Despite the encroachment of processor architectures like x86 and RISC-V, ARM has experienced counter-cyclical growth—over 30 billion ARM chips shipped globally in 2023, dominating 95% of the mobile market. It can be said that ARM remains resilient, but what is the reason behind this?
1. Absolute Notification of Energy Efficiency Ratio
① Performance per watt crushes x86
Data comparison:
ARM Cortex-X3: 5.6 SPECint/mW
Intel i9-13900K: 0.8 SPECint/mW
The gap is 7 times (at the same process node)
② Ingenious microarchitecture design
Pipeline optimization:
Short pipeline (8-15 stages vs. x86’s 20+ stages) reduces branch prediction penalties
Dynamic Voltage Frequency Scaling (DVFS) accuracy reaches 1MHz/1mV
③ Process adaptation advantages
Compatible across all nodes from 40nm to 3nm (Intel is still stuck below 10nm)
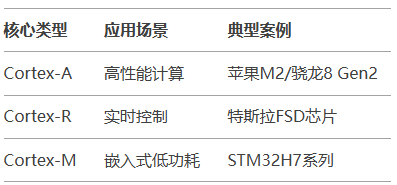
2. Scenario-based Customization Capability
3. Commercial Barriers of Licensing Models
① Three-tier licensing system
Architecture licensing (e.g., Apple’s self-developed microarchitecture)
Core licensing (e.g., Qualcomm’s Kryo CPU)
Chip licensing (e.g., STM32 directly using Cortex-M)
② Cost advantages
x86 development cost: $500M+ (requires building a wafer fab)
ARM development cost: $50M (Fabless model + IP reuse)
4. Software Ecosystem as a Moat
① Dominance in mobile
Android system has 100% native support for ARM
Apple’s iOS ecosystem is fully tied to ARM
② Developer toolchain
ARM Compiler 6 has 15% higher compilation efficiency than GCC
DS-5 debugger supports cache coherence analysis
This article is an original piece by Wanyi Education, please indicate the source when reprinting!