Follow+Star Public Number, don’t miss out on exciting content
Author | strongerHuang
WeChat Official Account | Embedded ColumnMany IoT terminal products are powered by batteries, which have certain power consumption requirements, and some products have extremely stringent low power consumption requirements.Today, we will discuss some factors that affect the low power consumption of MCUs.
Sources of MCU Power Consumption
We will illustrate this with the classic STM8 microcontroller.The power consumption of the STM8 is divided into static power consumption and dynamic power consumption.Static Power Consumption: Mainly generated by the bias current of transistors and leakage current.Dynamic Power Consumption: Depends on the supply voltage and operating clock frequency.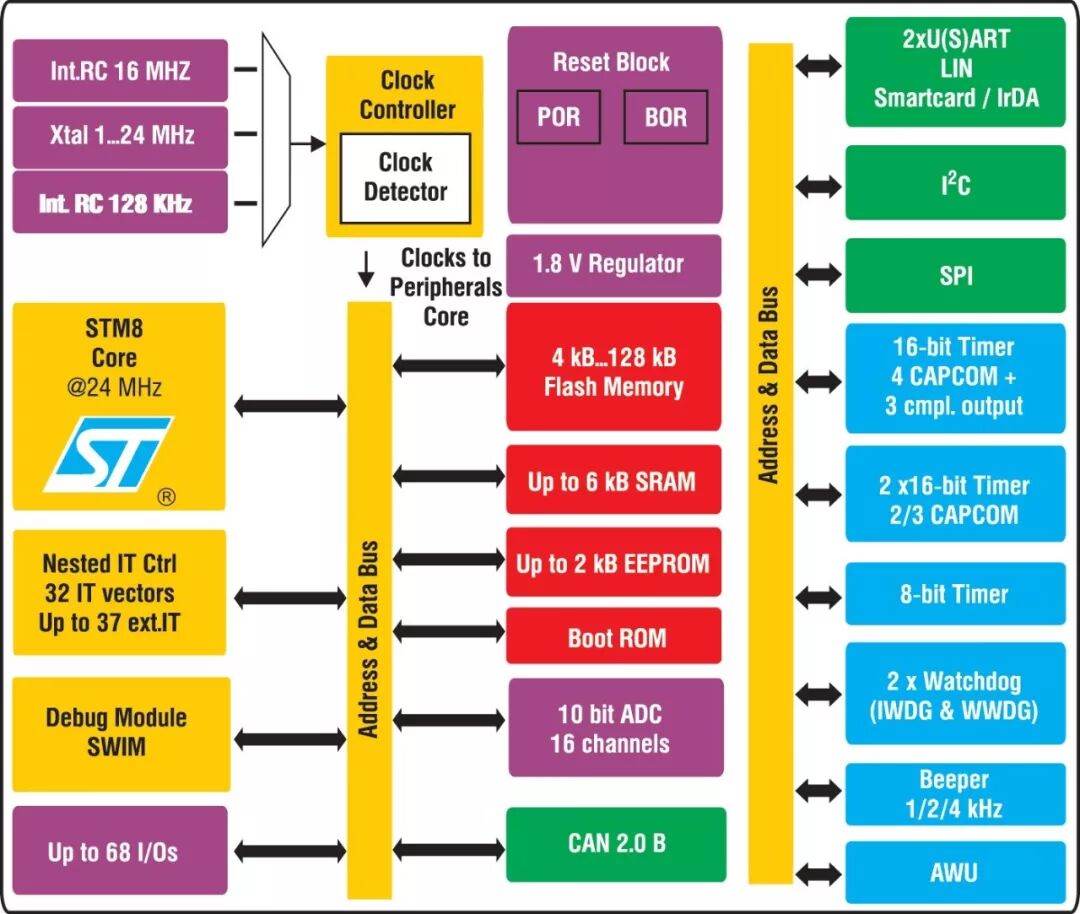 When CMOS logic circuits operate at a certain clock frequency, static power consumption can be neglected compared to dynamic power consumption. However, in some low power modes, when the clock is no longer running, static power consumption becomes the main source of power consumption.Therefore, power consumption mainly depends on:1. Chip area of the Microcontroller Unit (MCU): The process used, the number of transistors, and the integrated analog functions/peripherals on-chip.2. MCU supply voltage: The current consumed in CMOS logic circuits is proportional to the square of the supply voltage. Therefore, power consumption can be reduced by lowering the supply voltage.3. Clock frequency: In applications that do not require high-speed processing, reducing the clock frequency can lower power consumption.4. Number of activated peripherals or functions used by the MCU: The more peripherals activated or the more MCU functions used, the greater the power consumption.5. Operating mode: Power consumption varies with different power modes of the application (CPU on/off, oscillator on/off, etc.).
When CMOS logic circuits operate at a certain clock frequency, static power consumption can be neglected compared to dynamic power consumption. However, in some low power modes, when the clock is no longer running, static power consumption becomes the main source of power consumption.Therefore, power consumption mainly depends on:1. Chip area of the Microcontroller Unit (MCU): The process used, the number of transistors, and the integrated analog functions/peripherals on-chip.2. MCU supply voltage: The current consumed in CMOS logic circuits is proportional to the square of the supply voltage. Therefore, power consumption can be reduced by lowering the supply voltage.3. Clock frequency: In applications that do not require high-speed processing, reducing the clock frequency can lower power consumption.4. Number of activated peripherals or functions used by the MCU: The more peripherals activated or the more MCU functions used, the greater the power consumption.5. Operating mode: Power consumption varies with different power modes of the application (CPU on/off, oscillator on/off, etc.).
Microcontroller Clock
The following four clock sources can be used as the main clock for the STM8:
- 1-24MHz High-Speed External Crystal Oscillator (HSE)
- Maximum 24MHz High-Speed External Clock Signal (HSE user-ext)
- 16MHz High-Speed Internal RC Oscillator (HSI)
- 128KHz Low-Speed Internal RC (LSI)
Each clock source can be individually turned on or off, optimizing power consumption.Clock source comparison: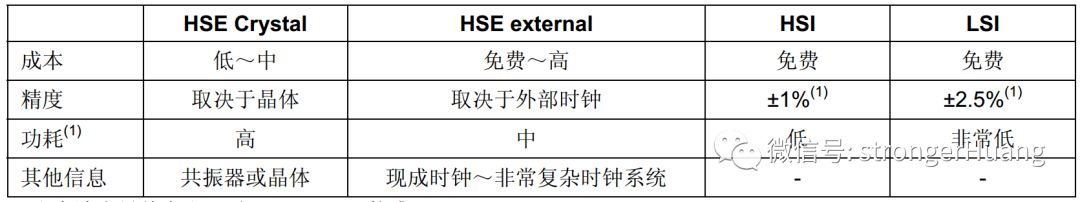 After reset, the default clock is HSI / 8, and then the user can switch the clock to different clock sources and frequencies:Methods to Reduce Power Consumption:1. Turn off the clock for unused peripherals;2. Reduce the CPU clock frequency;Note:The STM8S peripheral clock is enabled by default.Each peripheral can have its clock turned on or off individually when not in use to optimize system power consumption.
After reset, the default clock is HSI / 8, and then the user can switch the clock to different clock sources and frequencies:Methods to Reduce Power Consumption:1. Turn off the clock for unused peripherals;2. Reduce the CPU clock frequency;Note:The STM8S peripheral clock is enabled by default.Each peripheral can have its clock turned on or off individually when not in use to optimize system power consumption.
Low Power Modes
The STM8S has three low power modes:1. Wait Mode: CPU stops, peripherals remain operational.2. Active HALT Mode: Divided into fast and slow modes. CPU stops, but if AWU (Auto Wake-Up) and IWDG (Independent Watchdog) are enabled, they remain operational while other peripherals stop.3. HALT Mode: Everything stops.Besides these three low power modes, the STM8S is in run mode. Below is a comparison of these modes: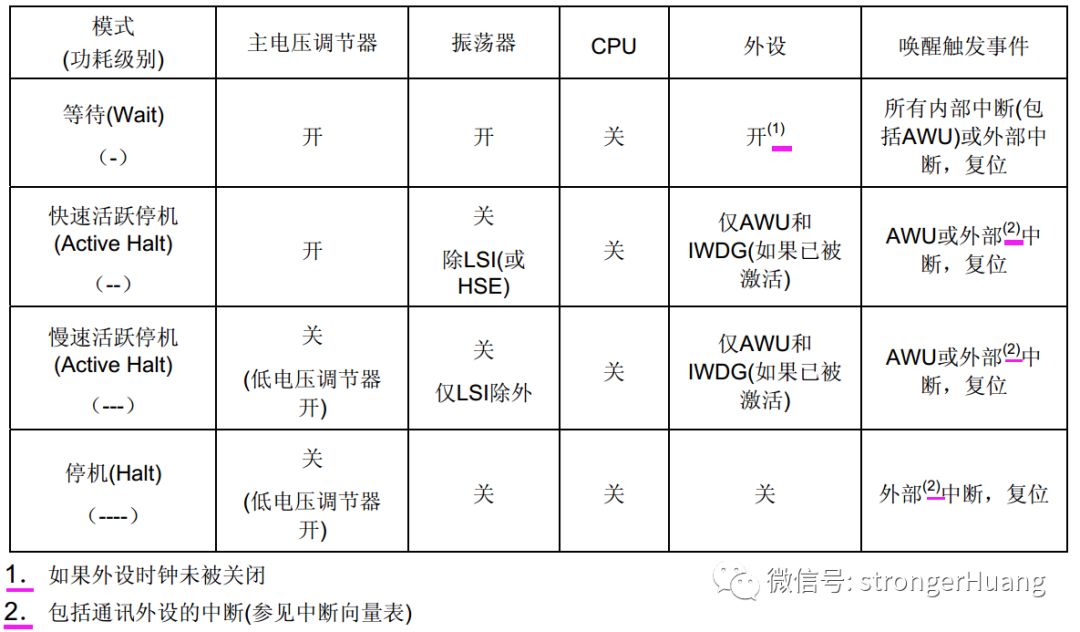
Low Power Measurement Data
Now let’s look at the theoretical data measured by the official sources.1. Wait Mode: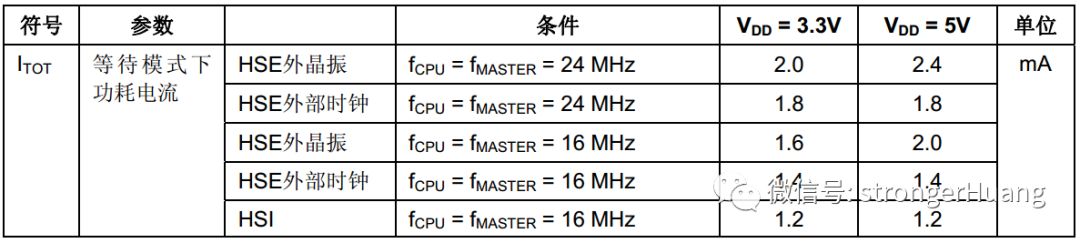 The power consumption in this mode is relatively high among low power modes.The higher the frequency, the higher the power consumption; simultaneously, the higher the voltage, the higher the power consumption.2. Active HALT Mode:
The power consumption in this mode is relatively high among low power modes.The higher the frequency, the higher the power consumption; simultaneously, the higher the voltage, the higher the power consumption.2. Active HALT Mode: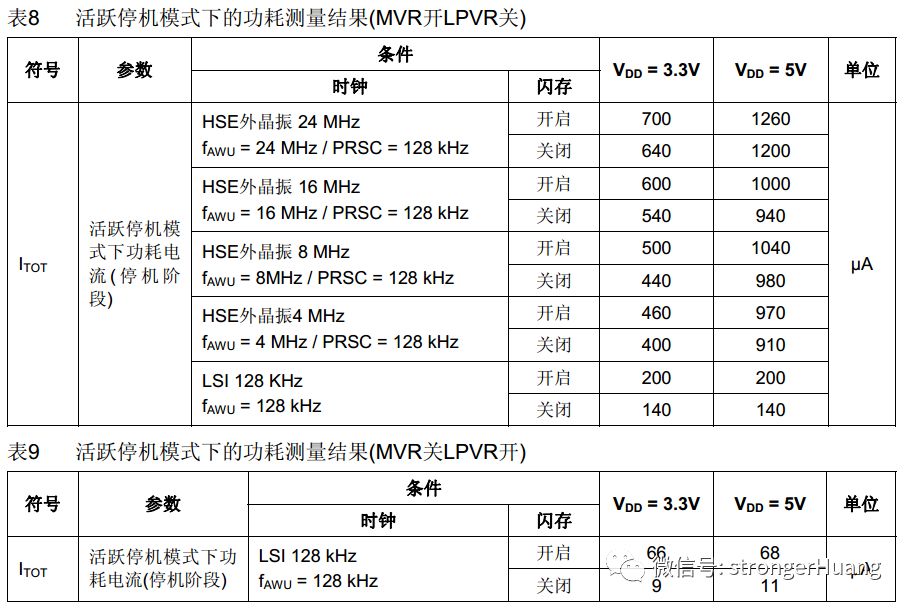 This mode follows the same pattern as the previous mode:The higher the frequency, the higher the power consumption; simultaneously, the higher the voltage, the higher the power consumption.3. HALT Mode:
This mode follows the same pattern as the previous mode:The higher the frequency, the higher the power consumption; simultaneously, the higher the voltage, the higher the power consumption.3. HALT Mode: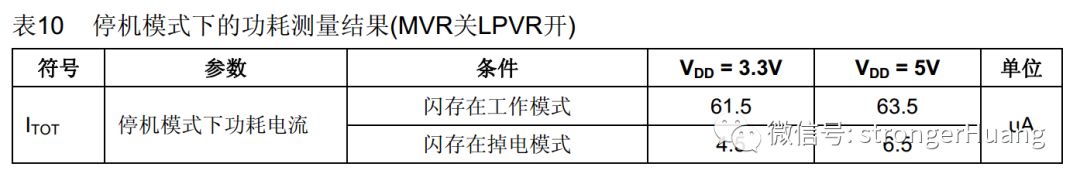 It can be observed that the power consumption in HALT mode is relatively low, but these are theoretical values, and the actual values should be larger than these values.For example: in HALT mode, if you measure 12us instead of the theoretical 9us, this should be within the normal range.However, if your actual values are significantly greater than these theoretical values, you need to check your hardware or software.
It can be observed that the power consumption in HALT mode is relatively low, but these are theoretical values, and the actual values should be larger than these values.For example: in HALT mode, if you measure 12us instead of the theoretical 9us, this should be within the normal range.However, if your actual values are significantly greater than these theoretical values, you need to check your hardware or software.
———— END ————

● Column “Embedded Tools”
● Column “Embedded Development”
● Column “Keil Tutorials”
● Selected Tutorials from the Embedded Column
Follow the official account and reply “Join Group” to join the technical exchange group according to the rules, reply “1024” to see more content.
Click “Read the Original” to see more shares.