1. Introduction
The industrial internet is a product of the integration of new generation information and communication technologies with industrial systems. Ensuring the integration and transformation of industries and building a security assurance system for industrial internet is a prerequisite for the development of industrial internet security. With the trend of network connectivity and data intercommunication, the industrial system is accelerating its open integration. The traditional industrial system, which operates in a relatively closed and isolated environment with a focus on production safety, cannot adapt to the complex and changing application environment of the industrial internet. At the same time, industrial control systems and devices themselves have vulnerabilities and backdoors. Given the fragility of industrial control systems and devices and their high real-time requirements, it is difficult to provide security protection in the same way as traditional information systems. Therefore, building relevant network security capabilities has become a key issue.
The integration of information technology and traditional industrial operation technology is deepening. The network security protection capabilities of industrial internet devices will directly affect industrial production and business operations, becoming an important part of network security policy control and industrial protection practices. In recent years, product safety of devices has gradually become a focus for traditional industrial powers, viewed as a key element in strengthening network security control and ensuring supply chain security and industrial development. For example, the United States has established a supply chain control system with network security review as a means and has enacted the Internet of Things Cybersecurity Improvement Act. Currently, there has been considerable research and application in the areas of industrial equipment measurement, operation, maintenance, and quality management, focusing on utilizing equipment quality control, predictive maintenance, high-precision measurement, fault analysis, remote monitoring, and other means to ensure the functional safety and performance of devices[1~4]. In terms of functional safety applications, active research is being conducted on the application of new technologies such as industrial big data and artificial intelligence (AI)[5~8]. From the existing progress, the overall research on network security of industrial internet devices is still lacking; whether it is the security guarantee of the functional performance of the devices themselves or the use of new technologies to enhance device health management and monitoring, the network security issues faced by industrial devices should not be overlooked.
This article focuses on the network security issues of industrial internet devices, analyzing needs, sorting out the current situation, assessing problems, and demonstrating paths, while proposing specific development suggestions to provide reference ideas for basic and policy research in the field.
2. Security Protection Concepts and Demand Analysis for Industrial Internet Devices
(1) Security Protection Concepts for Industrial Internet Devices
Industrial internet devices refer to the equipment or devices that access the industrial internet network through wired or wireless means during the integration and application of new generation information technology with industrial production, manufacturing, operation, and management. They are characterized by diverse types, functions, and application forms. Industrial internet devices can be categorized into: industrial control devices, such as programmable logic controllers (PLC) and remote terminal units (RTU); industrial network and security devices, such as industrial switches and industrial firewalls; and industrial intelligent terminal devices, such as data acquisition gateways, video surveillance devices, and IoT-related devices. From the perspective of device security and protection during the application process, the security protection of industrial internet devices can be subdivided into hardware security, network communication security, system service security, application development security, and data security (see Figure 1).
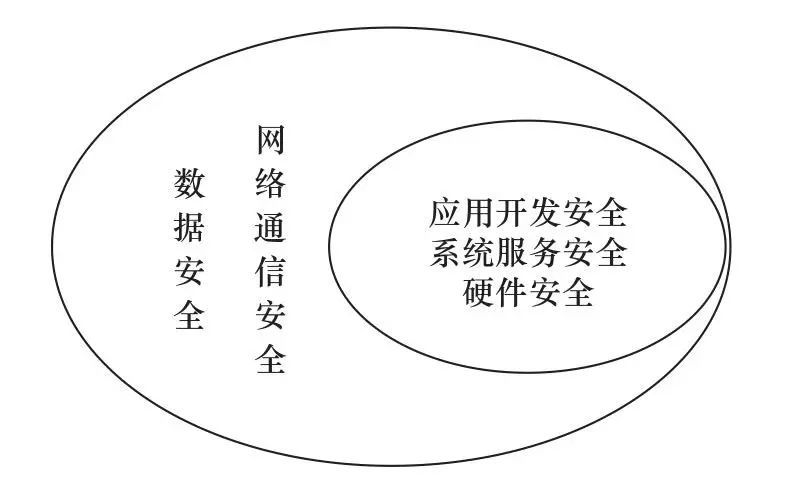
Figure 1: Scope of Network Security Protection for Industrial Internet Devices
Hardware security includes control of debugging interface permissions, chip security protection, and prevention of threats arising from statistical analysis of device power consumption information. Currently, most network devices and IoT devices retain hardware debugging interfaces, and some interfaces can even be accessed without verification, which may become entry points for malicious attacks and data theft, leading to the leakage of device keys, authentication, and other information.
Network communication security includes communication authentication and encryption, further divided into network layer encryption, transport layer encryption, and application layer data encryption. If access control for network communication is insufficient, attackers can impersonate identities to implement “man-in-the-middle attacks” between devices or between devices and host systems, which may rapidly spread to form a botnet, and such botnets can be used to launch large-scale attacks on networks. Additionally, insufficient encryption capabilities for device communications can lead to hackers stealing user or device identity information and important industrial data leakage.
System service security includes permission control for device operating systems, baseline security configurations, security mechanisms for system updates, intrusion prevention, and protection against malicious code. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities or defects in device systems (or firmware) to invade devices, embedding malicious code during upgrades, increasing the difficulty of post-incident tracing and investigation.
Application development security includes access control among component resources, user authentication and authorization, external interface security, protection of configuration files and important data, communication protocol encryption, vulnerability scanning for third-party component libraries, and secure design of the code itself. If the device’s own security mechanisms are insufficient, attackers can exploit application security vulnerabilities or defects to invade devices and systems, launching targeted attacks.
Data security includes the protection of data integrity, privacy, and availability, preventing data from being stolen, monitored, or tampered with. Industrial enterprises are accelerating their digital transformation, beginning to deploy data collection, edge computing, and other IoT and intelligent devices on a large scale, leading to an exponential increase in the open sharing and flow utilization of industrial production processes, business data, and user information. Many industrial devices and networks still exhibit plaintext transmission of data, making it difficult to detect non-intrusive, passive data monitoring activities targeting devices; if the data protection and privacy protection mechanisms of the devices are insufficient, key process parameters, process data, and other information are at risk of being leaked or maliciously controlled and tampered with.
(2) Demand Analysis for Security Protection of Industrial Internet Devices
The functional safety, network, and data security of industrial internet devices need to be combined with the actual application forms to prevent and resolve potential network security vulnerabilities, implementing differentiated management and protection based on the application cycle and intelligent attributes of the devices.
Some devices did not adequately consider network security issues during the design and development phases, and the long-term continuous operation makes it difficult to conduct in-depth security testing or deploy security protection measures, resulting in varying degrees of vulnerabilities and hidden dangers. According to statistics from the China National Vulnerability Database (CNVD)[9], there were 2,955 vulnerabilities related to industrial control system devices as of December 2020, with 593 new vulnerabilities added annually. According to security assessment and monitoring results from the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, a significant number of industrial internet devices exhibit medium to high-risk vulnerabilities such as command tampering, sensitive information acquisition, and permission bypass, with some industrial safety devices even having high-risk vulnerabilities, indicating clearly insufficient security protection capabilities. Some industrial internet device systems in China have been continuously subjected to targeted scanning and malicious infections from abroad, with increasing frequency and quantity of attacks from botnets, Trojans, worms, and viruses; serious high-risk vulnerabilities have been found in widely used devices in China’s industrial sector, such as Rockwell PLC and Siemens Windows Control Center. Therefore, in-depth security testing for vulnerabilities of industrial internet devices, especially non-destructive security testing and protection, has become a common urgent need for industrial enterprises and equipment suppliers.
From the perspective of device application cycles and applicable network security protection measures, industrial internet devices require differentiated, categorized, and graded network security management and protection. One category is the “stock” devices that have already been deployed; due to limited resources and performance, as well as long-term operation, these devices may not have undergone network security testing for a long time, making it difficult to fully grasp the threat risks; security protection for these devices needs to analyze actual application situations specifically, enhancing risk prevention through protective measures and monitoring awareness. The other category is the “incremental” devices newly put into application, especially intelligent devices with remote control, data collection, and analysis capabilities, which often use general operating systems (such as embedded Linux), reducing the difficulty of intrusion for attackers to some extent; if these intelligent devices suffer malicious control and attacks, they may possess large-scale active diffusion capabilities, becoming a part of intelligent attacks; security protection for these devices needs to integrate the devices’ own functions, application scenarios, and supporting business needs, enhancing the design of hardware security protection, network communication, data security, and other mechanisms, and adopting measures for network security awareness, monitoring, early warning, and emergency response.
3. International Progress in the Field of Industrial Internet Device Security
(1) Security Regulation and Review
The network security laws and regulatory measures of traditional industrial powers are continuously upgraded, gradually strengthening network security reviews, which involve the safety and security capability reviews of relevant device products, as well as safety mechanisms throughout the entire lifecycle of product development, design, and application.
The United States has elevated network security review to a national strategy and means of international competition, with its network security review covering government procurement, critical information infrastructure protection, foreign investment, and supply chains, establishing a relatively complete review system, procedures, and standards. Among them, the supply chain review system is a key aspect of US network security review, which is representative; the content and scope of security reviews for relevant technologies and device products in the supply chain are gradually being perfected, and a series of mandatory security review norms have been released, requiring companies to sign cybersecurity agreements. In 2000, the US National Telecommunications and Information Systems Security Committee issued the “National Information Systems Security Procurement Policy,” requiring products related to intrusion detection, firewalls, operating systems, database management, etc., to undergo risk assessment and certification under the National Information Assurance Partnership (NIAP) Common Criteria evaluation and certification framework[10]. In 2015, the US Treasury and Commerce Departments required the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to conduct supply chain security risk reviews based on relevant technical standards[11]. In 2020, the US enacted the Internet of Things Cybersecurity Improvement Act, prohibiting federal agencies from purchasing any IoT devices that do not meet minimum security standards, requiring NIST to publish standards and guidelines for the federal government’s use of IoT devices[12].
The UK requires relevant device products to pass security certification established by the Government Communications Headquarters before they can be sold. The Russian Ministry of Industry and Trade focuses on security reviews for strategic industries involving foreign investment[13].
(2) Security Testing and Certification
Network security testing and certification are important steps before device products enter the market; in some countries, this is also a legally mandated step. Currently, the international network information security certification and evaluation system is stabilizing, and internationally accepted certification criteria are gradually being established, with the Common Criteria (CC) and the Information Technology Security Evaluation Criteria (IT-SEC) coexisting.
Network security testing and certification in various countries are mostly managed by relevant institutions or associations, entrusting laboratories, enterprises, and professional institutions for implementation. The evaluation system typically consists of one evaluation certification coordination organization, one evaluation certification entity, and multiple technical testing institutions. For example, in the US, it is managed by NIAP, which authorizes relevant laboratories, companies, and other evaluation institutions, currently issuing only Common Criteria certificates; in the UK, it is managed by the Communications Electronics Security Group, and in Germany, it is managed by the Federal Office for Information Security, both of which authorize commercial assessment agencies to issue ITSEC and CC certificates.
Countries focus on evaluating compliance, functionality, security assurance, and controllability of device products in their testing and certification standards, classifying functional levels and assurance levels to meet the needs of different departments, industries, and users, with functional and security assurance evaluations being the core content of testing and certification. The US, Europe, and the International Organization for Standardization are all establishing protection profiles based on evaluations, emphasizing functional evaluations, security evaluations, and conducting grading separately. The international common criteria released by the International Organization for Standardization are currently the most comprehensive evaluation criteria, which, together with ITSEC, become universal evaluation methods. In addition, the US, Germany, and others focus on promoting a testing system shared by defense, government, and commercial sectors, meeting the security requirements of different subjects through grading and profiling.
In the security testing and certification of industrial internet devices, international organizations and some countries have established certification systems with different focuses. ① The ISA Secure certification system is an internationally recognized system promoted by the International Society of Automation Safety Compliance Institute (ISCI), aimed at providing universal industrial device certification, addressing industrial device security needs, and simplifying the procurement processes for owners and suppliers of equipment[14]; ISA Secure conducts independent certification of industrial automation and control products and systems to ensure network attack protection capabilities and eliminate known vulnerabilities. ② The NIST certification system refers to the standard certification system established under the leadership of NIST, with participation from relevant industry authorities and industry associations, covering national standards, industry norms, and testing certifications; in implementation, it promotes the formation of a security standard certification system covering industries such as electricity, natural gas, oil, and nuclear energy, becoming widely recognized as a factual standard and authoritative guide in the US and even the international security community. ③ The Rhine certification system refers to the safety certification and quality assurance review of industrial devices and technical products conducted by the German Technical Inspection Association (authorized and commissioned by the German government); it provides certification services for embedded systems and devices, intelligent electronic devices, industrial information technology security inspections, penetration testing, risk analysis, safety manuals, safety training, etc., covering aerospace, automotive transportation, chemical, energy, manufacturing, and industrial machinery, and electricity sectors.
4. Development Status and Challenges in China’s Industrial Internet Device Security Field
(1) Basic Situation of Security Regulation and Review
In terms of security regulation, national laws and regulations such as the “Cybersecurity Law” and “Cybersecurity Review Measures” have been successively introduced, gradually establishing cybersecurity review methods for critical information infrastructures and mandatory testing and certification requirements for key network devices and cybersecurity-specific products. The “Catalog of Key Network Devices and Cybersecurity-Specific Products (First Batch)” requires that devices or products listed in the catalog must be certified as safe by qualified agencies or meet safety testing requirements according to relevant national standards before they can be sold or provided[15]. In terms of policy requirements, the “Guiding Opinions on Strengthening Security Work for Industrial Internet” require strengthening the secure access and protection of industrial production, hosts, intelligent terminals, and other devices, reinforcing the security assurance of control network protocols, equipment, and industrial software, and promoting cooperation among equipment manufacturers, automation integrators, and security enterprises to enhance the inherent safety of devices and control systems[16].
(2) Basic Situation of Security Testing and Certification
The network and information security evaluation and certification system is mainly managed by the State Administration for Market Regulation, with the National Information Security Evaluation and Certification Management Committee, the China Cybersecurity Review Technology and Certification Center, and relevant laboratories and evaluation institutions jointly promoting implementation, essentially forming a comprehensive promotion system involving regulatory agencies, national certification entities, and authorized evaluation institutions. It should also be noted that the existing evaluation and certification system focuses on general basic equipment products and specialized key equipment in certain industries, such as medical, lacking normative and general network security evaluation and certification for key industrial internet devices, large automation equipment, and industrial network communication devices.
In terms of standards and evaluations related to industrial internet device security, China has released national and industry-related standards such as “Technical Requirements for Firewalls for Industrial Control Systems,” “Information Security Technology – Security Requirements for Measurement and Control Terminals of Industrial Control Systems,” and “Safety Protection Regulations for Power Monitoring Systems.” In terms of security protection for IoT device terminals, China has released standards or guidelines such as “Information Security Technology – Password Protection Guidelines for Intelligent Networked Devices” and “Information Security Technology – Safety Technical Requirements for Isolation Components of Network and Terminal Devices.” In recent years, institutions such as the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology have promoted the release of standards such as “Security Protection Requirements for Industrial Internet Devices” in line with the application assurance needs of the industrial internet industry, and have conducted security testing and evaluation work for industrial internet devices, establishing security assessment institutions and teams.
(3) Problem Analysis
First, there is a lack of specialized management measures and testing certification systems for industrial internet device security. Although relevant policies and standards have been formulated by industry authorities, the mandatory requirements and systematic degree are insufficient, lacking adaptability requirements for network security regarding new technologies and new application forms. The security protection of industrial internet devices is still fundamentally at the level of industry self-discipline.
Second, the “Catalog of Key Network Devices and Security Products” does not adequately cover key industrial internet devices, and products not included in the catalog lack necessary and systematic network security reviews. The safety and protective capabilities of key equipment products such as industrial production equipment, key devices, and cybersecurity-specific products are difficult to guarantee, posing security threats to industrial production and business operations, with unknown risks in the equipment supply chain.
Third, the variety and large number of industrial internet devices make the current security protection capabilities and assurance levels unable to meet the needs of industrial transformation and upgrading. The safety operation requirements of industrial equipment such as PLCs, industrial hosts, and industrial firewalls have not yet been clarified, and there is a lack of security standards and specifications for devices in the process of networking and digital application, with specialized evaluation and testing specifications and implementation systems needing improvement. The existing network security testing and certification system cannot meet the requirements of actual applications, market needs, and network security reviews in other countries.
Fourth, there are few national standards related to the safety of industrial internet devices and products, a lack of mandatory network security standards, and a clear absence of evaluation and testing processes, methods, institutions, and personnel. Currently, the safety of industrial internet devices themselves cannot meet the requirements of different industries and market levels, and at the same time, domestic industrial internet device products lack authoritative evaluation and certification when entering the international market, making it difficult to adapt to international mutual recognition and network security reviews in other countries.
5. Implementation Path for Security Protection of Industrial Internet Devices in China
Given the diverse types and large scale of industrial internet devices, along with the relatively decentralized security management and varying levels of industry self-discipline, it is necessary to comprehensively plan from national, industry, and application perspectives, strengthening national regulation, industry certification, and the application of cybersecurity engineering. This article demonstrates the specific implementation paths for network security management and protection of industrial internet devices in China (see Figure 2), aiming to improve the adaptability strategies and capabilities of industrial internet devices, implement differentiated and graded security assessments and management, and perfect mechanisms such as standards and specifications, testing and certification, and risk management and emergency response.
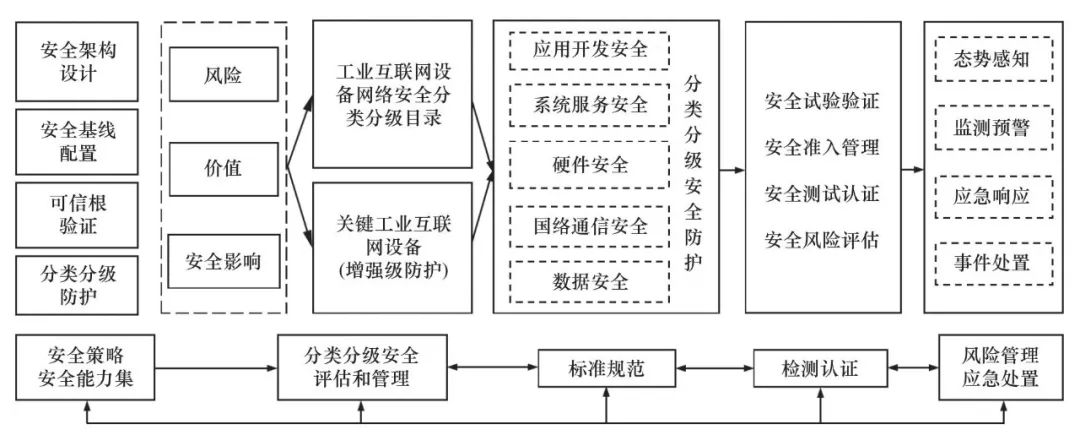
Figure 2: Diagram of Implementation Path for Security Protection of Industrial Internet Devices
First, establish the device’s own security policies and basic capability sets, including security architecture design, baseline configuration, trusted root verification, and basic requirements for classification and grading protection. Build a “baseline” of the device itself, enhancing its intrinsic security capabilities.
Second, based on network security risks, protection values, and the security impact of incidents, conduct classification and grading assessments for industrial internet devices of different types and application scenarios. Establish a classification and grading directory, forming key protected devices and their security strategies, and incorporate them into the catalog of key network devices and cybersecurity-specific products to efficiently carry out mandatory security testing and certification and review.
Third, improve the security protection specifications, classification, and grading protection requirements for industrial internet devices. For devices of different categories and protection levels, ensure that technical protection requirements for application development security, system service security, hardware security, network communication security, and data security are met, forming a differentiated and refined management model for network security of devices.
Fourth, establish a network security testing and evaluation system for industrial internet devices. Strengthen network security testing and verification, access review, testing certification, and regular security risk assessments during the application process, promoting the establishment of a closed-loop for device security protection.
Fifth, enhance security risk management and emergency response for industrial internet devices, including network security situational awareness and monitoring early warning for key industrial internet devices, emergency response and incident handling tools and mechanisms at the industry and enterprise levels. Maintain real-time awareness of device security status and risk views, providing regular technical means for risk warning and emergency work.
6. Recommendations
(1) Improve the Network Security Access Mechanism for Industrial Internet Devices at the National Level
It is recommended that relevant authorities formulate management measures related to the security of industrial internet devices, promulgate mandatory standards and industry specifications for industrial internet device security. Strengthen the network security specifications for the entire lifecycle of the design, development, implementation, and operation maintenance of industrial internet devices, providing a basis for enterprises’ product safety development, third-party testing and certification, and device deployment operation. After the release of the “Catalog of Key Network Devices and Cybersecurity-Specific Products (First Batch),” the testing and certification work for the devices listed in the catalog has gradually begun, but devices such as industrial internet devices that have not been mentioned are still in a regulatory blind spot. It is suggested to study and sort out key industrial internet devices and classify them as “key network devices and cybersecurity-specific products,” conducting classification and grading for the devices; improve relevant security standards and specifications, establish a sound regulatory and security access mechanism for industrial internet devices, and ensure strict security testing before devices enter the market for sale or use.
(2) Establish a Network Security Testing Certification System for Devices
It is recommended to establish a security testing and certification system for industrial internet devices, strengthening security testing and verification, especially for industrial devices in industrial field environments, including safety testing, non-destructive testing, and industrial-grade security protection applications. Promote the establishment of security-related evaluation and certification centers for industrial internet devices, design security certification levels around device safety and protective levels, and carry out classification and grading management and differentiated protection for devices. Provide safety level choices to different departments, industries, and enterprises, accurately dividing the safety capability levels of devices, enhancing a healthy competitive environment in the market, and promoting manufacturers to upgrade the safety of their devices. Promote security testing and certification and the enhancement of device capabilities, matching the applicability of industrial internet devices to industrial environments, hardware security, system/firmware security, application security, data security, access security, etc., and constructing capabilities for device security functions, intrusion resistance, malicious code prevention, resistance to distributed denial-of-service attacks, and vulnerability protection.
(3) Promote Research and Engineering Applications of Device Network Security Architecture
It is suggested to fully consider security factors during the design phase of industrial internet devices, enhancing the comprehensive protection capabilities of devices, including hardware security, access authentication security, data transmission security, code security, and system service security; establish a trusted computing environment for devices, introducing hardware trust roots to perform trusted verification of system booting, application running, and parameter modification behaviors. Regarding device security baseline configuration, it is recommended to urge device manufacturers to inform users of security usage guidelines at the time of product deployment, using technical means to ensure the security of baseline configurations. Manufacturers of industrial-related devices, automation integrators, research institutions, and security enterprises should strengthen cooperation, accelerate the application of new technologies such as blockchain, domestic encryption, and trusted computing, and promote the inherent safety and technological product research and innovation of devices.
(4) Strengthen Network Security Risk Monitoring and Awareness for Devices
With the diverse types of industrial internet devices, the protective technical capabilities applicable to different industries and scenarios vary widely. It is recommended that for industries (especially manufacturing), promote safety testing and evaluations for device procurement and application, network transformation, and enhance security monitoring and management for industrial production equipment, industrial hosts, and related intelligent terminals. It is recommended that relevant authorities guide the industry to strengthen the security monitoring and emergency response capabilities of industrial internet devices, enhancing device security monitoring awareness, situational assessment, information sharing and reporting, and emergency response, timely warning of Trojan infections, viruses, or controlled host network attacks; establish a security knowledge base for industrial internet device security testing and emergency response tool libraries, vulnerability libraries, threat intelligence libraries, etc., to quickly implement emergency responses and prevent hackers from exploiting vulnerabilities for wider attacks.
References
[1] Zhang Y. Discussion on high-precision measurement methods in the installation of industrial equipment [J]. Technology and Economic Guide, 2019, 27(24): 72.
[2] Zhang B, Teng J J, Man Y. Application research of improved parallel fp-growth algorithm in fault diagnosis of industrial equipment [J]. Computer Science, 2018, 45(S1): 508–512.
[3] Samigulina G, Samigulina Z. Diagnostics of industrial equipment and faults prediction based on modified algorithms of artificial immune systems [J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2021 (1): 1–18.
[4] Compare M, Baraldi P, Bani I, et al. Industrial equipment reliability estimation: A bayesian weibull regression model with covariate selection [J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2020, 200: 1–10.
[5] Yu P Y. Research and application of equipment health and failure analysis based on industrial big data [D]. Shenyang: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Master’s thesis), 2017.
[6] Jin H J. Research on remote monitoring system of industrial equipment based on Internet of things [J]. Industrial & Science Tribune, 2020, 19(14): 35–36.
[7] Dai R Z. The application of artificial intelligence technology in the intelligent operation and maintenance of industrial equipment and systems [J]. China Information, 2020 (7): 52–53.
[8] Mourtzis D, Angelopoulos J, Panopoulos N. Intelligent predictive maintenance and remote monitoring framework for industrial equipment based on mixed reality [J]. Frontiers in Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 6(12): 1–12.
[9] Critical Infrastructure Security Response Center. Industrial control system vulnerabilities [EB/OL]. (2020-12-01)[2021-01-05]. https://ics.cnvd.org.cn/.
[10] Committee on National Security Systems. Frequently asked questions (FAQ) [EB/OL]. (2001-10-16)[2021-01-05]. https://www.niap-ccevs.org/Ref/FAQ.cfm#cat32.
[11] Department of Homeland Security. National strategy for global supply chain security [EB/OL]. (2017-07-13)[2021-01-05]. https://www.dhs.gov/national-strategy-global-supply-chain-security.
[12] Warner S, Mark R. S.734 – Internet of Things cybersecurity improvement act of 2019 [EB/OL]. (2019-06-19)[2021-01-05]. https://www.congress.gov/bill/116th-congress/senate-bill/734.
[13] Cyberspace Administration of China. Cyberspace security review system and case analysis for several countries. [EB/OL]. (2015-04-17)[2021-01-05]. http://www.cac.gov.cn/2015-04/17/c_1114990146.htm.
[14] ISA Secure. IEC 62443 conformance certification certifying industrial control system equipment and systems [EB/OL]. (2021-01-05)[2021-01-05]. https://www.isasecure.org/en-US/Certification.
[15] Cyberspace Administration of China. Announcement on the issuance of the Critical network equipment and special network security products catalog (first batch) [EB/OL]. (2017-06-09)[2021-01-05]. http://www.cac.gov.cn/2017-06/09/c_1121113591.htm.
[16] Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People’s Republic of China. Guiding opinions on strengthening industrial Internet security work [EB/OL]. (2019-08-28)[2021-01-05]. https://www.miit.gov.cn/zwgk/zcwj/wjfb/txy/art/2020/art_c41cb8a2f6e74e239bae96068a2dc024.html.
This article was originally published in “Chinese Engineering Science” 2021, Issue 2, by authors Ma Juan1, Yu Guangchen1, Ke Haoren1, Yang Dongmei1, Wu Shouer Sila Mu2
1. China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, Security Research Institute
2. School of Information Science and Engineering, Xinjiang University
Reviewed | Chen Li, Shan Shan
Edited | Ling Xiao

Recommended Reading



