🎯Dissecting DDR5 Memory Architecture: New Approaches to PMIC and Power Management🔥
📌Keywords: DDR5, PMIC, Power Architecture, Power Supply Modes, VDD, VDDQ, VPP
💡01|Introduction: What is “New” About DDR5?
We all know that DDR5 has a high frequency (starting at 4800MT/s, soaring over 8000+), but itsunderlying architecture has undergone revolutionary changes, especially in power management!
You might think it’s just about “increasing frequency”? Wrong!
🎯DDR5 has completelyrestructured the logic of “memory power supply”, with core upgrades:
It introducesPMIC chips (Power Management IC)
The memory module powers itself! (Reducing the load on the motherboard)
⚙️02|What is PMIC? What Does It Do?
In the DDR4 era, all voltages were supplied by the motherboard. For example:
With DDR5, the situation has changed:
Doesn’t it look a bit like the power supply logic of laptops or GPUs?
🔋 PMIC is the “power management center” of the memory, converting the 5V or 12V supplied by the motherboard into various voltages needed by the memory subsystems👇
🧠03|Analysis of DDR5 Core Power Supply Structure
Let’s take a look at the main power supply paths on the DDR5 DIMM
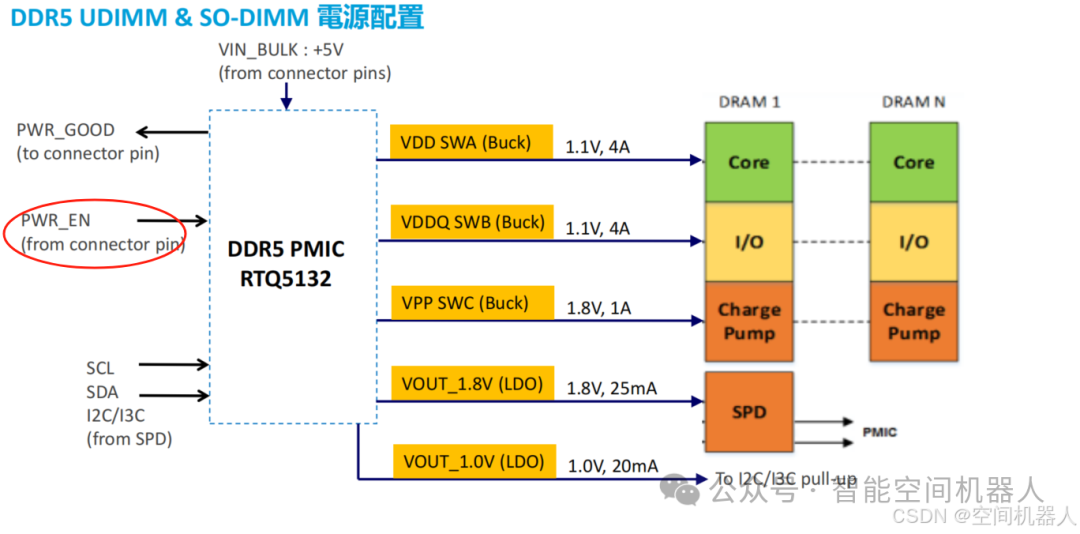
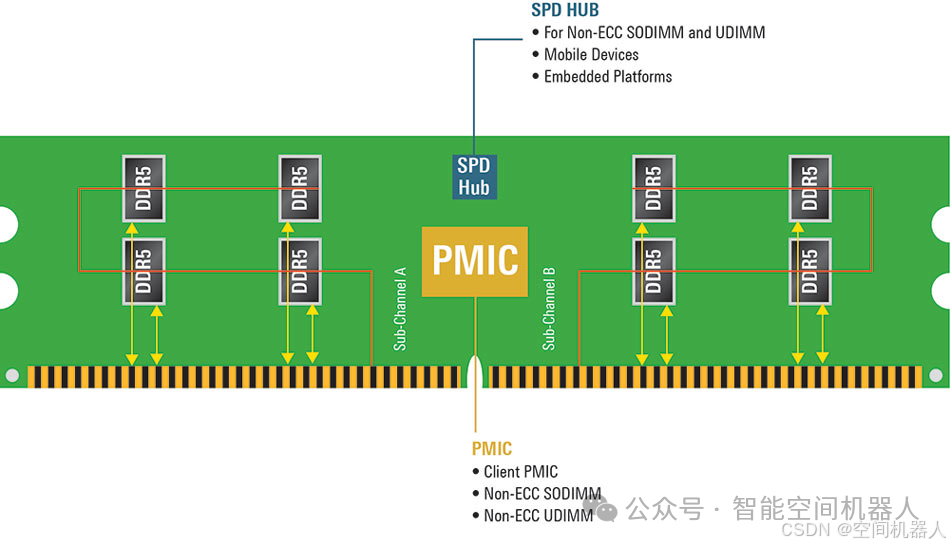
🎯 Overview of DDR5 Main Voltages:
| Voltage Name | Voltage Value | Function | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| VDD | 1.1V | Core Power Supply | DDR4 is 1.2V, reducing power consumption |
| VDDQ | 1.1V | IO Drive Voltage | Same as VDD |
| VPP | 1.8V | Wordline Activation | DDR4 is 2.5V, further optimization |
| 12V/5V | – | PMIC Input Power | Supplied by the motherboard |
🧮04|Why Move PMIC to the Memory Module?
There are three key reasons:
✅ 1) High-frequency memory requiresmore stable and closer power supply
- DDR5 has very high frequencies, making signals sensitive
- If power is supplied over long distances, voltage fluctuations can occur, affecting stability
- Deploying power “on-site” cangreatly reduce noise, ripple, and delay
✅ 2) Simplifies motherboard design, facilitating high-density memory slot layout
- Previously, motherboards had to allocate multiple voltage groups for each memory module
- Now, only a 12V or 5V input is needed
- 🎯Simplifying motherboard wiring enhances overall reliability
✅ 3) Lays the foundation for future intelligent power supply/energy saving (PMIC is programmable!)
- Future PMICs could even assist in intelligent frequency and voltage adjustments
- DDR5 standards define PMIC support forI²C communication interfaces, allowing remote parameter adjustments!
🧰05|A Glimpse into the Internal Structure of PMIC Chips
PMIC is essentially a multi-channel synchronous buck regulator, with a typical structure as follows:
It includes:
- Multiple DC-DC converters (synchronous buck type)
- Switch control circuits
- Thermal protection/overvoltage protection
- Digital interfaces (I²C/SMBus)
For example,Renesas P8911 and Infineon TDA215xx series are representative products.
🎮06|Does PMIC Affect Memory Overclocking Stability?
📌Answer:It does have an impact, but it is not a decisive factor.
- DDR5 overclocking stability mainly depends on PCB layout, heat dissipation, and power quality
- The response speed and anti-interference capability of PMIC can also affect “power supply fluctuations at high frequencies”
- 🎯 High-end DDR5 modules often use stronger PMICs, providing better overclocking headroom!
🔍07|Does PMIC Have Side Effects?
Of course, there are also:
- 💰Higher costs: DDR5 modules are significantly more expensive than DDR4
- 🧩More complex heat dissipation: PMIC generates heat, requiring careful layout and ventilation during design
- ⚠️More complex power supply issues: Memory problems may not necessarily be due to the motherboard; it could be triggered by the PMIC’s feedback/protection mechanisms
📦08|In Summary
DDR5 is not just “faster memory”; it represents an architectural reconstructionPMIC has ushered memory into a “self-sufficient” new era!
In the coming years, as DDR5 matures, we will also see PMICs becoming smarter, even integrating temperature compensation and adaptive voltage adjustments, making memory “smarter”.