InXilinx FPGA, the Site is the smallest configurable unit in the physical layout of the chip, representing the specific location of hardware resources.
1. Definition and Function of Site
Physical Level: A Site is the smallest independently configurable unit on an FPGA chip, with each Site corresponding to a fixed physical location, containing specific resources (such as LUT, registers, DSP, etc.).
Function Mapping: The designed logic units (such as flip-flops and adders) are ultimately mapped to specific Sites, implementing hardware functions.
2. Common Types of Site
Xilinx FPGA mainly includes the following Site types:
|
Site Type |
Function |
Example Resources |
|
SLICE |
Implement combinational and sequential logic |
LUT6,FF, carry chain (CARRY4) |
|
DSP48E1/2 |
High-performance mathematical operations (multiply-accumulate) |
Multipliers, pre-adders |
|
BRAM |
Data storage (block RAM) |
36Kb RAM,FIFO controllers |
|
IOB |
Pin connection and level conversion |
Input/output buffers, differential pairs |
|
MMCM/PLL |
Clock management and frequency synthesis |
Clock division, phase adjustment |
Below, the Device view will sequentially display.
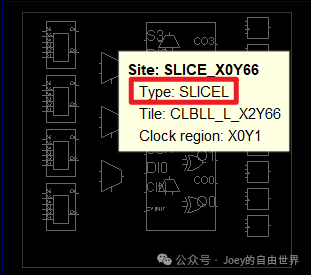
#SLICE type Site
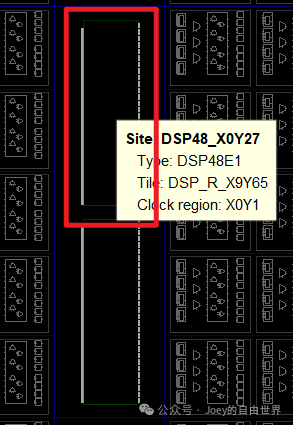
#DSP48E1 type Site
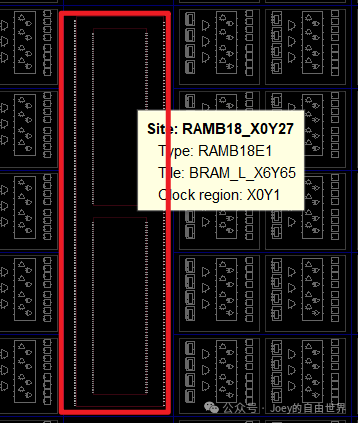
#BRAM type Site
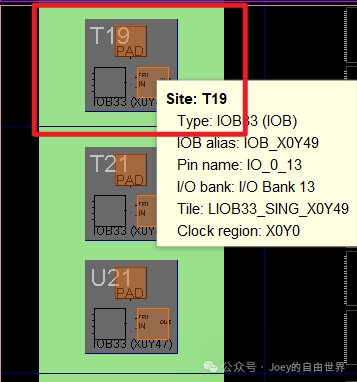
#IOB type Site
#MMCM/PLL type Site
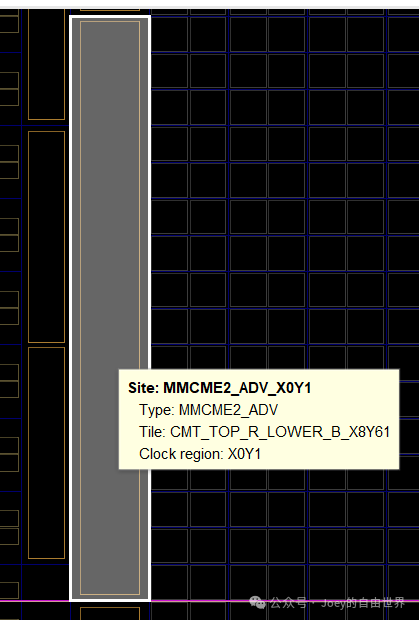
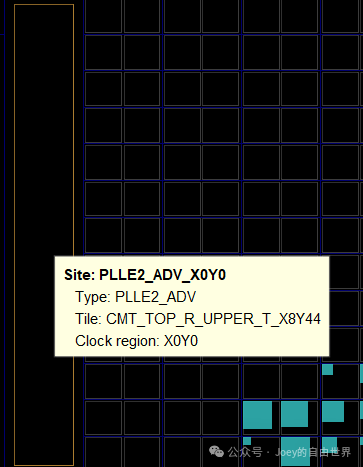
3. Relationship of Site with the Design Process
Synthesis and Mapping: Vivado converts HDL code into logic units and allocates them to specific Sites (e.g., mapping an adder to a DSP48 Site).
Layout Constraints: Through Tcl scripts or GUI tools, the position of logic units can be manually specified to optimize timing and routing:
set_property LOC SLICE_X12Y42 [get_cells my_adder]
Timing Analysis: Tools calculate path delays based on the physical distance and routing resources between Sites.
4. Relationship of Site with Other Levels
|
Level |
Description |
Relation to Site |
|
Cell |
Logic units in the design (e.g., registers, LUT) |
Cells are mapped to Sites |
|
Tile |
A logical block composed of multiple Sites (e.g., a CLB Tile). |
A Tile contains multiple adjacent Sites |
|
Clock Region |
Clock management partition |
Contains multiple Tiles and Sites, sharing clock resources |
5. Practical Application Scenarios
Scenario 1: Critical Path Optimization
Problem: The delay of a certain timing path exceeds the limit.
Solution:
- Use report_utilization to locate high-delay Sites;
- Use Pblock constraints to bind related logic to adjacent Sites;
- Re-layout to reduce routing distance.
Scenario 2: Resource Conflict
Problem: Insufficient DSP resources lead to layout failure.
Solution:
- Analyze whether the design excessively uses DSP48 Sites;
- Optimize algorithms or use LUTs to implement part of the calculations.
6. Debugging Tools and Commands
Vivado Device view: Visualizes Site layout and resource usage, supporting interactive drag-and-drop adjustments.
Key Tcl Commands: # View the resource type of a specified Site: get_property SITE_TYPE [get_sites SLICE_X0Y0]
Returns “SLICEL“

# Report design resource utilization: report_utilization
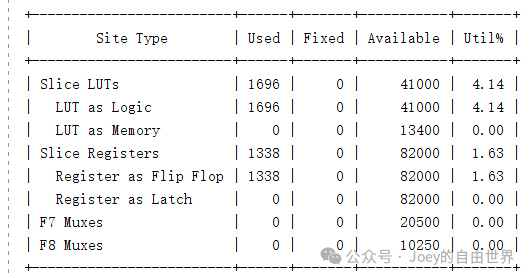
Summary
Site is the fundamental unit of physical implementation in an FPGA, directly affecting timing, power consumption, and resource utilization.
Mastering the distribution and constraint methods of Sites can significantly enhance design performance (e.g., reducing critical path delay by 20%).
In Vivado, precise control of Site-level layout can be achieved through toolchains and scripts to solve complex design issues.