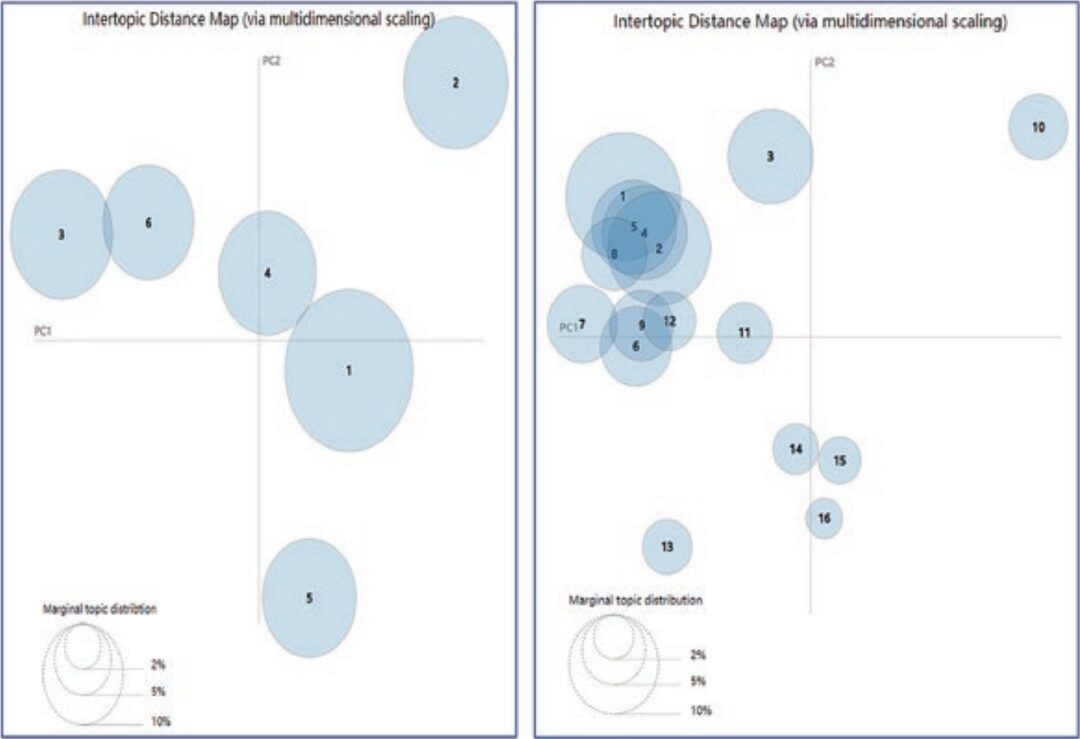
Figure 5 Distance Visualizations for Topic=6 and Topic=16
From the distribution of high-frequency words of the themes, it can be seen that the high-frequency words in LDA’s topic clustering have a high degree of repetition, but the main directions of each theme can basically be identified, as shown in Table 4.
Table 4 Distribution of TOP8 High-Frequency Words for 6 Themes
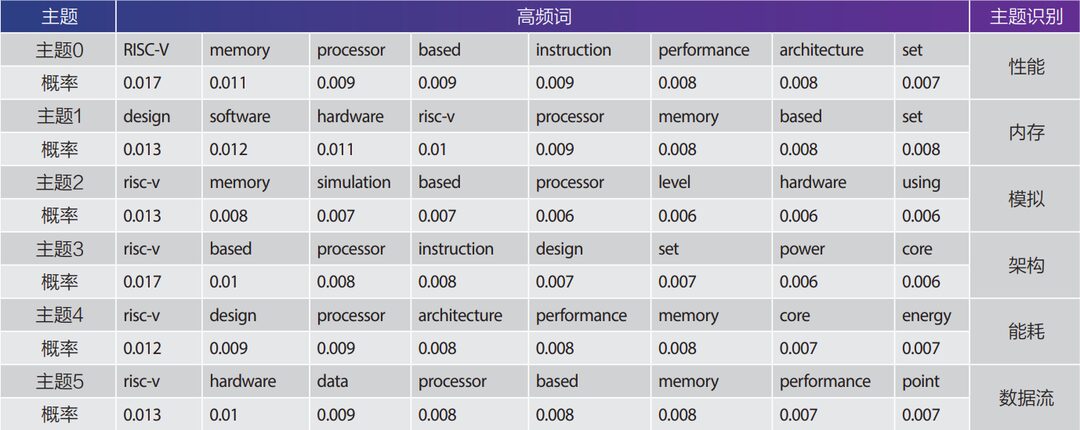
In summary, the main research themes in the RISC-V research field include: 1) Research on low-power design; 2) Research on fault and fault tolerance mechanisms of RISC-V architecture; 3) Research on verification technology for RISC-V processors; 4) Research on RISC-V chip simulation; 5) Research on RISC-V chip performance; 6) Research on the association between RISC-V technology and data pathways.
Since the birth of the RISC-V instruction set in 2011, research papers have rapidly increased, and it is expected to remain in an explosive research phase in the future. The United States ranks first in research on this topic, holding an absolute advantage, followed by India; these two countries are the main battlegrounds for RISC-V research in the world today. China ranks fifth, with relatively fewer publications compared to the United States. Due to the relocation of the RISC-V Foundation headquarters to Switzerland in 2020, Swiss research institutions are expected to increasingly join the field of research, with anticipated gradual increases in publication volume rankings for Switzerland in the future. In terms of research institutions, the University of California, Berkeley, as the birthplace of RISC-V, has the highest publication volume, followed by the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology. Among the top 20 institutions, only NVIDIA and the U.S. Tactical Computing Laboratory are companies, while the other 18 are research institutions. The only Chinese institution to enter the top 20 is the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The primary research distribution of RISC-V is in Engineering, Electrical and Electronics, followed by Computer Science, Hardware, and Architecture. Interdisciplinary applications mainly include Telecommunications, Automation and Control Systems, Industry, Nanoscience, Instrumentation, Nuclear Science and Technology, and Remote Sensing. Through co-occurrence analysis and LDA topic modeling, the main research themes of RISC-V include: 1) Research on low-power design; 2) Research on fault and fault tolerance mechanisms of RISC-V architecture; 3) Research on verification technology for RISC-V processors; 4) Research on RISC-V chip simulation; 5) Research on RISC-V chip performance; 6) Research on the association between RISC-V technology and data pathways.
References
[1] Samuel Greengard. 2020. Will RISC-V revolutionize computing? Commun. ACM 63, 5 (May 2020), 30–32.
[2] Vaneck N J P , Waltman L . Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping[J]. Scientometrics: an international journal for all quantitative aspects of the science of science, communication in science and science policy, 2010, 84.
[3] Tan Chunhui, Xiong Mengyuan. Comparative Analysis of Research Hotspots in Data Mining at Home and Abroad Based on LDA Model [J/OL]. Information Science: 1-12 [2020-11-18]


For more content, please subscribe to the magazine “High Technology and Industrialization”
Address: 33 North Fourth Ring West Road, Zhongguancun, Haidian District, Beijing (100190) Phone: 010-62539166
Email: [email protected]
Website: http://www.hitech.ac.cn
http://www.hitech.ac.cn
12 issues a year, 58 yuan/issue, annual subscription price 696 yuan
Postal code: 82-741
Journal Number: ISSN1006-222X CN11-3556/N